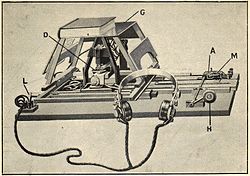
The optophone is a device, used by people who are blind, that scans text and generates time-varying chords of tones to identify letters. It is one of the earliest known applications of sonification. Dr. Edmund Fournier d'Albe of Birmingham University invented the optophone in 1913, which used selenium photosensors to detect black print and convert it into an audible output which could be interpreted by a blind person. The Glasgow company, Barr and Stroud, participated in improving the resolution and usability of the instrument.
Only a few units were built and reading was initially exceedingly slow; a demonstration at the 1918 Exhibition involved Mary Jameson reading at one word per minute. Later models of the Optophone allowed speeds of up to 60 words per minute, though only some subjects are able to achieve this rate.

See also
References
- d'Albe, E. E. F. (1 July 1914). "On a Type-Reading Optophone". Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 90 (619): 373–375. Bibcode:1914RSPSA..90..373D. doi:10.1098/rspa.1914.0061.
- d'Albe, E. E. Fournier (October 1920), "The Type-Reading Optophone" (PDF), Scientific American: 109–110, archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-26, retrieved 2011-12-01
- Jameson, M. (1966), "The Optophone: Its Beginning and Development" (PDF), Bulletin of Prosthetics Research: 25–28
- Fish, R.M. (1976), "An audio display for the blind", IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 23 (2), IEEE: 144–154, doi:10.1109/tbme.1976.324576, PMID 1248840
External links
- d'Albe, Edmund Edward Fournier (1922). "Optophone" . Encyclopædia Britannica (12th ed.).
- Mills, Mara. "Optophones and Musical Print." Sounding Out! (2015)
This sound technology article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |