| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (July 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Kai (και 'and'; Modern Greek: [ce]; Ancient Greek: [kai]; sometimes abbreviated k) is a word that is a conjunction in Greek, Coptic (ⲕⲁⲓ) and Esperanto (kaj; IPA: [kai̯]).
Kai is the most frequent word in any Greek text and thus used by statisticians to assess authorship of ancient manuscripts based on the number of times it is used.
Ligature
This article contains special characters. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols.Because of its frequent occurrence, kai is sometimes abbreviated in Greek manuscripts and in signage, by a ligature (comparable to Latin &), written as ϗ (uppercase variant Ϗ; Coptic variant ⳤ), formed from kappa (κ) with an extra lower stroke. It may occur with the varia above it: ϗ̀.
Ϗ ϗ
For representation in electronic texts the kai symbol has its own Unicode positions: GREEK KAI SYMBOL (U+03D7) and GREEK CAPITAL KAI SYMBOL (U+03CF).
Authorship of ancient texts
The number of common words which express a general relation ('and', 'in', 'but', 'I', 'to be') is random with the same distribution at least among the same genre. By contrast, the occurrence of the definite article "the" cannot be modeled by simple probabilistic laws because the number of nouns with definite article depends on the subject matter.
Table 1 has data about the epistles of Saint Paul. 2nd Thessalonians, Titus, and Philemon were excluded because they were too short to give reliable samples. From an analysis of these and other data the first 4 epistles (Romans, 1 Corinthians, 2 Corinthians, and Galatians) form a consistent group, and all the other epistles lie more than 2 standard deviations from the mean of this group (using statistics).
| Book | None | One | Two | Three+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Romans | 386 | 141 | 34 | 17 |
| 1 Corinthians | 424 | 152 | 35 | 16 |
| 2 Corinthians | 192 | 86 | 28 | 13 |
| Galatians | 128 | 48 | 5 | 6 |
| Philippians | 42 | 29 | 19 | 12 |
| Colossians | 23 | 32 | 17 | 9 |
| 1 Thessalonians | 34 | 23 | 8 | 16 |
| 1 Timothy | 49 | 38 | 9 | 10 |
| 2 Timothy | 45 | 28 | 11 | 4 |
| Hebrews | 155 | 94 | 37 | 24 |
Esperanto
Esperanto kaj comes from Greek. It may be abbreviated as k. or k (among other places, in the PIV dictionary), or, sometimes, as &.
See also
- Kaige revision, group of Greek-language Septuagint Bible versions that frequently use Koinē Greek: και γε [kai ge] ('and indeed').
- &
References
- Mor65, p. 224
- Zamenhof, L. L. (1990) . "Pri la vorto 'kaj'" [About the word 'kaj']. In Waringhien, G. (ed.). Lingvaj Respondoj [Language Answers] (in Esperanto). Originally from La Esperantisto, 1891, p. 49. (7th ed.). eldonejo ludovikito. Retrieved April 19, 2021 – via Bertilo Wenergreen.
La vorto 'kaj' ne sole ne estas maloportuna, sed ĝi ankaŭ tute ne estas arbitre elpensita (ĝi estas vorto greka = la latina 'et').
[The word 'kaj' is not just not inopportune, but it is also absolutely not arbitrarily devised (it is a Greek word = the Latin 'et').]. - ^ Wennergreen, Bertilo (November 14, 2020). "PMEG : Helposignoj". bertilow.com (in Esperanto). Retrieved April 19, 2021.
- "Mallongigoj kaj simboloj" [Abbreviations and symbols]. PIV (in Esperanto). 2020. Retrieved April 19, 2021.
- A. Q. Morton. The authorship of Greek prose (with discussion). Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series A, 128:169–233, 1965.
This article incorporates material from Econ 7800 class notes by Hans G. Ehrbar, which is licensed under GFDL.
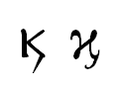

 statistics
statistics