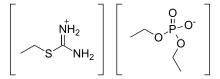
In organic chemistry, isothiouronium is a functional group with the formula (R = alkyl, aryl) and is the acid salt of isothiourea. The H centres can also be replaced by alkyl and aryl. Structurally, these cations resemble guanidinium cations. The CN2S core is planar and the C–N bonds are short.
Synthesis
Salts comprising these cations are typically prepared by alkylation of thiourea:
- SC(NH2)2 + RX → X
Reactions
Hydrolysis of isothiouronium salts gives thiols.
- X + NaOH → RSH + OC(NH2)2 + NaX
Isothiouronium salts in which the sulfur has been alkylated, such as S-methylisothiourea hemisulfate (CAS number: 867-44-7), will convert amines into guanidinium groups. This approach is sometimes called the Rathke synthesis after Bernhard Rathke who first reported it in 1881.
- RNH2 + X → X + CH3SH
Chelating resins with isothiouronium groups are used to recover mercury and other noble metals including platinum from solutions.
References
- Barker, J.; Powell, H. R. (1998). "S-Benzylisothiouronium Chloride". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 54 (12): 2019. doi:10.1107/S0108270198008166.
- Helmer Kofod (1963). "Furfuryl Mercaptan". Organic Syntheses. 4: 13; Collected Volumes, vol. 1, p. 66.
- Palmer, David C. (2001). "S-Methylisothiourea". E-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rm199s. ISBN 0471936235.
- "Heinrich Bernhard Rathke. (1840-1923)". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft (A and B Series). 57 (9): A83–A92. 8 October 1924. doi:10.1002/cber.19240570929.
- Rathke, B. (July 1881). "Ueber Derivate und Constitution des Schwefelharnstoffs". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 14 (2): 1774–1780. doi:10.1002/cber.18810140247.
- "Purolite S920 Isothiouronium Chelating Resin". Purolite. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2012-09-07.