| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "New Zealand Subantarctic Islands" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | New Zealand |
| Includes | |
| Criteria | Natural: (ix), (x) |
| Reference | 877 |
| Inscription | 1998 (22nd Session) |
| Area | 764.8 km (295.3 sq mi) |
| Coordinates | 50°45′S 166°6′E / 50.750°S 166.100°E / -50.750; 166.100 |
The New Zealand Subantarctic Islands comprise the five southernmost groups of the New Zealand outlying islands. They are collectively designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Most of the islands lie near the southeast edge of the largely submerged continent centred on New Zealand called Zealandia, which was riven from Australia 60–85 million years ago, and from Antarctica 85–130 million years ago. They share some features with Australia's Macquarie Island to the west.
History
Until 1995, scientific research staff were stationed permanently at a meteorological station on Campbell Island. Since then, the islands have been uninhabited, though they are periodically visited by researchers and tourists. Protection of reserves was strengthened in 2014, becoming the largest natural sanctuary in the nation.
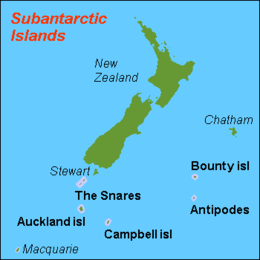
Islands
- Antipodes Islands
- Antipodes Island, Bollons Island, the Windward Islands, Orde Lees Island, Leeward Island, South Islet
- Auckland Islands
- Auckland Island, Adams Island, Disappointment Island, Enderby Island, Ewing Island, Rose Island
- Bounty Islands
- Main Group, Centre Group, and Eastern Group islets
- Campbell Islands
- Campbell Island / Motu Ihupuku, Dent Island, Folly Island, Jacquemart Island
- Snares Islands / Tini Heke
- Alert Stack, Broughton Island, High Island, North East Island, Western Chain islets
Territorial claims
New Zealand also has territorial claims, held in abeyance under the Antarctic Treaty System, over several islands close to the Antarctic mainland, including:
- Ross Island and the rest of the Ross Archipelago
- Balleny Islands: Young Island, Buckle Island, Sturge Island, plus several smaller islets
- Roosevelt Island
- Scott Island and Haggits Pillar
Of these, Ross Island is inhabited by the scientific staff of several research stations, notably at McMurdo Sound and Scott Base.
Ecology
The Antipodes, Auckland, Bounty and Campbell Islands are collectively designated the Antipodean Islands in the World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions. The Snares Islands / Tini Heke are included with the South Island in New Zealand South under the scheme.
See also
References
- "Data Table – Protected Areas – LINZ Data Service". Land Information New Zealand. Retrieved 27 August 2019.
- "New Zealand Sub-Antarctic Islands". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. World Heritage List. Retrieved 8 September 2019.
- Fox, M. (2 March 2014). "Birds, seals, penguins protected". Stuff News. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
External links
- Subantarctic islands, Department of Conservation
- UNESCO classification for the sub-antarctic islands
- Castaways: Wrecked on a subantarctic island – Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand
| Peri-Antarctic countries and overseas territories | |
|---|---|
| "Peri-Antarctic" (meaning "close to the Antarctic") does not include territorial claims in Antarctica itself. |
| World Heritage Sites in New Zealand | |
|---|---|
| See also: List of World Heritage Sites in Oceania |