You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Polish. (June 2022) Click for important translation instructions.
|
| Narach | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Location | Minsk Province |
| Coordinates | 54°51′09″N 26°44′59″E / 54.85250°N 26.74972°E / 54.85250; 26.74972 |
| Basin countries | Belarus |
| Max. length | 12.8 km (8.0 mi) |
| Surface area | 79.6 km (30.7 sq mi) |
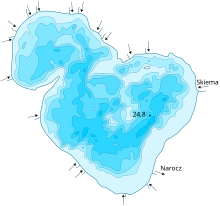
| Max. depth | 24.8 m (81 ft) |
| Water volume | 710 million cubic metres (580,000 acre⋅ft) |
| Shore length | 41 km (25 mi) |
| Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Lake Narach (Belarusian: На́рач, Narač pronounced [ˈnarat͡ʂ]; Russian: На́рочь, Naročj; Lithuanian: Narutis, Naročius, Polish: Narocz) is a lake in northwestern Belarus (Myadzyel District, Minsk Region), located in the basin of the Viliya river. It is the largest lake in Belarus (in 1921–39 it was the largest lake of Poland).
Narach is a part of the Narach lake group (the others being Miastra (Belarusian: Мястра), Batoryn (Belarusian: Баторын), and Blednaje (Belarusian: Бледнае). It was formed about 11 thousand years ago after the Pleistocene ice ages. It has a surface area of 79.6 km, a wider length of 12.8 km, a maximum depth of 24.8 m, average depth of 8.9 m, a volume of 710 million cubic meters. The lake is surrounded by pine forests. The Narach River flows out of it.
Narach is the abode of 22 genera of fish, including eel, pike, burbot, etc. The shore and islets are nested by different birds, such as the mute swan, fish hawk, tarrock and dabchick.
History
People settled near the lake about 10 thousand years ago. Linguists think that its name is probably from the Indo-European root *nar- often found in names of bodies of water (e.g., the Nara and Neris rivers). Archaeologists have excavated many burial mounds of the Baltic and Slavic people that lived around Narach.
Since the Middle Ages, the local inhabitants have lived mainly by fishing and farming. In the 19th century, the most profitable work was fishing of crayfish. In the 20th century, the eel became the main marketable fish.
During World War I, the surrounding area was a focal point of the Lake Naroch Offensive (March–April 1916), an inconclusive offensive operation mounted by forces of the Imperial Russian Army against the German army.
In 1919, German composer Siegfried Wagner set to music a poem by Günther Holstein (1892-1931) about a military battle, called Nacht am Narocz (Night at lake Narach).
In the 1930s, the fishers of Narach rose against Polish authorities defending their right to exploit the lake.
Since the 1950s, the lake has become a popular resort and tourism site, located in the resort town of Narach. A Young Pioneer camp of national importance Zubryonok was located near the lake. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union the camp was reformed into the National Children's Recreational Camp "Zubrania", which is now the most important children's recreational camp in Belarus.
In 1999, the government of Belarus created the Narachanski National Park.
See also
References
- "Main characteristics of the largest lakes. Main Geographic Characteristics of the Republic of Belarus". Land of Ancestors. 2012. Archived from the original on 29 September 2013. Retrieved 30 August 2013.
- E.M. Pospelov, Geograficheskie nazvaniya mira (Moscow: Russkie slovari, 1998), p. 283.
External links
 Media related to Narač Lake at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Narač Lake at Wikimedia Commons