Pharmaceutical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | MiraLax, ClearLax, Golytely, others |
| Other names | Polyethylene glycol (PEG), PEG 3350, PEG 4000, PEG 6000 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Professional Drug Facts |
| MedlinePlus | a603032 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Osmotic laxative |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | None |
| Excretion | Feces (100%) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | H–(OCH2CH2)n–OH |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Macrogol, also called polyethylene glycol (PEG), is used as a laxative to treat constipation in children and adults. It is taken by mouth. Benefits usually occur within three days. Generally it is only recommended for up to two weeks. It is also used as an excipient. It is also used to clear the bowels (bowel prep) before a colonoscopy, when the onset of the laxative effect is more rapid, typically within an hour.
Side effects may include increased bowel gas, abdominal pain, and nausea. Rare but serious side effects may include an abnormal heartbeat, seizures, and kidney problems. Use appears to be safe during pregnancy. It is classified as an osmotic laxative: It works by increasing the amount of water in the stool.
Macrogol came into use as a bowel prep in 1980 and was approved for medical use in the United States in 1999. It is available as a generic medication and over the counter. In 2022, it was the 209th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1 million prescriptions. It is also formulated together with electrolytes. In 2022, the combination with electrolytes was the 282nd most commonly prescribed medication in the US, with more than 600,000 prescriptions.
Medical uses

Constipation

Macrogol 3350, often in combination with electrolytes, is used for short-term relief of constipation as well as for long-term use in constipation of various causes, including in multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's disease patients (an often-overlooked non-motor symptom) as well as constipation caused by pharmaceutical drugs such as opioids and anticholinergics. Whole bowel irrigation with macrogol is part of the bowel preparation before surgery or colonoscopy. Limited data also support its use for the treatment of fecal impaction.
In those with chronic constipation it works better than lactulose.
A 2007 comparison showed that people with constipation had a better response to macrogol than to tegaserod. Popular types include: macrogol 3350, macrogol 4000, and macrogol 6000. The number represents the average molecular mass. Combining different molecular masses provides some control over the consistency.
Excipient
Macrogol is used as an excipient in pharmaceutical products. Lower-molecular-weight variants are used as solvents in oral liquids and soft capsules, whereas solid variants are used as ointment bases, tablet binders, film coatings, and lubricants.
For example, PEG-2000 is one of the excipients in the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine.
PEGylation
Macrogols are also attached to biopharmaceutical drugs to slow down their degradation in the human body and increase their duration of action, as well as to reduce immunogenicity. This process is called PEGylation.
Contraindications
Contraindications for macrogol taken orally as a laxative are intestinal perforation, bowel obstruction, ileus, inflammatory bowel diseases, and toxic megacolon.
The doses of macrogol as an excipient are too low to have relevant contraindications.
Allergy to macrogol is rare, and usually appears as an allergy to an increasing number of seemingly unrelated products, including cosmetics, drugs that use it as an excipient, and peri-procedural substances such as ultrasound gel.
Adverse effects
Oral macrogol is generally well tolerated. Possible side effects include headache, bloating, nausea, allergies, and electrolyte imbalance, mainly hypokalaemia (low blood potassium levels) and hyperkalaemia (high blood potassium levels). Hyperkalaemia is not an effect of macrogol itself but of potassium salts which are usually part of macrogol formulations. With excessive use, it can cause diarrhea.
Interactions
The interaction potential is low. Absorption of other pharmaceutical drugs can be reduced because oral macrogol accelerates intestinal passage, but this is seldom clinically relevant. For antiepileptic drugs, such a mechanism has been described in rare cases.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action as a laxative
Macrogol is an osmotically acting laxative; that is, an inert substance that passes through the gut without being absorbed into the body. It relieves constipation because it causes water to be retained in the bowel instead of being absorbed into the body. This increases the water content and volume of the stools in the bowel, making them softer and easier to pass, as well as improving gut motility.
Chemistry
Main article: Polyethylene glycol For the synthesis of macrogol, see Polyethylene glycol § Production.Available forms
When sold for gut cleansing (and as a laxative), it is usually in combination with salts such as sodium bicarbonate, sodium chloride and potassium chloride to help mitigate the possibility of electrolyte imbalance and dehydration. Brand names include CosmoCol, Cololyt, Glycoprep, Laxido, MiraLax, Molaxole, Movicol, and Osmolax.
Polyethylene glycol-electrolyte solution is a fixed-dose combination medication sold under various brand names in the US, including Colyte, Gavilyte, Golytely, Nulytely, Moviprep, and Trilyte. Brand names available in the UK include CosmoCol, Klean-Prep, Laxido, Molaxole, Movicol, Plenvu, TransiSoft, and VistaPrep. As of June 2023, polyethylene glycol 3350 is available in the US as a combination with sodium sulfate, potassium chloride, magnesium sulfate, and sodium chloride and sold under the brand name Suflave. It is indicated for cleansing of the colon in preparation for colonoscopy in adults.
Research
PEGylation
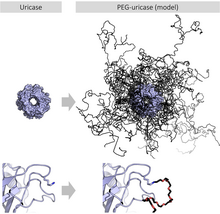
When attached to various biopharmaceutical medications (which are proteins), macrogol results in a slowed clearance of the carried protein from the blood. This makes for a longer-acting medicinal effect and reduces toxicity, and it allows for longer dosing intervals. It also reduces the proteins' immunogenicity. Examples for PEGylated proteins include peginterferon alfa-2a and -2b, which are used to treat hepatitis C, pegfilgrastim, which is used to treat neutropenia, and pegloticase for the treatment of gout.
Nerves and spinal cords
There is evidence demonstrating PEG-induced repair of specific nerve cells in animal models:
- It has been shown that macrogol can improve healing of spinal injuries in dogs.
- One of the earlier findings is that macrogol can aid in nerve repair in earthworms.
- The subcutaneous injection of macrogol 2000 in guinea pigs after spinal cord injury leads to rapid recovery through molecular repair of nerve membranes. The effectiveness of this treatment to prevent paraplegia in humans after an accident is not known yet.
- Macrogol is being used in the repair of motor neurons damaged in crush or laceration incidents in vivo and in vitro in rats. When coupled with melatonin, 75% of damaged sciatic nerves were rendered viable.
Cancer prevention
- High-molecular-weight macrogol (e.g., 8000 g/mol) has been shown to be a dietary preventive agent against colorectal cancer in animal models.
- The Chemoprevention Database shows macrogol is the most effective known agent for the suppression of chemical carcinogenesis in rats. Cancer prevention applications in humans, however, have not yet been tested in clinical trials.
Other
- Macrogol is also used to fuse B-cells with myeloma cells in monoclonal antibody production.
References
- ^ British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 57–58. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ^ "DailyMed - polyethylene glycol 3350 powder, for solution". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 26 April 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- ^ "Polyethylene Glycol 3350: MedlinePlus Drug Information". MedlinePlus. Archived from the original on 27 April 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- ^ "Macrogol as Excipient". Biesterfeld AG. Retrieved 10 June 2022.
- "Package leaflet: Information for the User - Moviprep, powder for oral solution" (PDF). Medicines.org.uk. Retrieved 11 February 2024.
- "PEG-3350 and Electrolytes for Oral Solution" (PDF). FDA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 August 2017. Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- "Polyethylene glycol 3350 Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 28 April 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- Mahmoud NN, Bleier JI, Aarons CB, Paulson EC, Shangmugan S, Fry RD (2016). "Colon and Rectum". In Townsend CM, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL (eds.). Sabiston Textbook of Surgery E-Book: The Biological Basis of Modern Surgical Practice. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1325. ISBN 9780323401630.
- "Prescription Polyethylene Glycol 3350; Denial of a Hearing and Order Withdrawing Approval of Abbreviated New Drug Applications". Federal Register. 2 April 2018. Archived from the original on 28 April 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- Schoeman M, Nguyen NQ (2011). "Patient Preparation and Pharmacotherapeutic Considerations". In Ginsberg GG, Kochman ML, Norton ID, Gostout CJ (eds.). Clinical Gastrointestinal Endoscopy E-Book: Expert Consult - Online and Print. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 87. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-41509-5.00008-6. ISBN 9781437735703. S2CID 78762418.
- "Polyethylene glycol 3350 Uses, Side Effects & Warnings". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 28 April 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- "Polyethylene Glycol 3350 Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- Aronson JK (2015). "Glycols". Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs: The International Encyclopedia of Adverse Drug Reactions and Interactions. Elsevier. p. 567. ISBN 9780444537164.
- "Polyethylene Glycol 3350 With Electrolytes Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ Haberfeld, ed. (2015). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag.
- Lee-Robichaud H, Thomas K, Morgan J, Nelson RL (July 2010). "Lactulose versus Polyethylene Glycol for Chronic Constipation". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (7): CD007570. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007570.pub2. PMID 20614462.
- Di Palma JA, Cleveland MV, McGowan J, Herrera JL (September 2007). "A randomized, multicenter comparison of polyethylene glycol laxative and tegaserod in treatment of patients with chronic constipation". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 102 (9): 1964–1971. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01365.x. PMID 17573794. S2CID 32055676.
- Hardikar W, Cranswick N, Heine RG (2007). "Macrogol 3350 plus electrolytes for chronic constipation in children: a single-centre, open-label study". Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health. 43 (7–8): 527–531. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1754.2007.01116.x. PMID 17635680. S2CID 42699177.
- Hyry H, Vuorio A, Varjonen E, Skyttä J, Mäkinen-Kiljunen S (August 2006). "Two cases of anaphylaxis to macrogol 6000 after ingestion of drug tablets". Allergy. 61 (8): 1021. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2006.01083.x. PMID 16867059. S2CID 36543393.
- ^ Smolinske SC (1992). Handbook of Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Excipients. CRC Press. p. 287. ISBN 9780849335853.
- "Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine Standing Orders for Administering Vaccine to Persons 12 Years of Age and Older" (PDF). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 March 2021. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
- "What Ingredients are in the COVID-19 Vaccine?" (PDF). Connecticut Department of Public Health. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 July 2021. Retrieved 11 July 2021.
- Veronese FM, Harris JM (June 2002). "Introduction and overview of peptide and protein pegylation". Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 54 (4): 453–456. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(02)00020-0. PMID 12052707.
- Porfiryeva NN, Moustafine RI, Khutoryanskiy VV (1 January 2020). "PEGylated Systems in Pharmaceutics". Polymer Science, Series C. 62 (1): 62–74. doi:10.1134/S181123822001004X. ISSN 1555-614X. S2CID 226664780.
- "Compound Macrogol Oral Powder Sugar Free. - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) - (emc)". www.medicines.org.uk. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 10 January 2020.
- Wenande E, Garvey LH (July 2016). "Immediate-type hypersensitivity to polyethylene glycols: a review". Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 46 (7): 907–922. doi:10.1111/cea.12760. PMID 27196817. S2CID 1247758.
- Mutschler E (2013). Arzneimittelwirkungen (in German) (10 ed.). Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft. p. 608. ISBN 978-3-8047-2898-1.
- Chaussade S (November 1999). "Mechanisms of action of low doses of polyethylene glycol in the treatment of functional constipation". Italian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 31 (Suppl 3): S242–S244. PMID 10726227.
- Meda Pharmaceuticals (February 2019). "COLYTE- peg-3350 and lectrolytes powder, for solution". dailymed. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Golytely- polyethylene glycol 3350, sodium sulfate anhydrous, sodium bicarbonate, sodium chloride, potassium chloride powder, for solution". DailyMed. 28 May 2021. Archived from the original on 31 March 2023. Retrieved 17 June 2023.
- "Nulytely- polyethylene glycol 3350, sodium chloride, sodium bicarbonate and potassium chloride powder, for solution". DailyMed. 16 June 2022. Retrieved 17 June 2023.
- "Moviprep- polyethylene glycol 3350, sodium sulfate, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, ascorbic acid, sodium ascorbate kit". DailyMed. 15 April 2022. Archived from the original on 3 February 2023. Retrieved 17 June 2023.
- "Trilyte (polyethylene glycol 3350, sodium chloride, sodium bicarbonate and potassium chloride for oral solution) with flavor packs Initial U.S. Approval: 1991". DailyMed. Retrieved 17 June 2023.
- "Polyethylene Glycol-Electrolyte Solution (Professional Patient Advice)". Drugs.com. 20 February 2020. Archived from the original on 8 June 2020. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- "Search or browse MIMS". mims.co.uk. Archived from the original on 24 April 2023. Retrieved 24 April 2023.
- ^ "SUFLAVE (polyethylene glycol 3350, sodium sulfate, potassium chloride, magnesium sulfate, and sodium chloride for oral solution)" (PDF). Braintree Laboratories, Inc. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. June 2023.
- Sherman MR, Saifer MG, Perez-Ruiz F (January 2008). "PEG-uricase in the management of treatment-resistant gout and hyperuricemia". Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 60 (1): 59–68. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2007.06.011. PMID 17826865.
- Bowman, Lee (4 December 2004). "Study on dogs yields hope in human paralysis treatment". seattlepi.com. Archived from the original on 22 September 2021. Retrieved 26 June 2016.
- Krause TL, Bittner GD (February 1990). "Rapid morphological fusion of severed myelinated axons by polyethylene glycol". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 87 (4): 1471–1475. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.1471K. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.4.1471. PMC 53497. PMID 2304913.
- Borgens RB, Bohnert D (December 2001). "Rapid recovery from spinal cord injury after subcutaneously administered polyethylene glycol". Journal of Neuroscience Research. 66 (6): 1179–1186. doi:10.1002/jnr.1254. PMID 11746451. S2CID 11902183.
- Stavisky RC, Britt JM, Zuzek A, Truong E, Bittner GD (March 2005). "Melatonin enhances the in vitro and in vivo repair of severed rat sciatic axons". Neuroscience Letters. 376 (2): 98–101. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2004.11.033. PMID 15698928. S2CID 24634247.
- Corpet DE, Parnaud G, Delverdier M, Peiffer G, Taché S (June 2000). "Consistent and fast inhibition of colon carcinogenesis by polyethylene glycol in mice and rats given various carcinogens". Cancer Research. 60 (12): 3160–3164. PMID 10866305.
- "Chemoprevention of Colorectal Cancer". Chemoprevention Database. Archived from the original on 23 November 2005. Retrieved 30 November 2012 – via Inra.fr.
- Lo MM, Tsong TY, Conrad MK, Strittmatter SM, Hester LD, Snyder SH (1984). "Monoclonal antibody production by receptor-mediated electrically induced cell fusion". Nature. 310 (5980): 792–794. Bibcode:1984Natur.310..792L. doi:10.1038/310792a0. PMID 6088990. S2CID 4357934.
External links
- Clinical trial number NCT04446299 for "Study 301: BLI4900 Versus an FDA-approved Comparator in Adult Subjects Prior to Colonoscopy" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT04446312 for "Study 302: BLI4900 Versus an FDA-approved Comparator in Adult Subjects Prior to Colonoscopy" at ClinicalTrials.gov
| Drugs for constipation (laxatives and cathartics) (A06) | |
|---|---|
| Stool softeners | |
| Stimulant laxatives | |
| Bulk-forming laxatives | |
| Lubricant laxatives | |
| Osmotic laxatives | |
| Enemas | |
| Opioid antagonists | |
| Others | |