 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
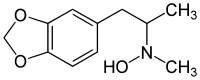
| Formula | C11H15NO3 |
| Molar mass | 209.245 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-hydroxy-N-methylamphetamine (MDHMA; FLEA) is an entactogen, psychedelic, and stimulant of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It is the N-hydroxy homologue of MDMA ("Ecstasy"), and the N-methyl homologue of MDOH. MDHMA was first synthesized and assayed by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved), Shulgin listed the dosage range as 100–160 mg, and the duration as approximately 4–8 hours. He describes MDHMA as causing entactogenic and open MDMA-like effects, easing communication, and increasing appreciation of the senses.
Legality
United Kingdom
This substance is a Class A drug in the Drugs controlled by the UK Misuse of Drugs Act.
References
- ^ Shulgin A, Shulgin A (September 1991). PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. Berkeley, California: Transform Press. ISBN 0-9630096-0-5. OCLC 25627628.
- "UK Misuse of Drugs act 2001 Amendment summary". Isomer Design. Archived from the original on 22 October 2017. Retrieved 12 March 2014.
External links
| Empathogens/entactogens | |
|---|---|
| Phenylalkyl- amines (other than cathinones) |
|
| Cyclized phenyl- alkylamines | |
| Cathinones | |
| Tryptamines | |
| Chemical classes | |
| Phenethylamines | |
|---|---|
| Phenethylamines |
|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|