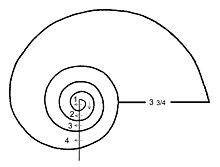


A whorl is a single, complete 360° revolution or turn in the spiral or whorled growth of a mollusc shell. A spiral configuration of the shell is found in numerous gastropods, but it is also found in shelled cephalopods including Nautilus, Spirula and the large extinct subclass of cephalopods known as the ammonites.
A spiral shell can be visualized as consisting of a long conical tube, the growth of which is coiled into an overall helical or planispiral shape, for reasons of both strength and compactness.
The number of whorls which exist in an adult shell of a particular species depends on mathematical factors in the geometric growth, as described in D'Arcy Wentworth Thompson's classic 1917 book On Growth and Form, and by David Raup. The main factor is how rapidly the conical tube expands (or flares-out) over time. When the rate of expansion is low, such that each subsequent whorl is not that much wider than the previous one, then the adult shell has numerous whorls. When the mathematical factors governing the pattern of growth are such that there is a very rapid expansion of the conical shape, of the shell tube, then the adult shell has very few whorls.
The number of whorls present in an adult shell differs greatly in various taxa. The extant marine gastropod families Turritellidae and Terebridae, and the extinct Mesozoic family Nerineidae, have very high spired shells with a large number of whorls, and a relatively small aperture.
The shells of a few genera of gastropods, and of the cephalopod genus Spirula, have whorls that are disconnected.
-
 The shell of the marine gastropod Haliotis asinina has fewer than two whorls
The shell of the marine gastropod Haliotis asinina has fewer than two whorls
-
 The shell of Spirula spirula has disconnected whorls
The shell of Spirula spirula has disconnected whorls
Counting the number of whorls
To count exactly the number of whorls in gastropods a straight line is drawn to separate the semi-circular nucleus (protoconch (1 - see image) from the younger part of the shell. An arrow placed at a 90° angle on this line, following the course of the whorl, reaches the end of the first whorl where it is parallel to its starting position. From that point all whorls are counted towards the margin of the shell, estimating the ultimate whorl with an accuracy of a quarter whorl.
Other authors (Ehrmann 1933; Richter & Seapy 1999) applied a slightly different measuring method, resulting in whorl numbers being a quarter higher.
Terminology
- Apical whorls—the whorls near the apex or tip of the shell of gastropods
- Body whorl—The most recently formed whorl of a spiral shell, in which most of the body of the animal is found
- Nuclear whorl(s)—small, generally smooth whorls formed within the egg, and constituting the apex of the shell
- Protoconch—a larval shell of a mollusc; also refers to protoconch whorls of an adult shell
- Teleoconch—all the whorls of a shell after the protoconch whorls
- Nepionic whorls : the whorls immediately following the embryonic whorls.
References
This article incorporates CC-BY-3.0 text from the reference.
- ^ Janssen, Ari (2007). "Holoplanktonic Mollusca (Gastropoda: Pterotracheoidea, Janthinoidea, Thecosomata and Gymnosomata) from the Pliocene of Pangasinan (Luzon, Philippines)". Scripta Geologica. 135: 29–178. ISSN 0375-7587.
- Ehrmann P. (1933). "Mollusca". In: Brohmer P., Ehrmann P. & Ulmer G. (eds.) Die Tierwelt mittel-europas 2: 1-264. Quelle & Meyer, Leipzig.
- Richter G. & Seapy R. R. (1999). "Heteropoda". In: Boltovskoy D. (ed.). South Atlantic zooplankton, 1. Backhuys, Leiden: 621-647.
Further reading
- Solem A. (1983) "Lost or kept internal whorls: ordinal differences in land snails". Journal of Molluscan Studies 49(supp. 12A): 172–178.
External links
| Cephalopod anatomy | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shell |
|    | ||||||||||||
| Mantle & funnel |
| |||||||||||||
| Head & limbs |
| |||||||||||||
| General |
| |||||||||||||
| Developmental stages: Spawn → Paralarva (Doratopsis stage) → Juvenile → Subadult → Adult • Egg fossils • Protoconch (embryonic shell) | ||||||||||||||