
International maritime signal flags are various flags used to communicate with ships. The principal system of flags and associated codes is the International Code of Signals. Various navies have flag systems with additional flags and codes, and other flags are used in special uses, or have historical significance.
Usage
There are various methods by which the flags can be used as signals:
- A series of flags can spell out a message, each flag representing a letter.
- Individual flags have specific and standard meanings; for example, diving support vessels raise the "A" flag indicating their inability to move from their current location because they have a diver underwater and to warn other vessels to keep clear to avoid endangering the diver(s) with their propellers.
- One or more flags form a code word whose meaning can be looked up in a code book held by both parties. An example is the Popham numeric code used at the Battle of Trafalgar.
- In yacht racing and dinghy racing, flags have other meanings; for example, the P flag is used as the "preparatory" flag to indicate an imminent start, and the S flag means "shortened course" (for more details see Race signals).

NATO uses the same flags, with a few unique to warships, alone or in short sets to communicate various unclassified messages. The NATO usage generally differs from the international meanings, and therefore warships will fly the Code/answer flag above the signal to indicate it should be read using the international meaning.
During the Allied occupations of Axis countries after World War II, use and display of those nations' national flags was banned. In order to comply with the international legal requirement that a ship identify its registry by displaying the appropriate national ensign, swallow-tailed versions of the C, D, and E signal flags were designated as, respectively, provisional German, Okinawan, and Japanese civil ensigns. Being swallowtails, they are commonly referred to as the "C-pennant" (German: C-Doppelstander), "D-pennant", and "E-pennant".
The signal flags for M, T, V and X are respectively similar to the flags of Scotland, France, the Saint Patrick's saltire and the flag of Finland.
Letter flags (with ICS meaning)
Main article: International Code of Signals| Letter / radio name |
Flag | Blazon | ICS meaning as single flag | Meaning when used with numeric complements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A Alfa |
 |
Swallowtailed, per pale argent and azure | "I have a diver down; keep well clear at slow speed." | Azimuth or bearing |
| B Bravo |
 |
Swallowtailed, gules | "I am taking in or discharging or carrying dangerous goods." (Originally used by the Royal Navy specifically for military explosives.) | |
| C Charlie |
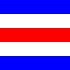 |
Azure, a fess gules fimbriated argent | "Affirmative." | Magnetic bearing |
| D Delta |
 |
Or, a Spanish fess azure | "Keep clear of me; I am maneuvering with difficulty." | Date |
| E Echo |
 |
Per fess azure and gules | "I am altering my course to starboard." | |
| F Foxtrot |
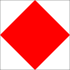 |
Argent, a lozenge throughout gules | "I am disabled; communicate with me." | |
| G Golf |
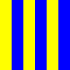 |
Paly of six or and azure | "I require a pilot."By fishing vessels near fishing grounds: "I am hauling nets." | Longitude (The first 2 or 3 digits denote degrees; the last 2 denote minutes.) |
| H Hotel |
 |
Per pale argent and gules | "I have a pilot on board." | |
| I India |
 |
Or, a pellet | "I am altering my course to port." | |
| J Juliett |
 |
Azure, a fess argent | "I am on fire and have dangerous cargo on board: keep well clear of me."or"I am leaking dangerous cargo." | |
| K Kilo |
 |
Per pale or and azure | "I wish to communicate with you." | "I wish to communicate with you by...":1) Morse signaling by hand-flags or arms;2) Loud hailer (megaphone);3) Morse signaling lamp;4) Sound signals. |
| L Lima |
 |
Quarterly or and sable | "Stop immediately." | Latitude (the first 2 digits denote degrees; the last 2 denote minutes.) |
| M Mike |
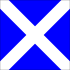 |
Azure, a saltire argent | "My vessel is stopped and making no way through the water." | |
| N November |
 |
Chequy of sixteen azure and argent | "Negative." | |
| O Oscar |
 |
Per bend gules and or | "Man overboard." (often attached to the man overboard pole on boats).With a sinister hoist, the semaphore flag. | |
| P Papa |
 |
Azure, an inescutcheon argent | The blue Peter.In harbour: All persons should report on board as the vessel is about to proceed to sea.At sea: It may be used by fishing vessels to mean: "My nets have come fast upon an obstruction." | |
| Q Quebec |
 |
Or | "My vessel is 'healthy' and I request free pratique." | |
| R Romeo |
 |
Gules, a cross or | No ICS meaning as single flag.
Prior to 1969: "The way is off my ship; you may feel your way past me." |
Distance (range) in nautical miles. |
| S Sierra |
 |
Argent, an inescutcheon azure | "I am operating astern propulsion." | Speed (velocity) in knots |
| T Tango |
 |
Tierced in pale gules, argent and azure | "Keep clear of me."Fishing boats: "Keep clear of me; I am engaged in pair trawling." | Local time. (The first 2 digits denote hours; the last 2 denote minutes.) |
| U Uniform |
 |
Quarterly gules and argent | "You are running into danger." | |
| V Victor |
 |
Argent, a saltire gules | "I require assistance." | Velocity in kilometres per hour. |
| W Whiskey |
 |
Azure, an inescutcheon gules fimbriated argent | "I require medical assistance." | |
| X Xray |
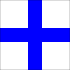 |
Argent, a cross azure | "Stop carrying out your intentions and watch for my signals." | |
| Y Yankee |
 |
Bendy sinister of ten or and gules | "I am dragging my anchor." | |
| Z Zulu |
 |
Per saltire or, sable, gules and azure | "I require a tug."By fishing vessels near fishing grounds: "I am shooting nets." | Time (UTC). (The first 2 digits denote hours; the last 2 denote minutes.) |
Notes
- ^ N and C together ("no" and "yes") is used as a distress signal.
- ^ Also signallable on a ship's whistle using Morse code. See International Code of Signals.
- Historically, in a CAM ship during World War II, Foxtrot was used to warn about launching the interceptor aircraft from the deck catapult.
- In Japan, this flag is now also used to indicate a tsunami warning, although the ICS recommends the flag combination "ND" for such a warning.
- The Z flag was also famously hoisted by Admiral Heihachiro Togo at the 1905 Battle of Tsushima as the Japanese fleet prepared to engage the Russian fleet. In Japanese coding at the time, the flag meant, "The fate of the Empire rests on the outcome of this battle. Let each man do his utmost." (「皇國ノ興廢此ノ一戰ニ在リ、各員一層奮勵努力セヨ」)
Number flags
| Number | NATO flag | ICS flag | Blazons |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Zero |
 |
 |
NATO: Argent, five crosses hummetty azure in saltire ICS: Or, a pale gules |
| 1 One |
 |
 |
NATO: Gules, a fess or ICS: Argent, a torteau |
| 2 Two |
 |
 |
NATO: Or, a fess gules ICS: Azure, a plate |
| 3 Three |
 |
 |
NATO: Azure, a fess gules ICS: Tierced in pale gules, argent and azure |
| 4 Four |
 |
 |
NATO: Gules, a saltire argent ICS: Gules, a cross of Saint Philip argent |
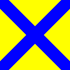
| 5 Five |
 |
 |
NATO: Or, a saltire azure ICS: Per pale or and azure |
| 6 Six |
 |
 |
NATO: Bendy sinister of seven argent and azure ICS: Per fess sable and argent |
| 7 Seven |
 |
 |
NATO: Gules, a pale argent ICS: Per fess or and gules |
| 8 Eight |
 |
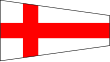 |
NATO: Or, a pale azure ICS: Argent, a cross of Saint Philip gules |
| 9 Nine |
 |
 |
NATO: Azure, a pale argent ICS: Quarterly argent, sable, gules and or |
Substitute
Substitute or repeater flags allow messages with duplicate characters to be signaled without the need for multiple sets of flags.
The four NATO substitute flags are as follows:
 |
 |
 |
 |
| First substitute | Second substitute | Third substitute | Fourth substitute |
The International Code of Signals includes only the first three of these substitute flags. To illustrate their use, here are some messages and the way they would be encoded:
| "N" |  | ||||
| "O" |  | ||||
| "NO" |  |
 | |||
| "NON" |  |
 |
 | ||
| "NOO" |  |
 |
 | ||
| "NOON" |  |
 |
 |
 | |
| "NONO" |  |
 |
 |
 | |
| "NONON" |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| "NONNN" |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
See also
- Bravo Zulu
- Character encoding
- Day shapes
- Diver down flag
- Dress ship
- England expects that every man will do his duty
- The fate of the Empire rests on the outcome of this battle. Let each man do his utmost
- Flag of Germany after World War II (C-Pennant)
- Flag semaphore
- Heliograph
- International Code of Signals
- International inspection pennant
- List of international common standards
- NATO phonetic alphabet
- Signal lamp
- Yellow Jack
References
- International Code of Signals, 2005 ed. (IMO IA994E), IMO – International Maritime Organization, 2005, ISBN 978-92-801-4198-6;International Code of Signals for Visual, Sound, and Radio Communications, United States Edition, 1969 (Revised 2003) (PDF), 1969, archived (PDF) from the original on 2015-03-20.
- United States Power Squadrons Flag and Etiquette Committee Signal Flags Archived 2013-11-04 at the Wayback Machine
- AB Nordbok. "The Lore of Ships", page 138. New York: Crescent Books, 1975. ISBN 9789174420050
External links
- "How Ships Talk With Flags", October 1944, Popular Science
- John Savard's flag page. Collection of different flag systems.
- Freeware to aid memorizing the flags
- La flag-alfabeto - signal flags used for the Esperanto language - the flags for the Esperanto letters with diacritical marks have the lighter color in the normal flag replaced with light green, which is not used in any normal flag.
| Telecommunications | |
|---|---|
| History |
|
| Pioneers |
|
| Transmission media | |
| Network topology and switching | |
| Multiplexing | |
| Concepts | |
| Types of network | |
| Notable networks | |
| Locations | |