In nuclear and materials physics, stopping power is the retarding force acting on charged particles, typically alpha and beta particles, due to interaction with matter, resulting in loss of particle kinetic energy. Stopping power is also interpreted as the rate at which a material absorbs the kinetic energy of a charged particle. Its application is important in a wide range of thermodynamic areas such as radiation protection, ion implantation and nuclear medicine.

Definition and Bragg curve
Both charged and uncharged particles lose energy while passing through matter. Positive ions are considered in most cases below. The stopping power depends on the type and energy of the radiation and on the properties of the material it passes. Since the production of an ion pair (usually a positive ion and a (negative) electron) requires a fixed amount of energy (for example, 33.97 eV in dry air), the number of ionizations per path length is proportional to the stopping power. The stopping power of the material is numerically equal to the loss of energy E per unit path length, x:
The minus sign makes S positive.
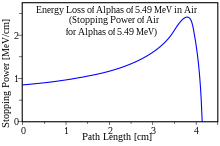
The force usually increases toward the end of range and reaches a maximum, the Bragg peak, shortly before the energy drops to zero. The curve that describes the force as function of the material depth is called the Bragg curve. This is of great practical importance for radiation therapy.
The equation above defines the linear stopping power which in the international system is expressed in N but is usually indicated in other units like MeV/mm or similar. If a substance is compared in gaseous and solid form, then the linear stopping powers of the two states are very different just because of the different density. One therefore often divides the force by the density of the material to obtain the mass stopping power which in the international system is expressed in m/s but is usually found in units like MeV/(mg/cm) or similar. The mass stopping power then depends only very little on the density of the material.
The picture shows how the stopping power of 5.49 MeV alpha particles increases while the particle traverses air, until it reaches the maximum. This particular energy corresponds to that of the alpha particle radiation from naturally radioactive gas radon (Rn) which is present in the air in minute amounts.
The mean range can be calculated by integrating the reciprocal stopping power over energy:
where:
- E0 is the initial kinetic energy of the particle
- Δx is the "continuous slowing down approximation (CSDA)" range and
- S(E) is the linear stopping power.
The deposited energy can be obtained by integrating the stopping power over the entire path length of the ion while it moves in the material.
Electronic, nuclear and radiative stopping
Electronic stopping refers to the slowing down of a projectile ion due to the inelastic collisions between bound electrons in the medium and the ion moving through it. The term inelastic is used to signify that energy is lost during the process (the collisions may result both in excitations of bound electrons of the medium, and in excitations of the electron cloud of the ion as well). Linear electronic stopping power is identical to unrestricted linear energy transfer.
Instead of energy transfer, some models consider the electronic stopping power as momentum transfer between electron gas and energetic ion. This is consistent with the result of Bethe in the high energy range.
Since the number of collisions an ion experiences with electrons is large, and since the charge state of the ion while traversing the medium may change frequently, it is very difficult to describe all possible interactions for all possible ion charge states. Instead, the electronic stopping power is often given as a simple function of energy which is an average taken over all energy loss processes for different charge states. It can be theoretically determined to an accuracy of a few % in the energy range above several hundred keV per nucleon from theoretical treatments, the best known being the Bethe formula. At energies lower than about 100 keV per nucleon, it becomes more difficult to determine the electronic stopping using analytical models. Recently real-time Time-dependent density functional theory has been successfully used to accurately determine the electronic stopping for various ion-target systems over a wide range of energies including the low energy regime.
Graphical presentations of experimental values of the electronic stopping power for many ions in many substances have been given by Paul. The accuracy of various stopping tables has been determined using statistical comparisons.
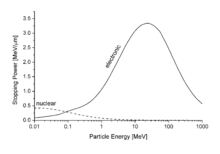
Nuclear stopping power refers to the elastic collisions between the projectile ion and atoms in the sample (the established designation "nuclear" may be confusing since nuclear stopping is not due to nuclear forces, but it is meant to note that this type of stopping involves the interaction of the ion with the nuclei in the target). If one knows the form of the repulsive potential energy between two atoms (see below), it is possible to calculate the nuclear stopping power . In the stopping power figure shown above for aluminium ions in aluminum, nuclear stopping is negligible except at the lowest energy. Nuclear stopping increases when the mass of the ion increases. In the figure shown on the right, nuclear stopping is larger than electronic stopping at low energy. For very light ions slowing down in heavy materials, the nuclear stopping is weaker than the electronic at all energies.
Especially in the field of radiation damage in detectors, the term "non-ionizing energy loss" (NIEL) is used as a term opposite to the linear energy transfer (LET), see e.g. Refs. Since per definition nuclear stopping power does not involve electronic excitations, NIEL and nuclear stopping can be considered to be the same quantity in the absence of nuclear reactions.
The total non-relativistic stopping power is therefore the sum of two terms: . Several semi-empirical stopping power formulas have been devised. The model given by Ziegler, Biersack and Littmark (the so-called "ZBL" stopping, see next chapter), implemented in different versions of the TRIM/SRIM codes, is used most often today.
Radiative stopping power, which is due to the emission of bremsstrahlung in the electric fields of the particles in the material traversed, must be considered at extremely high ion energies. For electron projectiles, radiative stopping is always important. At high ion energies, there may also be energy losses due to nuclear reactions, but such processes are not normally described by stopping power.
Close to the surface of a solid target material, both nuclear and electronic stopping may lead to sputtering.
The slowing-down process in solids
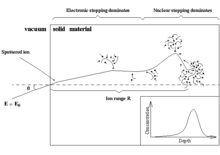
In the beginning of the slowing-down process at high energies, the ion is slowed mainly by electronic stopping, and it moves almost in a straight path. When the ion has slowed sufficiently, the collisions with nuclei (the nuclear stopping) become more and more probable, finally dominating the slowing down. When atoms of the solid receive significant recoil energies when struck by the ion, they will be removed from their lattice positions, and produce a cascade of further collisions in the material. These collision cascades are the main cause of damage production during ion implantation in metals and semiconductors.
When the energies of all atoms in the system have fallen below the threshold displacement energy, the production of new damage ceases, and the concept of nuclear stopping is no longer meaningful. The total amount of energy deposited by the nuclear collisions to atoms in the materials is called the nuclear deposited energy.
The inset in the figure shows a typical range distribution of ions deposited in the solid. The case shown here might, for instance, be the slowing down of a 1 MeV silicon ion in silicon. The mean range for a 1 MeV ion is typically in the micrometer range.
Repulsive interatomic potentials
At very small distances between the nuclei the repulsive interaction can be regarded as essentially Coulombic. At greater distances, the electron clouds screen the nuclei from each other. Thus the repulsive potential can be described by multiplying the Coulombic repulsion between nuclei with a screening function φ(r/a),
where φ(r/a) → 1 when r → 0. Here and are the charges of the interacting nuclei, and r the distance between them; a is the so-called screening parameter.
A large number of different repulsive potentials and screening functions have been proposed over the years, some determined semi-empirically, others from theoretical calculations. A much used repulsive potential is the one given by Ziegler, Biersack and Littmark, the so-called ZBL repulsive potential. It has been constructed by fitting a universal screening function to theoretically obtained potentials calculated for a large variety of atom pairs. The ZBL screening parameter and function have the forms
and
where x = r/au, and a0 is the Bohr atomic radius = 0.529 Å.
The standard deviation of the fit of the universal ZBL repulsive potential to the theoretically calculated pair-specific potentials it is fit to is 18% above 2 eV. Even more accurate repulsive potentials can be obtained from self-consistent total energy calculations using density-functional theory and the local-density approximation (LDA) for electronic exchange and correlation.
Channeling
Main article: Channelling (physics)In crystalline materials the ion may in some instances get "channeled", i.e., get focused into a channel between crystal planes where it experiences almost no collisions with nuclei. Also, the electronic stopping power may be weaker in the channel. Thus the nuclear and electronic stopping do not only depend on material type and density but also on its microscopic structure and cross-section.
Computer simulations of ion slowing down
Computer simulation methods to calculate the motion of ions in a medium have been developed since the 1960s, and are now the dominant way of treating stopping power theoretically. The basic idea in them is to follow the movement of the ion in the medium by simulating the collisions with nuclei in the medium. The electronic stopping power is usually taken into account as a frictional force slowing down the ion.
Conventional methods used to calculate ion ranges are based on the binary collision approximation (BCA). In these methods the movement of ions in the implanted sample is treated as a succession of individual collisions between the recoil ion and atoms in the sample. For each individual collision the classical scattering integral is solved by numerical integration.
The impact parameter p in the scattering integral is determined either from a stochastic distribution or in a way that takes into account the crystal structure of the sample. The former method is suitable only in simulations of implantation into amorphous materials, as it does not account for channeling.
The best known BCA simulation program is TRIM/SRIM (acronym for TRansport of Ions in Matter, in more recent versions called Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter), which is based on the ZBL electronic stopping and interatomic potential. It has a very easy-to-use user interface, and has default parameters for all ions in all materials up to an ion energy of 1 GeV, which has made it immensely popular. However, it doesn't take account of the crystal structure, which severely limits its usefulness in many cases. Several BCA programs overcome this difficulty; some fairly well known are MARLOWE, BCCRYS and crystal-TRIM.
Although the BCA methods have been successfully used in describing many physical processes, they have some obstacles for describing the slowing down process of energetic ions realistically. Basic assumption that collisions are binary results in severe problems when trying to take multiple interactions into account. Also, in simulating crystalline materials the selection process of the next colliding lattice atom and the impact parameter p always involve several parameters which may not have perfectly well defined values, which may affect the results 10–20% even for quite reasonable-seeming choices of the parameter values. The best reliability in BCA is obtained by including multiple collisions in the calculations, which is not easy to do correctly. However, at least MARLOWE does this.
A fundamentally more straightforward way to model multiple atomic collisions is provided by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, in which the time evolution of a system of atoms is calculated by solving the equations of motion numerically. Special MD methods have been devised in which the number of interactions and atoms involved in MD simulations have been reduced in order to make them efficient enough for calculating ion ranges. The MD simulations this automatically describe the nuclear stopping power. The electronic stopping power can be readily included in molecular dynamics simulations, either as a frictional force or in a more advanced manner by also following the heating of the electronic systems and coupling the electronic and atomic degrees of freedom.
Minimum ionizing particle
Beyond the maximum, stopping power decreases approximately like 1/v with increasing particle velocity v, but after a minimum, it increases again. A minimum ionizing particle (MIP) is a particle whose mean energy loss rate through matter is close to the minimum. In many practical cases, relativistic particles (e.g., cosmic-ray muons) are minimum ionizing particles. An important property of all minimum ionizing particles is that is approximately true where and are the usual relativistic kinematic quantities. Moreover, all of the MIPs have almost the same energy loss in the material which value is: .
See also
References
- Bragg, W. H. (1905). "On the α particles of radium, and their loss of range in passing through various atoms and molecules". Phil. Mag. 10 (57): 318. doi:10.1080/14786440509463378.
- Bohr, N. (1913). "On the Theory of the Decrease of Velocity of Moving Electrified Particles on passing through Matter". Phil. Mag. 25 (145): 10. doi:10.1080/14786440108634305.
- ICRU Report 73: Stopping of Ions heavier than Helium, Journal of the ICRU, 5 No. 1 (2005), Oxford Univ. Press ISBN 0-19-857012-0
- Podgorsak, E. B., ed. (2005). Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students (PDF). Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency. ISBN 978-92-0-107304-4. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (1970). Linear Energy Transfer (PDF). Washington D.C. ISBN 978-0913394090. ICRU report 16. Retrieved 1 December 2012.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Yang, C.; Di Li, Di Li; Geng Wang, Geng Wang; Li Lin, Li Lin; Tasch, A.F.; Banerjee, S. (2002). "Quantum mechanical model of electronic stopping power for ions in a free electron gas". Ion Implantation Technology. 2002. Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on. pp. 556–559. doi:10.1109/IIT.2002.1258065. ISBN 0-7803-7155-0. S2CID 117936302.
- P. Sigmund: Stopping of heavy ions. Springer Tracts in Modern Physics Vol. 204 (2004) ISBN 3-540-22273-1
- Zeb, M. Ahsan; Kohanoff, J.; Sánchez-Portal, D.; Arnau, A.; Juaristi, J. I.; Artacho, Emilio (2012-05-31). "Electronic Stopping Power in Gold: The Role of d Electrons and the H/He Anomaly". Physical Review Letters. 108 (22): 225504. arXiv:1205.1728. Bibcode:2012PhRvL.108v5504Z. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.225504. PMID 23003620. S2CID 2682651.
- Ullah, Rafi; Corsetti, Fabiano; Sánchez-Portal, Daniel; Artacho, Emilio (2015-03-11). "Electronic stopping power in a narrow band gap semiconductor from first principles". Physical Review B. 91 (12): 125203. arXiv:1410.6642. Bibcode:2015PhRvB..91l5203U. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.91.125203. S2CID 31233417.
- "Stopping Power for Light Ions". Archived from the original on 2012-02-06. Retrieved 2014-02-19.
- Paul, H (2006). "A comparison of recent stopping power tables for light and medium-heavy ions with experimental data, and applications to radiotherapy dosimetry". Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B. 247 (2): 166–172. Bibcode:2006NIMPB.247..166P. doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2006.01.059.
- ^ International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (October 2011). Seltzer, Stephen M. (ed.). "Fundamental Quantities and Units for Ionizing Radiation" (PDF). Journal of the ICRU. 11 (1) (Revised ed.): NP.2–NP. doi:10.1093/jicru/ndr012. PMID 24174259. ICRU report 85a. Retrieved 14 December 2012.
- Huhtinen, Mika (2002). "Simulation of non-ionising energy loss and defect formation in silicon". Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B. 491 (1–2): 194–215. Bibcode:2002NIMPA.491..194H. doi:10.1016/s0168-9002(02)01227-5.
- Barry, AL; Houdayer, AJ; Hinrichsen, PF; Letourneau, WG; Vincent, J (1995). "The energy dependence of lifetime damage constants in GaAs LEDs for 1-500 MeV protons". IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science. 42 (6): 2104–2107. Bibcode:1995ITNS...42.2104B. doi:10.1109/23.489259.
- Lindström, G (2001). "Radiation hard silicon detectors - developments by the RD48 (ROSE) collaboration". Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A. 466 (2): 308–326. Bibcode:2001NIMPA.466..308L. doi:10.1016/S0168-9002(01)00560-5. hdl:11568/67464.
- ^ J. F. Ziegler, J. P. Biersack, and U. Littmark. In The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter, volume 1, New York, 1985. Pergamon. ISBN 0-08-022053-3
- J. F. Ziegler, J. P. Biersack, and M. D. Ziegler: SRIM - The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter, SRIM Co., 2008. ISBN 0-9654207-1-X
- ^ "James Ziegler - SRIM & TRIM". www.srim.org.
- Nordlund, K; Runeberg, N; Sundholm, D (1997). "Repulsive interatomic potentials calculated using Hartree-Fock and density-functional theory methods". Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B. 132 (1): 45. Bibcode:1997NIMPB.132...45N. doi:10.1016/S0168-583X(97)00447-3.
- Eisen, F. H. (1968-03-15). "Channeling of medium-mass ions through silicon". Canadian Journal of Physics. 46 (6): 561–572. Bibcode:1968CaJPh..46..561E. doi:10.1139/p68-070. ISSN 0008-4204.
- Ntemou, Eleni; Holeňák, Radek; Primetzhofer, Daniel (2022-05-01). "Energy deposition by H and He ions at keV energies in self-supporting, single crystalline SiC foils". Radiation Physics and Chemistry. 194: 110033. Bibcode:2022RaPC..19410033N. doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2022.110033. ISSN 0969-806X.
- Robinson, Mark; Torrens, Ian (1974). "Computer simulation of atomic-displacement cascades in solids in the binary-collision approximation". Physical Review B. 9 (12): 5008. Bibcode:1974PhRvB...9.5008R. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.9.5008.
- Biersack, J; Haggmark, L (1980). "A Monte Carlo computer program for the transport of energetic ions in amorphous targets☆". Nuclear Instruments and Methods. 174 (1): 257. Bibcode:1980NucIM.174..257B. doi:10.1016/0029-554X(80)90440-1.
- Robinson, M (1992). "Computer simulation studies of high-energy collision cascades1". Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B. 67 (1–4): 396–400. Bibcode:1992NIMPB..67..396R. doi:10.1016/0168-583X(92)95839-J.
- ^ Nordlund, K (1995). "Molecular dynamics simulation of ion ranges in the 1–100 keV energy range". Computational Materials Science. 3 (4): 448–456. doi:10.1016/0927-0256(94)00085-Q. Archived from the original on 2011-06-17. Retrieved 2010-03-07.
- ^ Beardmore, Keith; Grønbech-Jensen, Niels (1998). "Efficient molecular dynamics scheme for the calculation of dopant profiles due to ion implantation". Physical Review E. 57 (6): 7278–7287. arXiv:physics/9901054. Bibcode:1998PhRvE..57.7278B. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.285.6727. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.57.7278. S2CID 13994369.
- Hobler, G. (2001). "On the useful range of application of molecular dynamics simulations in the recoil interaction approximation". Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B. 180 (1–4): 203. Bibcode:2001NIMPB.180..203H. doi:10.1016/s0168-583x(01)00418-9.
- Caturla, M. (1996). "Ion-beam processing of silicon at keV energies: A molecular-dynamics study". Physical Review B. 54 (23): 16683–16695. Bibcode:1996PhRvB..5416683C. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.54.16683. PMID 9985796.
- Smith, R. (1997). "Molecular Dynamics Simulation of 0.1 -- 2 keV ion bombardment of Ni {100}". Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids. 141: 425. doi:10.1080/10420159708211586.
- Duvenbeck, A. (2007). "Electron promotion and electronic friction in atomic collision cascades". New Journal of Physics. 9 (2): 38. Bibcode:2007NJPh....9...38D. doi:10.1088/1367-2630/9/2/038.
- Hou, M. (2000). "Deposition of AuN clusters on Au(111) surfaces. I. Atomic-scale modeling". Physical Review B. 62 (4): 2825. Bibcode:2000PhRvB..62.2825H. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.62.2825.
- Bjorkas, C. (2009). "Assessment of the relation between ion beam mixing, electron-phonon coupling, and damage production in Fe". Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B. 267 (10): 1830. Bibcode:2009NIMPB.267.1830B. doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2009.03.080.
- Pronnecke, S. (1991). "The effect of electronic energy loss on the dynamics of thermal spikes in Cu" (PDF). Journal of Materials Research. 6 (3): 483. Bibcode:1991JMatR...6..483P. doi:10.1557/jmr.1991.0483. S2CID 96618269.
- Duffy, D. M. (2007). "Including the effects of electronic stopping and electron-ion interactions in radiation damage simulations". Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 17 (1): 016207. Bibcode:2007JPCM...19a6207D. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/19/1/016207. S2CID 122777435.
- Tamm, A. (2016). "Electron-phonon interaction within classical molecular dynamics". Physical Review B. 94 (1): 024305. Bibcode:2016PhRvB..94a4305L. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.94.014305.
- ^ "Passage of particles through matter" (PDF). pdg.lbl.gov.
Further reading
- (Lindhard 1963) J. Lindhard, M. Scharff, and H. E. Shiøtt. Range concepts and heavy ion ranges. Mat. Fys. Medd. Dan. Vid. Selsk., 33(14):1, 1963.
- (Smith 1997) R. Smith (ed.), Atomic & ion collisions in solids and at surfaces: theory, simulation and applications, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1997.
External links
- Stopping power and energy loss straggling calculations in solids by MELF-GOS model Archived 2010-09-25 at the Wayback Machine
- A Web-based module for Range and Stopping Power in Nucleonica
- Passage of charged particles through matter
- Stopping-Power and Range Tables for Electrons, Protons, and Helium Ions
- Stopping Power: Graphs and Data
- Penetration of charged particles through matter; lecture notes by E. Bonderup Archived 2019-05-28 at the Wayback Machine


 which is an average taken over all energy loss processes for different charge states. It can be theoretically determined to an accuracy of a few % in the energy range above several hundred keV per
which is an average taken over all energy loss processes for different charge states. It can be theoretically determined to an accuracy of a few % in the energy range above several hundred keV per  between two atoms (see below), it is possible to calculate the nuclear stopping power
between two atoms (see below), it is possible to calculate the nuclear stopping power  . In the stopping power figure shown above for aluminium ions in aluminum, nuclear stopping is negligible except at the lowest energy. Nuclear stopping increases when the mass of the ion increases. In the figure shown on the right, nuclear stopping is larger than electronic stopping at low energy. For very light ions slowing down in heavy materials, the nuclear stopping is weaker than the electronic at all energies.
. In the stopping power figure shown above for aluminium ions in aluminum, nuclear stopping is negligible except at the lowest energy. Nuclear stopping increases when the mass of the ion increases. In the figure shown on the right, nuclear stopping is larger than electronic stopping at low energy. For very light ions slowing down in heavy materials, the nuclear stopping is weaker than the electronic at all energies.
 . Several semi-empirical stopping power formulas have been devised. The model given by Ziegler, Biersack and Littmark (the so-called "ZBL" stopping, see next chapter), implemented in different versions of the
. Several semi-empirical stopping power formulas have been devised. The model given by Ziegler, Biersack and Littmark (the so-called "ZBL" stopping, see next chapter), implemented in different versions of the 
 and
and  are the charges of the interacting nuclei, and r the distance between them; a is the so-called screening parameter.
are the charges of the interacting nuclei, and r the distance between them; a is the so-called screening parameter.


 is approximately true where
is approximately true where  and
and  are the usual relativistic kinematic quantities. Moreover, all of the MIPs have almost the same energy loss in the material which value is:
are the usual relativistic kinematic quantities. Moreover, all of the MIPs have almost the same energy loss in the material which value is:  .
.