| This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. Please review the contents of the article and add the appropriate references if you can. Unsourced or poorly sourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Ingrown nail" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2020) |  |
Medical condition
| Ingrown nail | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Unguis incarnatus or Ingrown toenail |
 | |
| An ingrown toenail on the large toe of the right foot | |
| Specialty | Orthopedics |
An ingrown nail, also known as onychocryptosis (from Greek: ὄνυξ (onyx) 'nail' and κρυπτός (kryptos) 'hidden') is a common form of nail disease. It is an often painful condition in which the nail grows so that it cuts into one or both sides of the paronychium or nail bed. While ingrown nails can occur in the nails of both the hands and the feet, they occur most commonly with the toenails (as opposed to fingernails).
A common misconception is that the cause of an ingrown toenail is the nail growing into the paronychium, but it can also be caused by overgrown toe skin. The condition is caused by a microbial inflammation of the paronychium causing a granuloma within which the nail is buried. A true ingrown toenail is caused by actual penetration of flesh by a sliver of toenail.
Signs and symptoms
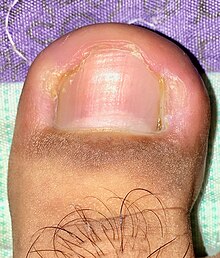
Symptoms include pain along the margins of the nail caused by hypergranulation, worsening of pain when wearing tight footwear, and sensitivity to pressure of any kind (in some cases this pressure can be as light as the weight of bedsheets). Bumping of an affected toe can cause pain as the nail's surrounding tissue is punctured further. Ingrown nails can become easily infected unless care is taken early to treat the condition.
Signs of infection include redness and swelling of the area around the nail, drainage of pus, and watery discharge tinged with blood. The main symptom is swelling at the base of the nail on the ingrowing side (though it may be present on both sides).
Onychocryptosis should not be confused with irregular nail growth patterns such as convex nails, involuted nails, or pincer nails. It also should not be confused with the presence of small corns, callus, or debris down the nail sulci.
Causes
| This section needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. Please review the contents of the section and add the appropriate references if you can. Unsourced or poorly sourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Ingrown nail" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2020) |  |
The main contributor to onychocryptosis is footwear, particularly ill-fitting shoes with inadequate toe box room and tight stockings that apply pressure to the top or side of the foot. Other factors may include the damp atmosphere of enclosed shoes, which soften the nail plate and cause swelling on the epidermal keratin (eventually increasing the convex arch permanently), genetics, trauma, and disease. Improper cutting of the nail may cause the nail to cut into the side-fold skin from growth and impact, whether or not the nail is truly "ingrown". The nail bends inwards or upwards depending on the angle of its cut. If the cutting tool, such as scissors, is at an attitude in which the lower blade is closer to the toe than the upper blade, the toenail will tend to grow upwards from its base, and vice versa. The process is visible along the nail as it grows, appearing as a warp advancing to the end of the nail. The upper corners turn more easily than the center of the nail tip. Holding the tool at the same angle for all nails may induce these conditions; as the nail turns closer to the skin, it becomes harder to fit the lower blade in the right attitude under the nail. When cutting a nail, it is not just the correct angle that is important, but also how short it is cut. A shorter cut will bend the nail more, unless the cut is even on both top and bottom of the nail.

Causes may include:
- Shoes causing a bunching of the toes in the developmental stages of the foot (frequently in people under 21), which can cause the nail to curl and dig into the skin. This is particularly the case in ill-fitting shoes that are too narrow or too short, but any toed shoes may cause an ingrown nail.
- Poor nail care, including cutting the nail too short, rounded off at the tip or peeled off at the edges instead of being cut straight across.
- Broken toenails.
- Trauma to the nail plate or toe, which can occur by dropping objects on or stubbing the toenail, or by the nail protruding through the shoe (as during sports or other vigorous activity), can cause the flesh to become injured and the nail to grow irregularly and press into the flesh.
- Predisposition, such as abnormally shaped nail beds, nail deformities caused by diseases or a genetic susceptibility, increases the chance of an ingrown nail, but the ingrowth cannot occur without pressure from a shoe.
- A bacterial infection, treatable with antibiotics.
One study compared patients with ingrown toenails to healthy controls and found no difference in the shape of toenails between those of patients and of the control group. The study suggested that treatment should not be based on the correction of a non-existent nail deformity. In some cases, however, there is nail deformity.
Ingrown toenails are caused by weight-bearing (activities such as walking and running) in patients that have too much soft skin tissue on the sides of their nail. Weight bearing causes this excessive amount of skin to bulge up along the sides of the nail. The pressure on the skin around the nail results in the tissue being damaged, resulting in swelling, redness and infection. Many treatments are directed at the nail itself and often include partial or full removal of the healthy nail. However, failure to treat the cutaneous condition can result in a return of the ingrowth and a deformity or mutilation of the nail.
Prevention
The most common digit to become ingrown is the big toe, but ingrowth can occur on any nail. Ingrown nails can be avoided by cutting nails straight across; not along a curve, not too short and no shorter than the flesh around it. Footwear that is too small or too narrow, or with too shallow a "toe box", will exacerbate any underlying problem with a toenail. Sharp square corners may be uncomfortable and cause snagging on socks. Proper cutting leaves the leading edge of the nail free of the flesh, precluding it from growing into the toe. Filing of the corner is reasonable.
Some nails require cutting of the corners far back to remove edges that dig into the flesh; this is often done as a partial wedge resection by a podiatrist. Ingrown toe nails can be caused by injury, commonly blunt trauma in which the flesh is pressed against the nail causing a small cut that swells. Injury to the nail can cause it to grow abnormally, making it wider or thicker than normal, or even bulged or crooked.
Management
The treatment of an ingrown toenail partly depends on its severity.
Conservative treatment
Mild to moderate cases are often treated conservatively with warm water and epsom salt soaks, antibacterial ointment and the use of dental floss. If conservative treatment of a minor ingrown toenail does not succeed, or if the ingrown toenail is severe, surgical treatment may be required. A "gutter splint" may be improvised by slicing a cotton-tipped wooden applicator diagonally to form a bevel and using this to insert a wisp of cotton from the applicator head under the nail to lift it from the underlying skin after a foot soak.
Some over-the-counter ingrown toenail pain relief kits include a sodium sulfide gel with cushions and elastic bandages.
Nail bracing
Main article: Nail brace
Nail bracing is more conservative than surgery, but less widely used. Nail braces work by gently lifting the sides of the toenail and eventually retraining the nail to grow to a flatter shape over time. The total time needed for the nail to be reshaped is one full nail growth or about 18 months. There are two main types of nail braces: adhesive and hooked. Adhesive nail braces are generally made of a thin strip of composite material that is glued to the top of the nail. The strip naturally tries to return to a flat state and lifts the edges of the nails in the process. Hooked nail braces consist of a hook (usually made of dental wire) placed under either side of the nail with some type of tensioning system pulling the hooks together.
Because of the curved shape of the nail, the tensioning device rests on the higher middle of the nail by applying upward pressure to the sides of the nail. In studies of diabetics, who need to avoid surgery when possible, nail bracing was found to be effective at providing immediate, as well as long-term, relief.
Surgery
Main article: Surgical treatment of ingrown toenailsSurgical treatment for an ingrown nail is carried out by a podiatrist, a foot and ankle specialist. This is typically an in-office procedure requiring local anesthesia and special surgical instruments. The surgical approach is the removal of the offending part of the nail plate known as a wedge resection. If the ingrown toenail recurs despite this treatment, destruction of the sides of the nail with chemicals or excision is done; this is known as a matrixectomy. Antibiotics may be used after the procedure but are not recommended, as they may delay healing. Surgical treatment for ingrown nails is more effective at preventing the nail from regrowing inwards compared to non-surgical treatments.

References
- James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2002). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (10th ed.). Saunders. p. 789. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
- Chapeskie H (2008). "Ingrown toenail or overgrown toe skin?". Canadian Family Physician. 54 (11): 1561–2. PMC 2592332. PMID 19005128. Archived from the original on 14 March 2011.
- Ingrown toenail: Overview. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). 28 June 2018.
- Ingrown Toenail: "Ingrown Toenail – NHS Choices". Archived from the original on 30 November 2010. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
- SHULMAN, SAMUEL B. (1949). "Survey in China and India of Feet That Have Never Worn Shoes". The Journal of the National Association of Chiropodists. Archived from the original on 28 December 2012. Retrieved 27 September 2012.
- Howell, Daniel (2010). The Barefoot Book. Hunter House.
- Pearson HJ, Bury RN, Wapples J, Watkin DF (November 1987). "Ingrowing toenails: is there a nail abnormality? A prospective study". J Bone Joint Surg Br. 69 (5): 840–2. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.69B5.3680356. PMID 3680356. Archived from the original on 31 May 2009.
- Chapeskie, H (November 2008). "Ingrown toenail or overgrown toe skin?: Alternative treatment for onychocryptosis". Canadian Family Physician. 54 (11): 1561–2. PMC 2592332. PMID 19005128.
- Haneke, E (2012). "Controversies in the treatment of ingrown nails". Dermatology Research and Practice. 2012: 783924. doi:10.1155/2012/783924. PMC 3362847. PMID 22675345.
- ^ Heidelbaugh, JJ; Lee, H (15 February 2009). "Management of the ingrown toenail". American Family Physician. 79 (4): 303–8. PMID 19235497.
- American Association of Orthopedic Specialists, "ingrown toenail" at "Ingrown Toenail – OrthoInfo – AAOS". Archived from the original on 16 August 2014. Retrieved 10 September 2014.
- "Treating ingrown toenails with the Bracing technique". Archived from the original on 8 September 2013. Retrieved 8 October 2013.: "Treating ingrown toenails with the Bracing technique". Archived from the original on 8 September 2013. Retrieved 8 October 2013.
- Erdogan, Fatma Gülru; Erdogan, Gürbüz (January 2008). "Long-term results of nail brace application in diabetic patients with ingrown nails". Dermatol Surg. 34 (1): 84–6, discussion 86–7. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2007.34013.x. PMID 18053045. S2CID 44434107.
- Eekhof, Just A. H.; Van Wijk, Bart; Knuistingh Neven, Arie; van der Wouden, Johannes C. (18 April 2012). "Interventions for ingrowing toenails" (PDF). The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD001541. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001541.pub3. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 22513901.
Further reading
- Aksakal AB, Ozsoy E, Gürer M (2003). "Silicone gel sheeting for the management and prevention of onychocryptosis". Dermatol Surg. 29 (3): 261–4. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2003.29061.x. PMID 12614420. S2CID 28708033.
- Boll OF (1945). "Surgical correction of ingrowing toenails". J Natl Assoc Chiroprod. 35: 8–9.
- Chapeskie H (2008). "Ingrown toenail or overgrown toe skin?". Canadian Family Physician. 54 (11): 1561–1562. PMC 2592332. PMID 19005128.
- Kominsky SJ, Daniels MD (2000). "A modified approach to the phenol and alcohol chemical partial matrixectomy". J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 90 (4): 208–10. doi:10.7547/87507315-90-4-208. PMID 10800276.
- Boberg JS, Frederiksen MS, Harton FM (2002). "Scientific analysis of phenol nail surgery". J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 92 (10): 575–9. doi:10.7547/87507315-92-10-575. PMID 12438504.
External links
 Media related to Ingrown nail at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ingrown nail at Wikimedia Commons
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Diseases of the skin and appendages by morphology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growths |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rashes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellaneous disorders |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||