Ethnic group
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| Approximately 1,200 in 1600 1,000 (1990) | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| United States (Delaware, New Jersey, Maryland, Oklahoma), Canada (Ontario) | |
| Languages | |
| English, formerly Nanticoke language | |
| Religion | |
| Native American religion, Christianity | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Assateague, Choptank, Conoy, Patuxent, Piscataway, Pocomoke |
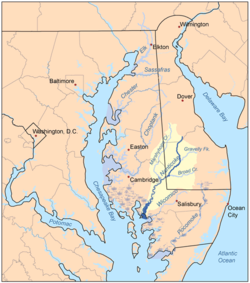
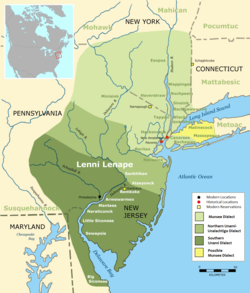
The Nanticoke people are a Native American Algonquian people, whose traditional homelands are in Chesapeake Bay and Delaware. Today they live in the Northeastern United States and Canada, especially Delaware; in Ontario; and in Oklahoma.
The Nanticoke people consisted of several tribes: The Nanticoke proper (the subject of this article), the Choptank, the Assateague, the Piscataway, and the Doeg.
History
The Nanticoke people may have originated in Labrador, Canada, and migrated through the Great Lakes region and the Ohio Valley to the east, along with the Shawnee and Lenape peoples.
In 1608, the Nanticoke came into European contact, with the arrival of British captain John Smith. They allied with the British and traded beaver pelts with them. They were located in today's Dorchester, Somerset and Wicomico counties.
In 1668, the Nanticoke Emperor Unnacokasimon signed a peace treaty with the proprietary government of the Province of Maryland. In 1684, the Nanticoke and English governments defined a reservation for their use, situated between Chicacoan Creek and the Nanticoke River in Maryland, see Vienna. Non-native peoples encroached upon their lands, so the tribe purchased a 3,000-acre tract of land in 1707 on Broad Creek in Somerset County, Maryland (now Sussex County, Delaware). In 1742, the tribe met with neighboring tribes in nearby Wimbesoccom Neck to discuss a Shawnee plot to attack the local English settlers, but the gathering was discovered, and the leaders involved were arrested. Some moved up to Pennsylvania in 1744, where they gained permission from the Iroquois Confederacy to settle near Wyoming, Pennsylvania, and along the Juniata River. The city of Nanticoke is named after one of their settlements. While settled along the Susquehanna River, the Nanticoke used a path that they had established during their migration to return to the Delmarva Peninsula for seasonal gathering and fishing. They moved upriver a decade later. They joined the Piscataway tribe, and were both under the jurisdiction of the League of the Iroquois. The reservation on Broad Creek was sold in 1768. Some Nanticoke migrated slightly north into New York, where they established a settlement in what became the town of Nanticoke there.
Members of the Conoy people joined the Nanticoke in the 1740s. Together they were neutral in the French and Indian War. During the American Revolution, they allied with the British. In 1778, two hundred Nanticoke moved north to Fort Niagara because of their alliance. Later the British resettled them at the Six Nations Reserve near Brantford, Ontario, Canada, giving them land in compensation for what they had lost. Other Nanticoke stayed at Buffalo River, New York. Another group of Nanticoke joined the Lenape and migrated to Kansas; in 1867, they moved with the Lenape to Indian Territory.
There are several towns and places named for this tribe. This includes Nanticoke, Pennsylvania and Nanticoke, New York, as well as Nanticoke and Nanticoke Acres in Maryland, and Nanticoke, Ontario.
Winnesoccum Incident
In the early summer of 1742, members of the Nanticoke, Shawnee, and Choptank tribes, wanted to avenge themselves against the English colonists. The tribes decided to meet on Winnesoccum Island in the middle of the Pocomoke Swamp located in Maryland. Chief Robin Hood, Hopping Sam, Simon Alsechqueck, and Messowan gathered their people to meet in the swamp for six days where they discussed plans of attack as well as their stories of encounters with the English. As all members of the tribes-including women and children-had left their villages to gather in the swamp, colonists had become suspicious of the disappearance of the natives from their local villages. Soldiers were then sent to round up the tribes in the swamp. Leaders of each of the tribes were questioned by the English, each one telling a different story as to why they had gathered in the swamp. Some stated that they gathered in the swamp solely to hunt while others said they were there to elect a new chief. The English had decided that since no attacks had been executed, no harm should be done to the local tribes. A treaty of peace was signed on July 24, 1792.
Name
Their autonym is Nentego, which means, "Tidewater People." The Nanticoke chiefdoms are now described as the Wicomoco, Monie and Manokin, which occupied areas along the rivers that were named after them. The Nanticoke had an extensive an trading network with tribes throughout the Chesapeake Bay area. Early accounts described the Nanticoke tribes as the Arseek, Cuscarawoc, and Nause.
Language
The Nanticoke language was distinct from the Algonquian languages spoken by tribes on the Western Shore of Maryland and along the Potomac River. The last fluent speaker was Lydia E. Clark, who died in 1856. Efforts to revive the language are currently being taken by tribal members and linguists from Georgetown University.
Modern day
Today, some Nanticoke people are part of the federally recognized Six Nations of the Grand River First Nation in Ontario, Canada. The ones who traveled west with the Delaware are part of the federally recognized Delaware Tribe of Indians in Oklahoma.
The Nanticoke Indian Association of Millsboro has been a state recognized tribe in Delaware since 1922. The Nanticoke Lenni-Lenape Indians are a state recognized tribe in New Jersey.
Nanticoke Indian Association
In 1744 some Nanticoke settled near the Indian River in Delaware. They reorganized as the Nanticoke Indian Association and were recognized as a tribe by the state in 1881. They have their headquarters in Millsboro. In 1922 they were chartered as a non-profit organization. They organized annual powwows, carrying them on until the mid-1930s, during the Great Depression. In 1977 the tribe revived the annual event. Later they built a museum in honor of their heritage, to teach their children and other Americans.
Sites listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979, and associated with the Indian River Community, include: the Robert Davis Farmhouse, Harmon School, Isaac Harmon Farmhouse, Harmony Church, Ames Hitchens Chicken Farm, Indian Mission Church, Indian Mission School, Johnson School, Coursey and Daisey Indian Burial Ground and Warren T. Wright Farmhouse Site.
In 2002 Kenneth S. "Red Deer" Clark Sr., the head chief of the association, and Assistant Chief, his son "Little Owl" Clark, resigned.
"Tee" Norwood was elected chief and served until 2008. That year Larry Jackson was elected as chief, and Chief William H. "Thunder Eagle" Daisey lead the organization until 2016. Natosha Carmine was elected in 2016 and was chief of the association until 2023. Avery "Leaving Tracks" Johnson is currently chief of the association as of 2023.
Nanticoke Lenni-Lenape Indians
Some Nanticoke settled across the Delaware Bay in southern New Jersey, where they joined the Lenape and intermarried with them. The Nanticoke Lenni-Lenape Indians of New Jersey are recognized by that state and based in Bridgeton. They have numerous members with mixed Nanticoke and Lenape ancestry. Both tribes were historically Algonquian speaking, and there have been years of intermarriage between them.
See also
Notes
- ^ Pritzker, Barry M. (2000). "Nanticoke". A Native American Encyclopedia: History, Culture, and Peoples. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 440–442. ISBN 978-0-19-513877-1.
- ^ Wayne E. Clark, "Indians in Maryland, an Overview", Maryland Online Encyclopedia', 2004-2005, accessed 18 Mar 2010
- Wallace, Paul A. W. Indian paths of Pennsylvania / by Paul A.W. Wallace. State Library of Pennsylvania. Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission. p. 108.
- "Archives of Maryland, Volume 0028, Page 0269 - Proceedings of the Council of Maryland, 1732:1753".
- Weslager, Clinton (1943). Delaware's Forgotten Folk. University of Pennsylvania Press. pp. 50–58. ISBN 9780812219838.
- Hodge, Frederick Webb (Editor), Handbook of American Indians North of Mexico, Part 2. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office, 1910
- "History", Nanticoke Tribe, accessed 8 Oct 2009
- Harold B. Hancock (1976). The History of Sussex County, Delaware. p. 6.
- Cunningham, Keith. "A Phonological Analysis of the Heckewelder Vocabulary of Nanticoke".
- Howard, James H. "The Nanticoke-Delaware Skeleton Dance." American Indian Quarterly. 1975
- "Welcome." Nanticoke Indian Tribe. 2004 (retrieved 3 Jan 2010)
- ^ Brown, Robin (January 1, 2008). "The backstory on the Nanticoke Indian Tribe". delawareonline.com. Retrieved August 11, 2008.
- "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- Nanticoke Indian Community TR
- Jim Cresson, "Chiefs resign from Nanticoke Indian Association", Cape Gazette, 15 Mar 2002, Mitsawokett, accessed 8 Oct 2009
- "William Harrison Daisey Sr., former Nanticoke chief".
- "Natosha Carmine: Nanticoke Indian Association chief".
- "Nanticoke Indian Tribe appoints new chief". January 12, 2023.
- "South Jersey land once inhabited by tribe is returned to Native American group". August 22, 2023.
Further reading
- Weslager, C. A. (1948). The Nanticoke Indians: A Refugee Tribal Group of Pennsylvania. The Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission. OCLC 2222529.
External links
- Nanticoke Indian Association, Delaware, official website
- Nanticoke Lenni-Lenape Indian Of New Jersey, New Jersey, official website
- Delaware Tribe of Indians, Oklahoma, official website
- Six Nations of the Grand River, Ontario, official website
| Native Americans in Maryland | |
|---|---|
| Historic and present tribes | |
| Historical languages | |
| Present territories | Tayac Territory |
| Historic figures | |
| Historic communities | |
| Prehistoric peoples | |
| Prehistoric communities |
|
| Other prehistoric places | |
| Institutions | |
| Other topics | |
- Nanticoke
- Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands
- Eastern Algonquian peoples
- Native American history of Delaware
- Native American history of Maryland
- Chesapeake Bay
- First Nations in Ontario
- Native American tribes in Maryland
- Native American tribes in New Jersey
- Native American tribes in Oklahoma
- Algonquian ethnonyms
- Native American tribes in Pennsylvania
- State-recognized tribes in the United States