| Part of a series on | ||||
| Christianity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
|
||||
| Theology | ||||
|
||||
| Related topics | ||||
| Part of a series on |
| Serbs |
|---|
 |
| Native |
DiasporaEurope
Overseas |
| Culture |
| History |
| Language |
| Religion |
| Related nations |
Eastern Orthodoxy is the primary Christian denomination in Serbia, representing 81% of the population as of 2022, followed traditionally by the majority of Serbs, and also Romanians and Vlachs, Montenegrins, Macedonians and Bulgarians living in Serbia. The dominant Eastern Orthodox church in Serbia is the Serbian Orthodox Church. Also, the Romanian Orthodox Church has its own Diocese of Dacia Felix that operates among Orthodox Romanians in Serbian Banat and the Timok Valley.
History
Late Antiquity and early Middle Ages
Main articles: Archbishopric of Justiniana Prima and Archbishopric of OhridDuring Late Antiquity, on the territory of present-day Serbia there were several major Christian centers and episcopal sees, including Sirmium, Singidunum, Viminacium, Naissus, Ulpiana and others. In 535, Byzantine emperor Justinian I created new Archbishopric of Justiniana Prima, centered in the city of Justiniana Prima near present-day town of Lebane in central Serbia.
Middle Ages and early Modern Period
Main articles: History of the Serbian Orthodox Church and Serbia in the Middle AgesThe identity of ethnic Serbs was historically based on Orthodox Christianity; the Serbian Orthodox Church, to the extent that some people claimed that those who were not Orthodox, were not Serbs. The Christianization of the Serbian lands took place in the 9th century, and Serbia (the Serbian Principality) is accounted Christian as of 870. The Serbian bishoprics became part of the Archbishopric of Ohrid, after the Byzantine conquest of the Bulgarian Empire in 1018. The Slavic language replaced the Greek in liturgical language.
With the Great Schism in 1054 (precipitated by Humbert of Silva Candida and his colleagues who entered the church of the Hagia Sophia during Michael I Cerularius's divine liturgy and placed the Charter on the altar.), Serbia remained under Constantinople, while neighbouring Croatia remained under Rome. The Serbian Orthodox Church was given autocephaly in 1219, when Archbishop Sava received recognition from the exiled Ecumenical Patriarch. In 1346, it was raised to the rank of Patriarchate. During the late Middle Ages and Early Modern period, Serbian Patriarchate of Peć (1346-1766) had at its peak more than forty eparchies.
Serbian Orthodox Church in Serbia
Fifteen eparchies (dioceses) of the Serbian Orthodox Church cover the territory of Serbia:
- Archbishopric of Belgrade and Karlovci, patriarchal eparchy
- Eparchy of Bačka, with seat in Novi Sad
- Eparchy of Banat, with seat in Vršac
- Eparchy of Braničevo, with seat in Požarevac
- Eparchy of Kruševac, with seat in Kruševac
- Eparchy of Mileševa, with seat in Prijepolje (partially covers southwestern region of Serbia and northwestern region of Montenegro)
- Eparchy of Niš, with seat in Niš
- Eparchy of Raška and Prizren, with seat in Prizren
- Eparchy of Šabac, with seat in Šabac
- Eparchy of Srem, with seat in Sremski Karlovci
- Eparchy of Šumadija, with seat in Kragujevac
- Eparchy of Timok, with seat in Zaječar
- Eparchy of Valjevo, with seat in Valjevo
- Eparchy of Vranje, with seat in Vranje
- Eparchy of Žiča, with seat in Kraljevo
Gallery
-
 Eparchies of the Serbian Orthodox Church, in its primatial canonical territory, including Serbia
Eparchies of the Serbian Orthodox Church, in its primatial canonical territory, including Serbia
-
Remains of the city Justiniana Prima, seat of the Archbishopric of Justiniana Prima, near modern city of Lebane in Serbia
-
 Church of Saints Peter and Paul, the oldest known medieval church building of Serbia
Church of Saints Peter and Paul, the oldest known medieval church building of Serbia
-
Studenica Monastery, established in the 12th century
-
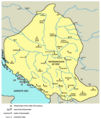 Jurisdiction of the Serbian Patriarchate of Peć in 16th and 17th century
Jurisdiction of the Serbian Patriarchate of Peć in 16th and 17th century
-
 Church of Saint Sava, one of the largest Orthodox church buildings
Church of Saint Sava, one of the largest Orthodox church buildings
See also
- Christianity in Serbia
- Religion in Serbia
- Demographics of Serbia
- Serbian Orthodox Church
- Eastern Orthodoxy in Europe
References
- "Мother tongue, religion and ethnic affiliation | ABOUT CENSUS". popis2022.stat.gov.rs. Retrieved 2024-11-29.
- Vlasto 1970, p. 208
- Ćorović, Drugi Period, IV. Pokrštavanje Južnih Slovena
- Charanis 1969, p. 210.
Sources
- Vlasto, A. P. (1970). The Entry of the Slavs into Christendom: An Introduction to the Medieval History of the Slavs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521074599.
- Ćorović, Vladimir (1941). "Iсторија српског народа (Istorija srpskog naroda)". Internet, 2001) (in Serbian). Пројекат Растко: Библиотека српске културе; Projekat Rastko: Biblioteka srpske kulture.
- Charanis, Peter (1969) . "The Byzantine Empire in the Eleventh Century". A History of the Crusades. Vol. 1 (2nd ed.). Madison: University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 177–219. ISBN 978-0-299-04834-1.
- Ćirković, Sima (2004). The Serbs. Malden: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 9781405142915.
| Eastern Orthodoxy in Europe | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |