| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Mast cell stabilizer" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

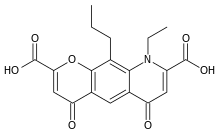
Mast cell stabilizers are medications used to prevent or treat certain allergic disorders. They block mast cell degranulation, stabilizing the cell and thereby preventing the release of histamine and related mediators. One suspected pharmacodynamic mechanism is the blocking of IgE-regulated calcium channels. Without intracellular calcium, the histamine vesicles cannot fuse to the cell membrane and degranulate.
As inhalers they are used to treat asthma, as nasal sprays to treat hay fever (allergic rhinitis) and as eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis. Finally, in oral form, they are used to treat the rare condition of mastocytosis.
Examples
Mast cell stabilizer medications include:
- Cromoglicic acid (Cromolyn/cromoglycate)
- Lodoxamide
- Nedocromil
References
- ^ "Allergy medications: Know your options". Mayoclinic.com. 2022-03-05. Retrieved 2023-04-02.
- Castillo M, Scott NW, Mustafa MZ, Mustafa MS, Azuara-Blanco A (2015). "Topical antihistamines and mast cell stabilisers for treating seasonal and perennial allergic conjunctivitis". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 (6): CD009566. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009566.pub2. hdl:2164/6048. PMC 10616535. PMID 26028608.
- ^ "Mast Cell Stabilizers: Uses, most common brand names, and safety information". nicerx.com. Retrieved 2023-04-02.
- ^ "Mast cell stabilizers". drugs.com. Retrieved 2023-04-02.
- Finn, D F; Walsh, J J (2013-08-15). "Twenty-first century mast cell stabilizers". British Journal of Pharmacology. 170 (1): 23–37. doi:10.1111/bph.12138. PMC 3764846. PMID 23441583.
- Lui, ZQ; Lii, XX; Qui, ZQ; Yu, Y; Li, MG (2017). "Vitamin D contributes to mast cell stabilization". Allergy. 72 (8): 1184–1192. doi:10.1111/all.13110. PMID 27998003. S2CID 4643742.
- Weng, Zuyi; Zhang, Bodi; Asadi, Shahrzad; Sismanopoulos, Nikolaos; Butcher, Alan; Fu, Xueyan; Katsarou-Katsari, Alexandra; Antoniou, Christina; Theoharides, Theoharis C. (28 March 2012). "Quercetin Is More Effective than Cromolyn in Blocking Human Mast Cell Cytokine Release and Inhibits Contact Dermatitis and Photosensitivity in Humans". PLOS ONE. 7 (3): e33805. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...733805W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0033805. PMC 3314669. PMID 22470478.
| Decongestants and other nasal preparations (R01) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topical |
| ||||||||||
| Systemic use: Sympathomimetics | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
This drug article relating to the respiratory system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |