| Otomakoan | |
|---|---|
| Otomaco–Taparita | |
| Geographic distribution | Venezuelan Llanos |
| Linguistic classification | Macro-Otomakoan ?
|
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | otom1276 |
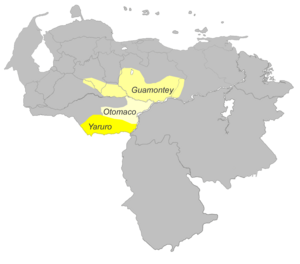 | |
Otomaco and Taparita are two long-extinct languages of the Venezuelan Llanos.
In addition to Otomaco and Taparita, Loukotka (1968) also lists Maiba (Amaygua), an unattested extinct language that was once spoken in Apure State, Venezuela between the Cunaviche River and Capanaparo River.
Vocabulary
Loukotka (1968) lists the following basic vocabulary items for Otomac and Taparita.
gloss Otomac Taparita one engá enda two dé deñiaro three yakia deni head dapad dupea eye inbad indó tooth miʔi mina man andua mayná water ya ia fire núa muita sun nua mingua maize onona jaguar maéma house augua ñaña
Additional vocabulary for Otomaco and Taparita are documented in Rosenblat (1936).
References
- Campbell, Lyle (2012). "Classification of the indigenous languages of South America". In Grondona, Verónica; Campbell, Lyle (eds.). The Indigenous Languages of South America. The World of Linguistics. Vol. 2. Berlin: De Gruyter Mouton. pp. 59–166. ISBN 9783110255133.
- ^ Rosenblat, Angel. 1936. Los Otomacos y Taparitas de los llanos de Venezuela. Estudio etnográfico y lingüístico. Tierra Firme 1. 227-377.
- ^ Loukotka, Čestmír (1968). Classification of South American Indian languages. Los Angeles: UCLA Latin American Center.
| Indigenous language families and isolates of South America (based on Campbell 2012 classification) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language families and isolates |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proposed groupings |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Linguistic areas | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Countries | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article related to the Indigenous languages of the Americas is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |