| Nimbacinus Temporal range: 26–12 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Late Oligocene to Middle Miocene | |
|---|---|
| |
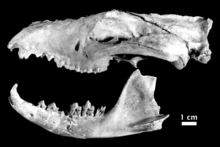
| Skull and mandible of N. dicksoni | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Infraclass: | Marsupialia |
| Order: | Dasyuromorphia |
| Family: | †Thylacinidae |
| Genus: | †Nimbacinus Muirhead & Archer, 1990 |
| Type species | |
| Nimbacinus dicksoni Muirhead & Archer, 1990 | |
| Other species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |

The genus Nimbacinus contains two species of carnivorous, quadrupedal marsupials in Australia both of which are extinct:
Like all thylacinids, Nimbacinus dicksoni was a dog-like marsupial, though its smaller size makes its appearance more comparable to that of a fox. Unlike its relatives, its jaws were likely strong enough for it to take down prey larger than itself.
The name of the genus combines Nimba and cinus, derived from a word meaning "little" in the Wanyi language, indigenous peoples associated with the Riversleigh fossil site, and the Ancient Greek word kynos, meaning dog.
Taxonomy
The description of N. richi was published in 2000 by researchers Peter F. Murray, working at the Museum of Central Australia and Dirk Megirian of the Northern Territory Museum. The holotype is fossilised material excavated at "Top Site" at the Bullock Creek fossil area, a partial left dentary with a premolar and several molars that is dated to the mid-Miocene. The specific epithet commemorates Tom Rich, who introduced the authors to the site of their discovery.
References
- ^ Muirhead, J.; Archer, M. (1990). "Nimbacinus dicksoni, a plesiomorphic thylacine (Marsupialia: Thylacinidae) from Tertiary deposits of Queensland and the Northern Territory". Memoirs of the Queensland Museum. 28: 203–221.
- Rovinsky, Douglass S.; Evans, Alistair R.; Adams, Justin W. (2019-09-02). "The pre-Pleistocene fossil thylacinids (Dasyuromorphia: Thylacinidae) and the evolutionary context of the modern thylacine". PeerJ. 7: e7457. doi:10.7717/peerj.7457. ISSN 2167-8359. PMC 6727838.
- Churchill, T. J.; Archer, M.; Hand, S. J. (2024). "Three new thylacinids (Marsupialia, Thylacinidae) from late Oligocene deposits of the Riversleigh World Heritage Area, northwestern Queensland". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. doi:10.1080/02724634.2024.2384595.
- Attard, Marie R. G.; Parr, William C. H.; Wilson, Laura A. B.; Archer, Michael; Hand, Suzanne J.; Rogers, Tracey L.; Wroe, Stephen (2014). "Virtual Reconstruction and Prey Size Preference in the Mid Cenozoic Thylacinid, Nimbacinus dicksoni (Thylacinidae, Marsupialia)". PLOS ONE. 9 (4): e93088. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...993088A. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0093088. PMC 3981708. PMID 24718109.
- ^ Murray, P.; Megirian, D. (2000). "Two New Genera and Three New Species of Thylacinidae (Marsupialia) from the Miocene of the Northern Territory, Australia". The Beagle: Occasional Papers of the Northern Territory Museum of Arts and Sciences. 16: 145–162.
| Agreodontia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Nimbacinus | |
This article about a prehistoric marsupial is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
