| Nemertodermatida | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Xenacoelomorpha |
| Subphylum: | Acoelomorpha |
| Class: | Nemertodermatida Karling, 1940 |
Nemertodermatida is a class of Acoelomorpha, comprising 18 species of millimetre-sized turbellariform, mostly interstitial worms.
Taxonomy
The order Nemertodermatida contains two families with 6 genera. The high level of cryptic diversity in this meiofauna group however implies that the number of nemertodermatid taxa may be underestimated.
Ascopariidae
The family Ascopariidae Sterrer, 1998 contains two genera.
- Ascoparia Sterrer, 1998
- Flagellophora Faubel & Dorjes, 1978
There are 3 species in the family Ascopariidae.
| Name | Image | Distribution | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ascoparia neglecta Sterrer, 1998 | |||
| Ascoparia secunda Sterrer, 1998 | |||
| Flagellophora apelti Faubel & Dorjes, 1978 |
Nemertodermatidae
The family Nemertodermatidae Steinböck, 1930 contains four genera.
There are 15 species in the family Nemertodermatidae.
| Name | Image | Distribution | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meara stichopi Westblad, 1949 |

|
||
| Nemertinoides elongatus Riser, 1987 |

|
||
| Nemertinoides glandulosum Meyer-Wachsmuth, Curini Galletti & Jondelius, 2014 |

|
||
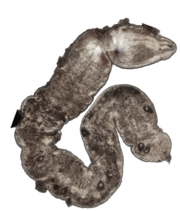
| Nemertinoides wolfgangi Meyer-Wachsmuth, Curini Galletti & Jondelius, 2014 |
|
||
| Nemertoderma bathycola Steinböck, 1930 |
|||
| Nemertoderma westbladi (Westblad, 1937) Steinbock, 1938 |
|||
| Sterreria boucheti Meyer-Wachsmuth, Curini Galletti & Jondelius, 2014 |
|||
| Sterreria lundini Meyer-Wachsmuth, Curini Galletti & Jondelius, 2014 |
|||
| Sterreria martindalei Meyer-Wachsmuth, Curini Galletti & Jondelius, 2014 |

|
||
| Sterreria monolithes Meyer-Wachsmuth, Curini Galletti & Jondelius, 2014 |
|||
| Sterreria papuensis Meyer-Wachsmuth, Curini Galletti & Jondelius, 2014 |
|||
| Sterreria psammicola (Sterrer, 1970) |

|
||
| Sterreria rubra (Faubel, 1976) |

|
||
| Sterreria variabilis Meyer-Wachsmuth, Curini Galletti & Jondelius, 2014 |

|
||
| Sterreria ylvae Meyer-Wachsmuth, Curini Galletti & Jondelius, 2014 |

|
Notes
- ^ A binomial authority in parentheses indicates that the species was originally described in a different genus.
References
- Nielsen C (2012). Animal Evolution: Interrelationships of the Living Taxa. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 69–70. ISBN 978-0-19-960602-3.
- ^ Tyler S (2010). "Isodiametridae". World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- Meyer-Wachsmuth I, Curini Galletti M, Jondelius U (2014-09-16). "Hyper-cryptic marine meiofauna: species complexes in Nemertodermatida". PLOS ONE. 9 (9): e107688. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9j7688M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0107688. PMC 4166464. PMID 25225981.
- Tyler S, Schilling S, Hooge M, Bush LF (2006–2016). "Nemertodermatida". Turbellarian taxonomic database. Version 1.7. Retrieved 2016-02-03.
- Zhang ZQ (2011-12-23). "Animal biodiversity: An outline of higher-level classification and survey of taxonomic richness". Zootaxa. 3148. Magnolia Press: 1–237. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3148.1.1. Retrieved 2016-02-03.
| Extant animal phyla | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Nemertodermatida | |
This Xenacoelomorpha-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |