
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 4-{(2S,3S)-3-oxiran-2-yl}butanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Abbreviations | LTA4 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | D017572 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C20H30O3 |
| Molar mass | 318.457 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Leukotriene A4 (LTA4) is a leukotriene, and is the precursor for the productions of leukotriene B4 (LTB4) and leukotriene C4 (LTC4).
Biosynthesis
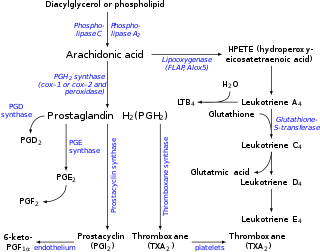
Following the biosynthesis of eicosanoid, triggered as a result of infection or inflammation, the resulting arachidonic acid substrate is released from the cell membrane phospholipid will enter the lipooxygenase pathway to produce leukotriene A4. In this pathway, arachidonic acid is converted into 5-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-HPETE) as a result of a catalytic complex consisting of the enzyme 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) and 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein (FLAP) in the presence of ATP and calcium ions. The resulting 5-HPETE yields the unstable allylic epoxide substrate LTA4 which is quickly hydrolyzed by the leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4H) enzyme to produce LTB4, or synthesized by leukotriene C4 synthase (LTC4S) with the addition of glutathione to produce LTC4 which can be further metabolized to produce leukotriene D4 (LTD4) and leukotriene E4 (LTE4). The lipooxygenase pathway is one of several possible pathways including the cyclooxygenase pathway (also PGH synthase pathway), isoprostane pathway, and cytochrome P450 epoxygenases pathway following the arachidonic acid metabolism, but is the only pathway in which the subsequent steps will lead to the production of leukotrienes.
References
- ^ Abu, J.I.; Konje, J.C. (March 2000). "Leukotrienes in gynaecology: the hypothetical value of anti-leukotriene therapy in dysmenorrhoea and endometriosis". Human Reproduction Update. 6 (2): 200–205. doi:10.1093/humupd/6.2.200. ISSN 1355-4786. PMID 10782578.
- ^ Marx, J.L. (1982-03-12). "The leukotrienes in allergy and inflammation". Science. 215 (4538): 1380–1383. Bibcode:1982Sci...215.1380M. doi:10.1126/science.6278589. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 6278589.
- Nicolls, Mark R.; Voelkel, Norbert F.; Peters-Golden, Marc; Rajadas, Jayakumar; Fridlib, Marina; Inayathullah, Mohammed; Zamanian, Roham T.; Rabinovitch, Marlene; Farkas, Laszlo (2013-08-28). "Blocking Macrophage Leukotriene B4 Prevents Endothelial Injury and Reverses Pulmonary Hypertension". Science Translational Medicine. 5 (200): 200ra117. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3006674. ISSN 1946-6234. PMC 4016764. PMID 23986401.
- ^ Serhan, C.N.; Rouzer, C.A.; Lindgren, J.A.; Dahlen, S.E.; Samuelsson, B. (1987-09-04). "Leukotrienes and lipoxins: structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects". Science. 237 (4819): 1171–1176. Bibcode:1987Sci...237.1171S. doi:10.1126/science.2820055. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 2820055.
- Nicolls, Mark R.; Dixon, J. Brandon; Kitajewski, Jan; Peters-Golden, Marc; Voelkel, Norbert F.; Dhillon, Gundeep S.; Zamanian, Roham T.; Feroze, Abdullah H.; Nepiyushchikh, Zhanna (2017-05-10). "Leukotriene B4 antagonism ameliorates experimental lymphedema". Science Translational Medicine. 9 (389): eaal3920. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3920. ISSN 1946-6234. PMID 28490670.
- O'Connor, J. Patrick; Lysz, Thomas (September 2008). "Celecoxib, NSAIDs and the skeleton". Drugs of Today. 44 (9): 693–709. doi:10.1358/dot.2008.44.9.1251573. ISSN 1699-3993. PMID 19137124.
| Eicosanoids | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precursor | |||||||||||||||
| Prostanoids |
| ||||||||||||||
| Leukotrienes (LT) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Eoxins (EX) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Nonclassic |
| ||||||||||||||
| By function | |||||||||||||||
| Leukotriene signaling modulators | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||