| This article may have misleading content. Please help clarify the content. (July 2019) |
The Oren–Nayar reflectance model, developed by Michael Oren and Shree K. Nayar, is a reflectivity model for diffuse reflection from rough surfaces. It has been shown to accurately predict the appearance of a wide range of natural surfaces, such as concrete, plaster, sand, etc.
Introduction
Reflectance is a physical property of a material that describes how it reflects incident light. The appearance of various materials are determined to a large extent by their reflectance properties. Most reflectance models can be broadly classified into two categories: diffuse and specular. In computer vision and computer graphics, the diffuse component is often assumed to be Lambertian. A surface that obeys Lambert's Law appears equally bright from all viewing directions. This model for diffuse reflection was proposed by Johann Heinrich Lambert in 1760 and has been perhaps the most widely used reflectance model in computer vision and graphics. For a large number of real-world surfaces, such as concrete, plaster, sand, etc., however, the Lambertian model is an inadequate approximation of the diffuse component. This is primarily because the Lambertian model does not take the roughness of the surface into account.
Rough surfaces can be modelled as a set of facets with different slopes, where each facet is a small planar patch. Since photo receptors of the retina and pixels in a camera are both finite-area detectors, substantial macroscopic (much larger than the wavelength of incident light) surface roughness is often projected onto a single detection element, which in turn produces an aggregate brightness value over many facets. Whereas Lambert’s law may hold well when observing a single planar facet, a collection of such facets with different orientations is guaranteed to violate Lambert’s law. The primary reason for this is that the foreshortened facet areas will change for different viewing directions, and thus the surface appearance will be view-dependent.

Analysis of this phenomenon has a long history and can be traced back almost a century. Past work has resulted in empirical models designed to fit experimental data as well as theoretical results derived from first principles. Much of this work was motivated by the non-Lambertian reflectance of the moon.
The Oren–Nayar reflectance model, developed by Michael Oren and Shree K. Nayar in 1993, predicts reflectance from rough diffuse surfaces for the entire hemisphere of source and sensor directions. The model takes into account complex physical phenomena such as masking, shadowing and interreflections between points on the surface facets. It can be viewed as a generalization of Lambert’s law. Today, it is widely used in computer graphics and animation for rendering rough surfaces. It also has important implications for human vision and computer vision problems, such as shape from shading, photometric stereo, etc.
Formulation

The surface roughness model used in the derivation of the Oren-Nayar model is the microfacet model, proposed by Torrance and Sparrow, which assumes the surface to be composed of long symmetric V-cavities. Each cavity consists of two planar facets. The roughness of the surface is specified using a probability function for the distribution of facet slopes. In particular, the Gaussian distribution is often used, and thus the variance of the Gaussian distribution, , is a measure of the roughness of the surfaces. The standard deviation of the facet slopes (gradient of the surface elevation), ranges in .
In the Oren–Nayar reflectance model, each facet is assumed to be Lambertian in reflectance. If is the irradiance when the facet is illuminated head-on, the radiance of the light reflected by the faceted surface, according to the Oren-Nayar model, is
where the direct illumination term and the term that describes bounces of light between the facets are defined as follows.
where
- ,
- ,
- ,
and is the albedo of the surface, and is the roughness of the surface. In the case of (i.e., all facets in the same plane), we have , and , and thus the Oren-Nayar model simplifies to the Lambertian model:
Results
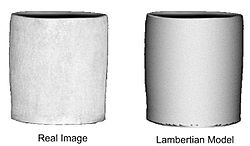
Here is a real image of a matte vase illuminated from the viewing direction, along with versions rendered using the Lambertian and Oren-Nayar models. It shows that the Oren-Nayar model predicts the diffuse reflectance for rough surfaces more accurately than the Lambertian model.


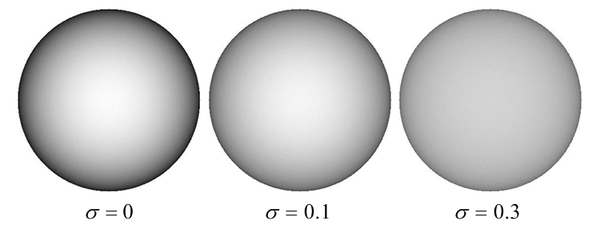
Here are rendered images of a sphere using the Oren-Nayar model, corresponding to different surface roughnesses (i.e. different values):
Connection with other microfacet reflectance models
| Oren-Nayar model | Torrance-Sparrow model | Microfacet model for refraction |
|---|---|---|
| Rough opaque diffuse surfaces | Rough opaque specular surfaces (glossy surfaces) | Rough transparent surfaces |
| Each facet is Lambertian (diffuse) | Each facet is a mirror (specular) | Each facet is made of glass (transparent) |
See also
References
- ^ Oren, M.; Nayar, S. K. (1994). "Generalization of Lambert's reflectance model". Proceedings of the 21st annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques - SIGGRAPH '94. pp. 239–246. doi:10.1145/192161.192213. ISBN 0897916670. S2CID 122480.
- Torrance, K. E.; Sparrow, E. M. (1967). "Theory for off-specular reflection from roughened surfaces". J. Opt. Soc. Am. 57 (9): 1105–1114. Bibcode:1967JOSA...57.1105T. doi:10.1364/JOSA.57.001105.
- Walter, B.; et al. "Microfacet Models for Refraction through Rough Surfaces". Egsr 2007.
 , is a measure of the roughness of the surfaces. The standard deviation of the facet slopes (gradient of the surface elevation),
, is a measure of the roughness of the surfaces. The standard deviation of the facet slopes (gradient of the surface elevation),  ranges in
ranges in  .
.
 is the irradiance when the facet is illuminated head-on, the radiance
is the irradiance when the facet is illuminated head-on, the radiance  of the light reflected by the faceted surface, according to the Oren-Nayar model, is
of the light reflected by the faceted surface, according to the Oren-Nayar model, is

 and the term
and the term  that describes bounces of light between the facets are defined as follows.
that describes bounces of light between the facets are defined as follows.


 ,
,

 ,
, ,
, is the
is the  (i.e., all facets in the same plane), we have
(i.e., all facets in the same plane), we have  , and
, and  , and thus the Oren-Nayar model simplifies to the Lambertian model:
, and thus the Oren-Nayar model simplifies to the Lambertian model: