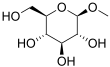
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name Methyl D-glucopyranoside | |||
| Other names 1-O-Methyl-D-glucopyranose | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.620 | ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C7H14O6 | ||
| Molar mass | 194.183 g·mol | ||
| Appearance | White crystalline solid | ||
| Density | 1.46 g/cm (α) | ||
| Melting point | 168 °C (334 °F; 441 K) (α) | ||
| Solubility in water | 108 g/100 mL | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |||
Methylglucoside is a monosaccharide derived from glucose. It can be prepared in the laboratory by the acid-catalyzed reaction of glucose with methanol.
It is used as a chemical intermediate in the production of a variety of products including emollients, emulsifiers, humectants, moisturizers, thickening agents, plasticizers, surfactants, varnishes, and resins. The formation of methyl glycoside indicates that the structure of glucose is not open chain.
References
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 5997
- B. Helferich and W. Schäfer (1926). "α-METHYL d-GLUCOSIDE". Organic Syntheses. 6: 64.
- "Methyl Glucoside Derivatives". Lubrizol. Archived from the original on April 14, 2014. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |