| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Anilinobenzoic acid | |
| Other names N-phenylanthranilic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.879 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C13H11NO2 |
| Molar mass | 213.23 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
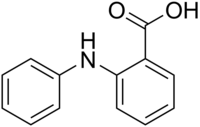
Fenamic acid is an organic compound, which, especially in its ester form, is called fenamate. serves as a parent structure for several nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including mefenamic acid, tolfenamic acid, flufenamic acid, and meclofenamic acid. These drugs are commonly referred to as "anthranilic acid derivatives" or "fenamates" because fenamic acid is a derivative of anthranilic acid.
Fenamic acid can be synthesized from 2-chlorobenzoic acid and can be converted into acridone.
References
- Gupta, PK. Drug NomenclatureUnited States Adopted Names. Ch 27 in Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy, Vol 1. Eds. David B. Troy, Paul Beringer. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006 ISBN 9780781746731
- ^ Sriram D, Yogeeswari P. Medicinal Chemistry, 2nd Edition. Pearson Education India, 2010. ISBN 9788131731444
- Auburn University course material. Jack DeRuiter, Principles of Drug Action 2, Fall 2002 1: Non-Steroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS)
- C. F. H. Allen, G. H. W. McKee (1939). "Acridone". Organic Syntheses. 2: 6. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.019.0006.
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (primarily M01A and M02A, also N02BA) | |
|---|---|
| pyrazolones / pyrazolidines | |
| salicylates | |
| acetic acid derivatives and related substances | |
| oxicams | |
| propionic acid derivatives (profens) |
|
| n-arylanthranilic acids (fenamates) | |
| COX-2 inhibitors (coxibs) | |
| other | |
| NSAID combinations | |
| Key: underline indicates initially developed first-in-class compound of specific group; WHO-Essential Medicines; withdrawn drugs; veterinary use. | |