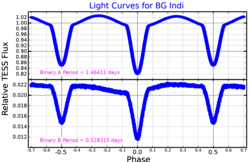
 Light curves from TESS data for the two eclipsing binaries comprising BG Indi, adapted from Borkovits et al. (2021) | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Indus |
| Right ascension | 21 58 30.04050 |
| Declination | −59° 00′ 43.4938″ |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.141 (6.11 - 6.36) |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F3V |
| Variable type | Algol |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 19.0 ± 0.5 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 24.729 mas/yr Dec.: 15.315 mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 19.5917 ± 0.2028 mas |
| Distance | 166 ± 2 ly (51.0 ± 0.5 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 2.45 / 3.02 / 7.23 / 7.83 |
| Absolute bolometric magnitude (Mbol) | 2.45 / 3.04 / 6.72 / 7.09 |
| Orbit | |
| Primary | BG Ind A |
| Companion | BG Ind B |
| Period (P) | 720.9+3.4 −3.1 d yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 540.4+2.7 −2.2 R☉ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.209+0.028 −0.048 |
| Inclination (i) | 85.5+3.1 −6.3° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2458699+14 −21 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 1.6+9.2 −8.8° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 12.57+0.17 −0.24 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 26.02+0.31 −0.50 km/s |
| Orbit | |
| Primary | BG Ind Aa |
| Companion | BG Ind Ab |
| Period (P) | 1.464065(2) d yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 7.602+0.038 −0.043 R☉ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0 |
| Inclination (i) | 73.27+0.06 −0.13° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2458326.1362+0.0011 −0.0012 |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 120.47+1.12 −0.75 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 130.99+0.48 −0.50 km/s |
| Orbit | |
| Primary | BG Ind Ba |
| Companion | BG Ind Bb |
| Period (P) | 0.528349(2) d yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 3.025+0.011 −0.016 R☉ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0 |
| Inclination (i) | 84.29+0.85 −0.87° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2458325.8072+0.0025 −0.0022 |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 138.98+1.23 −1.39 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 149.25+1.09 −1.13 km/s |
| Details | |
| κ Ind Aa | |
| Mass | 1.432+0.015 −0.024 M☉ |
| Radius | 2.339+0.016 −0.021 R☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | 8.433+0.199 −0.169 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.852+0.011 −0.005 cgs |
| Temperature | 6442+29 −28 K |
| κ Ind Ab | |
| Mass | 1.315+0.026 −0.023 M☉ |
| Radius | 1.592+0.047 −0.019 R☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | 4.934+0.279 −0.179 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.150+0.007 −0.016 cgs |
| Temperature | 6816±26 K |
| κ Ind Ba | |
| Mass | 0.688+0.008 −0.011 M☉ |
| Radius | 0.642+0.005 −0.007 R☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | 0.167±0.009 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.660+0.003 −0.002 cgs |
| Temperature | 4609+48 −49 K |
| κ Ind Bb | |
| Mass | 0.640+0.010 −0.011 M☉ |
| Radius | 0.611+0.008 −0.009 R☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | 0.118±0.009 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.672±0.004 cgs |
| Temperature | 4327+62 −57 K |
| Other designations | |
| κ Ind, BG Ind, CD−59° 7830, FK5 3752, HD 208496, HIP 108478, HR 8369, SAO 247247 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
BG Indi, also known as κ Indi (Kappa Indi) is a multiple star system in the southern constellation of Indus. Its average apparent magnitude is 6.141, meaning it can only be seen by the naked eye under exceptionally good viewing conditions. Stellar parallax measurements by Gaia put the system at about 166 light-years (51 parsecs) away.
Nomenclature
The star system is most commonly known as BG Indi. BG Indi is its variable star designation, a unique name given to variable stars based on its constellation and when it was discovered to be a variable. It also has the name κ Indi (Latinized to Kappa Indi), which is its Bayer designation.
Properties
BG Indi consists of four stars in two compact, orbiting pairs. The brighter pair is known as BG Indi A, and consists of two F-type main-sequence stars Aa and Ab. As F-type stars, they are more massive, larger, and hotter than the Sun, and with a metallicity of −0.2 ± 0.1, it is less metal-rich than the Sun. BG Indi is about 2.65 billion years old, and is just starting to leave the main sequence.
BG Indi Aa and Ab orbit each other on a circular orbit, with a period of 1.46 days. Periodically, one star passes in front of the other, blocking its light. Therefore, the apparent magnitude varies from 6.11 to 6.36. Its status as an eclipsing binary was confirmed by J. Manfroid and G. Mathys in 1984.
The other two stars, BG Indi Ba and Bb, form the pair BG Indi B. Both are less massive than the Sun, and orbit each other on a tighter orbit with a period of 0.53 days. Collectively, BG Indi A and B orbit each other with a period of 720.9 days with a moderate eccentricity of 0.209. All three orbits are likely to be more or less coplanar. BG Indi is the nearest quadruple star system consisting of two eclipsing binaries.
Notes
References
- ^ Borkovits, T.; Rappaport, S. A.; Maxted, P F L.; Terentev, I.; Omohundro, M.; Gagliano, R.; Jacobs, T.; Kristiansen, M. H.; Lacourse, D.; Schwengeler, H. M.; Vanderburg, A.; Blackford, M. G. (2021). "BG Ind: The nearest doubly eclipsing, compact hierarchical quadruple system". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 503 (3): 3759–3774. arXiv:2103.00925. doi:10.1093/mnras/stab621.
- ^ Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ Høg, E.; et al. (2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355: L27 – L30. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H.
- ^ Samus', N. N.; Kazarovets, E. V.; Durlevich, O. V.; Kireeva, N. N.; Pastukhova, E. N. (2017). "General catalogue of variable stars: Version GCVS 5.1". Astronomy Reports. 61 (1): 80–88. Bibcode:2017ARep...61...80S. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. S2CID 125853869.
- ^ Manfroid, J.; Mathys, G. (1984). "The Bright Eclipsing Binary HD 208496". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars. 2616 (2616): 1. Bibcode:1984IBVS.2616....1M.
- ^ "* kap01 Ind". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2021-07-17.
- Holmberg, J.; Nordström, B.; Andersen, J. (2007). "The Geneva-Copenhagen survey of the Solar neighbourhood II. New uvby calibrations and rediscussion of stellar ages, the G dwarf problem, age-metallicity diagram, and heating mechanisms of the disk". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 475 (2): 519. arXiv:0707.1891. Bibcode:2007A&A...475..519H. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20077221. S2CID 119054949.
- Rozyczka, M.; Kaluzny, J.; Pych, W.; Konacki, M.; Małek, K.; Mankiewicz, L.; Sokołowski, M.; Żarnecki, A. F. (2011). "Absolute properties of BG Ind - a bright F3 system just leaving the main sequence". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 414 (3): 2479–2485. arXiv:1010.1355. Bibcode:2011MNRAS.414.2479R. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.18567.x. S2CID 118422112.
| Constellation of Indus | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stars |
| ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Galaxies |
| ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||