| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Parallel 36°30′ north" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
 36.5°class=notpageimage| 36.5th parallel north
Map all coordinates using OpenStreetMap
36.5°class=notpageimage| 36.5th parallel north
Map all coordinates using OpenStreetMap
Download coordinates as:

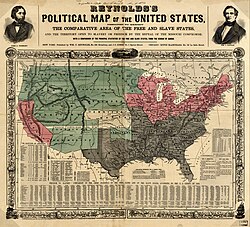
The parallel 36°30′ north is a circle of latitude that is 361⁄2 degrees north of the equator of the Earth. This parallel of latitude is particularly significant in the history of the United States as the line of the Missouri Compromise, which was used to divide the prospective slave and free states west of the Mississippi River, with the exception of Missouri, which is mostly north of this parallel. The line continues to hold cultural, economic, and political significance to this day; the Kinder Institute for Urban Research defines the Sun Belt as being south of 36°30′N latitude.
In the United States
In the United States, the parallel 36°30′ forms part of the boundary between Tennessee and Kentucky, in the region west of the Tennessee River and east of the Mississippi River. This parallel also forms part of the boundary between Missouri and Arkansas in the region west of the St. Francis River, and part of the boundary between the Oklahoma Panhandle and the Texas Panhandle. The rest of the boundaries between Virginia and North Carolina; between Virginia and Tennessee; and between Tennessee and Kentucky lie close to the parallel 36°30′. The boundary between Kentucky and Tennessee was defined as 36°30′, based on the Royal Colonial Boundary of 1665 that set the boundary of the Colony of Virginia and the Province of Carolina.
In 1779 and 1780, surveyors were sent to mark the line on the ground as far as the Tennessee River. As they worked west their line drifted north until by the time they reached the river they were about 10′ north of 36°30′. Despite this error the boundary was set along the line surveyed. The final part of the Kentucky-Tennessee boundary, between the Tennessee River and the Mississippi River, was not surveyed until after 1819 when treaties extinguished Native American claims in the area. The final portion was surveyed east from the Mississippi River along 36°30′. Due to the relative precision of the survey of 36°30′ on the Mississippi River, Congress decided to continue the line west as the northern boundary of Arkansas Territory, with the exception of the Missouri Bootheel.
The parallel 36°30′ north is part of a nearly straight east–west line of state borders (with small variations) starting on the East Coast of the United States, beginning with the border between Virginia and North Carolina. However, this boundary and the one between Kentucky and Tennessee lie a few miles north of 36°30′ in places. The line west of Arkansas is slightly further north at 37°.
In southeastern Missouri, the Missouri Bootheel along the Mississippi River extends about 50 miles (80 kilometers) to the south, all the way to the 36th parallel north, and about 30 miles (50 kilometers) inland. This was because politicians in that region along that major river felt that it would be advantageous to be located in Missouri rather than in the Arkansas Territory, which became the State of Arkansas in 1836. The parallel 36°30′ then forms the rest of the boundary between Missouri and Arkansas.
The Missouri Compromise of 1820 established the latitude 36°30′ as the northern limit for slavery to be legal in the territories of the west. As part of this compromise, Maine (formerly a part of Massachusetts) was admitted as a free state. This addition maintained the balance of power in the U.S. Senate between the free states and the slaveholding states.
The bulk of Missouri lies north of the 36°30′ line, but Southern planters who lived in southeastern Missouri supported slavery, especially for farming on their cotton plantations. Hence, part of the Missouri Compromise arose from this. Also, the slave states of the Southern United States wanted to have the support of another slave state so the Senate could not abolish slavery in the United States. This situation remained in effect for decades because as the free states of Michigan, Wisconsin, and Iowa were admitted to the Union, the new slave states of Arkansas, Florida, and Texas were also admitted.
When the Republic of Texas joined the United States in 1845 as a slave state, it was required to cede all of its claimed land north of the 36°30′ latitude to the Federal Government. Over the following half-century, this land became parts of Kansas, Colorado, New Mexico, and Oklahoma. The Compromise of 1850 confirmed that the 36°30′ parallel was the northmost boundary of Texas. Then Kansas was admitted to the Union as a free state in 1861.
The creation of the New Mexico Territory and the Utah Territory in 1850, the Kansas Territory in 1854, and the Colorado Territory in 1861 moved the boundaries of one of the western territories, New Mexico, north to the 37th parallel north. New Mexico Territory was eventually split in two states, New Mexico and Arizona, which were admitted in 1912, but this was long after the 13th Amendment had abolished slavery in all of the United States.
The gap between the northern boundary of Texas on the parallel 36°30′ north and the southern boundaries of Kansas and Colorado on the parallel 37° north created the No Man's Land that later became the Oklahoma Panhandle in 1889. While a significant part of Nevada (containing Las Vegas) is south of 36°30′, at the time of the admission of Nevada in 1864, it was in the New Mexico Territory. This land was not split off from the new Arizona Territory until 1871, when it was given to Nevada by the Federal government.
The Compromise of 1850 made no attempt to divide California along the line of 36°30′, or to allow slavery south of it; the social and political conditions created by the California Gold Rush ruled out any such idea, and California was admitted to the union as a free state.
During the American Civil War (1861–65), all of the states located wholly south of 36°30′ north joined the Confederate States of America. All of the states with land north of the parallel, except Virginia, stayed in the Union, although Kentucky and Missouri had Confederate legislatures that were elected in parallel with their regular legislatures. Also Maryland, another slave state, was occupied by the Union Army under the commands of President Abraham Lincoln, and its legislature was thus pressured into voting not to secede. Naturally, Lincoln and the remaining members of the U.S. Congress wanted Maryland to stay in the Union in order to prevent the national capital city of Washington, D.C. from being surrounded by Confederate states, and hence being cut off from the rest of the Union. If such a thing had happened, then the Federal government would have been forced to move somewhere else further north, such as to Philadelphia.
Around the world
Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the parallel 36°30′ north passes through:
See also
- Territorial evolution of the United States
- The Mason–Dixon line – another line linked to the slave-free division in the U.S.
- Royal Colonial Boundary of 1665 – the border between the Colony of Virginia and the Province of Carolina that follows the parallel 36°30′ north latitude that came to be associated with the Missouri Compromise of 1820.
- The 49th parallel north – another important parallel of latitude in American history, since it became the boundary between the United States and Canada from northern Minnesota all the way west to the Pacific Ocean at Puget Sound. This boundary was established in two separate treaties with the British Empire, the first one in 1818.
- The Parallel 54°40′ north – another important parallel of latitude in American history.
References
- "Large, young and fast-growing Sun Belt metros need urban policy innovation | Kinder Institute for Urban Research".
- Hubbard, Bill (2009). American Boundaries: The Nation, the States, the Rectangular Survey. University of Chicago Press. p. 140. ISBN 978-0-226-35591-7. Retrieved 27 September 2012.
- "An Act to provide a temporary Government for the Territory of Colorado" (PDF). Thirty-sixth United States Congress. 1861-02-28. Retrieved 2007-02-22.
