| La Crosse - La Crescent Canadian Pacific Railway, Main Channel Bridge | |
|---|---|
 Looking South downstream. Larger barges have to stop and back up to recenter to stay in the main navigation channel when heading downstream. Looking South downstream. Larger barges have to stop and back up to recenter to stay in the main navigation channel when heading downstream. | |
| Coordinates | 43°50′00″N 91°16′53″W / 43.8332°N 91.2813°W / 43.8332; -91.2813 |
| Carries | Canadian Pacific Railway and the Amtrak Empire Builder |
| Crosses | Mississippi River |
| Locale | La Crosse, Wisconsin |
| Official name | Canadian Pacific Rail Road Bridge #283.27 Tomah Subdivision, La Crescent, MN, Houston County |
| Other name(s) | L4B |
| Maintained by | Canadian Pacific Railway |
| ID number | L4B |
| Characteristics | |
| Design | Swing bridge |
| Total length | 1,042 feet (318 m) |
| Width | 20 feet (6 m) |
| Clearance below | 21.9 feet (7 m) |
| Rail characteristics | |
| No. of tracks | 1 |
| History | |
| Opened | Existing structure, 1902 |
| Statistics | |
| Daily traffic | 20.0 trains per day (as of 2014) |
| Location | |


The La Crosse Rail Bridge is a swing bridge that spans the Mississippi River between La Crescent, Minnesota and La Crosse, Wisconsin. The first bridge in this location initially was designed and ready to build by June 1876, and was completed in November 1876 by the Milwaukee and St. Paul Railway, a predecessor of the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad. It was later replaced in 1902. It is at the Western end of the Canadian Pacific Railway Tomah Subdivision. Amtrak's Empire Builder crosses this bridge.
History
Prior to its bridging, the Mississippi River connected the country north to south, but was an obstacle for those going east to west. The railroad relied on ferry boats to transport rail cars across the river into La Crosse, which cost a considerable amount of money and time. In addition, many of the ferry boats were unreliable because they had no fixed schedule. In the early 1800s, it was difficult to construct bridges, as they needed to provide enough clearance for the abundance of steamboats on the river. In the winter months when the river froze over and boat traffic stopped, the railroad would lay down seasonal tracks across the ice and remove them by spring.
Rock Island Bridge
Main article: Government BridgeIn 1856, the first swing bridge to span the Mississippi river was constructed in Rock Island, Illinois, upstream of the place where Government Bridge is today. Only a few days after that bridge was opened, a steamboat crashed into it. The boat and bridge caught on fire, and the steamboat owner sued for damages, claiming the bridge was a hazard to navigation. It was defended in court by an Illinois lawyer: Abraham Lincoln. Lincoln won the case for the railroad, arguing that a person has a much right to build a bridge to cross a river as another person has to travel up and down the water. This victory led to the construction of even more railroad bridges over the Mississippi.
Construction of the La Crosse bridge
The Milwaukee and St. Paul Railway had two disconnected segments of a railway between Chicago, Illinois and St. Paul, Minnesota: one rail line from La Crescent, Minnesota to St. Paul, and the other rail line from La Crosse to Milwaukee. The Railroad used the Winona Rail Bridge belonging to the Winona & Saint Peter Railroad, constructed in 1871, until the La Crosse Rail Bridge was built. A charter from Congress in 1872 permitted the railway to construct the bridge. The Secretary of War assumed control of Mississippi crossings. The railroad selected their optimal location in North La Crosse, bridging the Black River to French Island. A group of military engineers had selected a site at the foot of Mt. Vernon Avenue, which was approved by the Secretary of War. Another source states Vine Street for the location. This would have lengthened the railway, required flagged street crossings in downtown La Crosse, and also set the river crossing to the south of La Crescent over property owned by Wall Street speculators. The original 1873 Secretary of War report allowed the railroad company to build at any point selected by the company. After much legal wrangling, final approval for the original desired site was granted by the Wisconsin State Assembly.
The initial construction began in June 1876 and was completed five months later in November. In 1876, the bridge cost US$500,000 to build. It paid for itself in a few years, with the railroad saving $90,000 a year in river tolls. Over the years, the La Crosse rail bridge has gone through many changes, including replacement of the original bridge in 1902.
The bridge is located over the west channel of the Mississippi River near Shore Acres and links to Minnesota Island. The La Crosse Rail Bridge itself is located entirely on the Minnesota side of the river and is 1,050 feet, 11 inches long. A second bridge connects Minnesota Island to the Wisconsin shore across the Black River.
Present usage
See also: Swing bridgeThe swing span has a Humpback truss, while the two adjoining spans are flat-top fixed through trusses. A section of the bridge swings on a pivot point, opening up two 150-foot- wide lanes for river traffic to pass through, similar to a gate. The bridge is operated from a tower and originally ran on steam power. Opening and closing the swing bridge takes about five minutes, which allowed the railroad to build a permanent track across the river to La Crosse without interfering with the towboats and barges that travel up and down the Mississippi.
River traffic has the right of way, and the swing bridge must even open for privately owned pleasure crafts or face fines from the Coast Guard. though it is speculated that the railroad would often take the fines over the cost of stopping a train.
The La Crosse Rail Bridge has taken a significant amount of abuse over the years. In 2011, it was ranked fourth in most boat-related collisions out of 22 states, 7,500 miles of railway and 1,200 other bridges. One incident was as recent as July 22, 2011, when a barge clipped the side of the bridge and halted river traffic. The Winona bridge became part of the Chicago and Northwestern system. That bridge was used until 1977. The Chicago and Northwestern gained trackage rights to use the La Crosse Rail Bridge. The C & NW successor, Union Pacific, accesses in this manner from Tomah to Winona.
Proposed alteration
The Coast Guard has proposed alterations to the bridge. The proposed plan would remove the swing bridge and install a lift span and create a 65-foot clearance and open a 300-foot wide lane for the boats. The alterations would move the bridge opening away from the shore line to the center of the channel. The Coast Guard has dropped plans to alter the bridge.
-
 A new 300 foot wide lift span in the center of the main channel.
A new 300 foot wide lift span in the center of the main channel.
-
 New 300' lift span with two new piers added
New 300' lift span with two new piers added
-
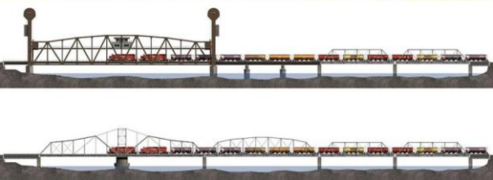 New 300' lift span in place of swing bridge
New 300' lift span in place of swing bridge
Gallery
 |
See also
References
- ^ Schuldt, Clay (2011-11-30). "Historic swing bridge an important cross country link". La Crosse Tribune. Retrieved 2018-02-23.
- Missouri Department of Transportation (2017). The Merchants Bridge rehabilitation program (PDF) (Grant application). Figure 10: Rail Traffic Volumes Overlaid with Seismic Hazard, 2014.
- ^ Mansfield Merriman (1919). History of La Crosse County, Wisconsin: Containing an Account of Its Settlement, Growth, Development and Resources : an Extensive and Minute Sketch of Its Cities, Towns and Villages-their Improvements, Industries, Manufactories, Churches, Schools and Societies : Its War Record, Biographical Sketches, Portraits of Prominent Men and Early Settlers : the Whole Preceded by a History of Wisconsin, Statistics of the State, and an Abstract of Its Laws and Constitution and the Constitution of the United States. pp. 40–.
- ^ Joan M. Rausch; Richard H. Zeitlin; Carol Lohry Cartwright (1996). City of La Crosse, Wisconsin architectural and historical intensive survey report. Architectural Researches, Inc.
- John Butler Johnson; Henry Harrison Suplee; Johannes H. Cuntz; Charles Buxton Going (1906). The Engineering Index. Engineering Magazine. pp. 108–.
- A Brief Historical Overview of the Chicago, Rock Island, and Pacific Railroad Archived 2008-03-17 at the Wayback Machine
- Ross, Michael (2009). "Hell Gate of the Mississippi: The Effie Afton Trial and Abraham Lincoln's Role in It". The Annals of Iowa. 68 (3): 312–314. doi:10.17077/0003-4827.1361. ISSN 0003-4827.
- John W. Cary (1892). The Organization and History of the Chicago, Milwaukee & St. Paul Railway Company. Press of Cramer, Aikens, & Cramer. pp. 320–.
- United States. War Dept (1873). Annual Report of the Secretary of War. U.S. Government Printing Office. pp. 563–.
- "Hometown Icon: Railroad swing bridge". La Crosse Tribune. Retrieved 2018-02-23.
- La Crosse County Comprehensive Plan Draft Archived 2020-03-13 at the Wayback Machine Transportation. La Crosse County. January 2016
- Chiu, Philip. "Alteration of the Canadian Pacific Railway Drawbridge Over the Upper Mississippi River, La Crosse, Wisconsin Under the Provisions of Truman-Hobbs Act" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-03-13. Retrieved 2021-03-12.
Bibliography
- Costello, Mary Charlotte (2002). Climbing the Mississippi River Bridge by Bridge, Volume Two: Minnesota. Cambridge, MN: Adventure Publications. ISBN 0-9644518-2-4.
External links
| Crossings of the Mississippi River | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Truss bridges in the United States
- Swing bridges in the United States
- Railroad bridges in Minnesota
- Railroad bridges in Wisconsin
- Bridges over the Mississippi River
- Bridges completed in 1876
- Canadian Pacific Railway bridges in the United States
- Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad
- Buildings and structures in Houston County, Minnesota
- Buildings and structures in La Crosse, Wisconsin
- Interstate railroad bridges in the United States

