| Black-tailed rattlesnake | |
|---|---|

| |
| Conservation status | |
 Least Concern (IUCN 3.1) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Viperidae |
| Genus: | Crotalus |
| Species: | C. molossus |
| Binomial name | |
| Crotalus molossus Baird & Girard, 1853 | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
The black-tailed rattlesnake (Crotalus molossus) is a venomous pit viper species found in the southwestern United States and Mexico. Four subspecies are currently recognized, including the nominate subspecies described here.
Taxonomy
A 2012 revision showed that eastern populations from Texas and central and eastern New Mexico form a distinct species separate from C. molossus: Crotalus ornatus Hallowell 1854.
Alternate common names are green rattler, and Northern black-tailed rattlesnake.
Subspecies
| Subspecies | Taxon author | Common name | Geographic range |
|---|---|---|---|
| C. m. molossus | Baird & Girard, 1853 | Northern black-tailed rattlesnake | United States (Arizona, New Mexico, southwest Texas), Mexico |
| C. m. nigrescens | Gloyd, 1936 | Mexican black-tailed rattlesnake | Mexico (South Sonora, southwest Chihuahua, southern Coahuila, south to Oaxaca and Veracruz, Tlaxcala) |
| C. m. oaxacus | Gloyd, 1948 | Oaxacan black-tailed rattlesnake | Mexico (Oaxaca) |
Description

This medium-sized species averages from 76 to 107 cm (30 to 42 in) in length. Large specimens are usually not much more than 100 cm (39 in) long, although lengths of 125.0 cm (49.2 in) (Gloyd, 1940), 125.7 cm (49.5 in) (Klauber, 1972), and 129.5 cm (51.0 in) (Shaw & Campbell, 1974) have been reported. The females tend to be larger than the males.
They range in color from yellows and olive greens to browns and black. As their name implies, one of their most distinguishing features is, despite variations in body color, entirely black tail scales. Often, this rattlesnake has a black band across its eyes extending diagonally down to the corners of its mouth, forming a sort of facial 'mask'.
Like other rattlesnakes, C. molossus has a rattle composed of keratin on the end of its tail. Each time the snake sheds its skin, a new segment is added to the rattle. A snake can shed its skin several times a year, and the rattle is fairly fragile and can be broken, so that the length of a rattlesnake's rattle is not an accurate measure of its age, unless the terminal button is intact.
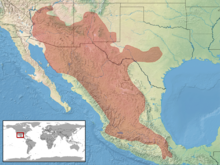
Distribution and habitat
The black-tailed rattlesnake is found in the southwestern United States in Arizona, New Mexico and west and central Texas, and Mexico as far south as Oaxaca. Also it is found in the Gulf of California on San Estéban and Tiburón Islands. Its distribution reaches a maximum elevation of 2930 m, although it has been recorded at as high as 6900 feet at the McDonald Observatory in the Davis Mountains of west Texas. The type locality given is "Fort Webster, St. Rita del Cobre, N. Mex." (Fort Webster, Santa Rita del Cobre, Grant County, New Mexico, USA).
Behavior and ecology

All rattlesnakes are carnivorous, their primary food sources being rodents, other small mammals, birds, and small reptiles (such as small lizards). The behavior of northern black-tailed rattlesnakes varies over the course of a year. In the spring and fall, they are primarily diurnal. In the summer, they shift to a nocturnal behavior, to avoid the heat of summer. In the winter, they hibernate in dens created and abandoned by other animals, often with other species of snakes. They are variable in their form of locomotion depending on what substrate they need to traverse and will actively change between sidewinding or rectilinear movement. Although it is an able climber and expert swimmer, C. molossus is primarily a terrestrial species and inhabits grasslands, desert areas, and rocky and mountainous areas, as well as high-altitude forests.
Docility and defense
Crotalus molossus is considered to be one of the most docile rattlesnakes because of its calm demeanor and curious nature. Bites are accordingly fairly rare. The snake relies mostly on camouflage to avoid discovery. It normally tries to slither away when confronted, but will rattle when cornered.
Venom
The venom of the C. molossus is primarily hemotoxic, like that of most crotalids. However, it is only about two-thirds as toxic as western diamondback venom and is generally not fatal to humans. CroFab antivenom is often used to treat bites.
Crotalus molossus has larger venom glands than most rattlesnakes in its region. Because its venom is less toxic than that of most other crotalids, it needs to inject large quantities into its prey to be effective.
Reproduction
Breeding occurs in the spring when males follow the pheromone trails of the females. Copulation can sometimes last for hours and occur multiple times over a period of days. After mating, the male often stays near the female for several days to prevent any other males from mating with her. The female gives birth to live young in the summer, and the babies stay with the mother only until they wander off on their own, usually in less than a day or two. Females are believed to breed every year, and can have litters as large as 10-12 young but usually averaging four to six. Their lifespans average 15–20 years.
Conservation status
This species is classified as Least Concern IUCN Red List of Threatened Species (v3.1, 2001). Species are listed as such owing to their wide distribution or presumed large population or because they are unlikely to be declining fast enough to qualify for listing in a more threatened category. The population trend was stable when assessed in 2007.
References
- Hammerson, G. A. (March 2007). "IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: Crotalus molossus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
- ^ McDiarmid RW, Campbell JA, Touré T. 1999. Snake Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, vol. 1. Herpetologists' League. 511 pp. ISBN 1-893777-00-6 (series). ISBN 1-893777-01-4 (volume).
- ^ "Crotalus molossus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 24 February 2007.
- Anderson, C. G., and E. Greenbaum. 2012. Phylogeography of northern populations of the black-tailed rattlesnake (Crotalus molossus Baird and Girard, 1853), with the revalidation of C. ornatus Hallowell, 1854. Herpetol. Monogr. 26: 19–57.
- ^ Campbell JA, Lamar WW. 2004. The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere. Comstock Publishing Associates, Ithaca and London. 870 pp. 1500 plates. ISBN 0-8014-4141-2.
- Wright AH, Wright AA. 1957. Handbook of Snakes of the United States and Canada. Comstock Publishing Associates. Ithaca and London. (7th printing, 1985). 1105 pp. ISBN 0-8014-0463-0.
- Conant R. 1975. A Field Guide to Reptiles and Amphibians of Eastern and Central North America. Second Edition. . Houghton Mifflin Company. Boston. 429 pp. 48 plates. ISBN 0-395-19979-4 (hc), ISBN 0-395-19977-8 (pb).
- "Crotalus molossus (Black Tailed Rattlesnake)".
- Crotalus molossus at the IUCN Red List. Accessed 13 September 2007.
- 2001 Categories & Criteria (version 3.1) at the IUCN Red List. Accessed 13 September 2007.
External links
- Crotalus molossus at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 12 December 2007.
- Crotalus molossus at Herps of Texas Archived 2012-07-17 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed 24 February 2007.
- Black-tailed Rattlesnake at Centennial Museum & Chihuahuan Desert Gardens Natural and Cultural History. Accessed 24 February 2007.
- Crotalus molossus, Black-tailed Rattlesnake at California Reptiles and Amphibians. Accessed 24 February 2007.
- Crotalus molossus molossus at Munich AntiVenom INdex. Accessed 24 February 2007.
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Crotalus molossus | |