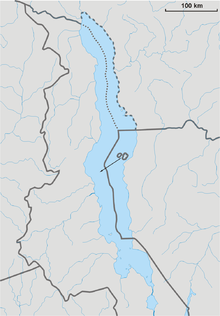
The Malawi–Tanzania border is an international boundary that separates Malawi and Tanzania in East Africa. Most of the border is formed by the river Songwe, whose source is found in the mountains to the south-west of Mount Rungwe and the town of Tukuyu. The Songwe is fast-flowing and changes its course regularly in a short period of time, forming new meanders and causing the precise border location to shift and become ambiguous. A dam is currently being constructed to regulate the river's flow.
The border follows the Songwe into Lake Malawi, where it meets the tripoint between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania. The border at Malawi Lake is disputed, as are the rights to the lake.
Following the Heligoland-Zanzibar Treaty of 1890, the two colonial powers, the United Kingdom (for Nyasaland, which later became Malawi) and Germany (for Tanganyika, which later became Tanzania) agreed that the border would follow the Tanzanian shore of the lake. When Malawi and Tanzania respectively gained independence, the agreement was never modified. Oil-prospecting projects on the lake conducted by a British company have revived border disagreements between the two countries.
References
- International, Lahmeyer. "Lahmeyer International: Songwe River Basin Development Programme between Malawi and Tanzania". www.lahmeyer.de. Retrieved 2016-11-07.
- "GHDI - Document". germanhistorydocs.ghi-dc.org. Retrieved 2016-11-07.
- "Malawi-Tanzania Border Dispute Flares Up Over Potential Oil Discovery". www.worldpoliticsreview.com. 2 September 2014. Retrieved 2016-11-07.
This Malawi location article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This Tanzania location article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |