
 Assorted tempera (top) and gouache (bottom) paints
Assorted tempera (top) and gouache (bottom) paints
| Part of a series on | ||||
| Pollution | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Air pollution from a factory Air pollution from a factory | ||||
| Air | ||||
| Biological | ||||
| Digital | ||||
| Electromagnetic | ||||
| Natural | ||||
| Noise | ||||
| Radiation | ||||
| Soil | ||||
| Solid waste | ||||
| Space | ||||
| Thermal | ||||
| Visual | ||||
| War | ||||
Water
|
||||
| Topics | ||||
Misc
|
||||
Paint is a material or mixture that, when applied to a solid material and allowed to dry, adds a film-like layer. As art, this is used to create an image or images known as a painting. Paint can be made in many colors and types. Most paints are either oil-based or water-based, and each has distinct characteristics.
Primitive forms of paint were used tens of thousands of years ago in cave paintings.
Clean-up solvents are also different for water-based paint than oil-based paint. Water-based paints and oil-based paints will cure differently based on the outside ambient temperature of the object being painted (such as a house). Usually, the object being painted must be over 10 °C (50 °F), although some manufacturers of external paints/primers claim they can be applied when temperatures are as low as 2 °C (35 °F).
History
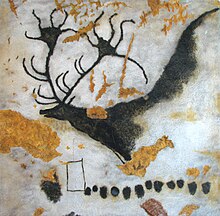
Paint was used in some of the earliest known human artworks. Some cave paintings drawn with red or yellow ochre, hematite, manganese oxide, and charcoal may have been made by early Homo sapiens as long as 40,000 years ago. Paint may be even older. In 2003 and 2004, South African archeologists reported finds in Blombos Cave of a 100,000-year-old human-made ochre-based mixture that could have been used like paint. Further excavation in the same cave resulted in the 2011 report of a complete toolkit for grinding pigments and making a primitive paint-like substance.
Interior walls at the 5,000-year-old Ness of Brodgar have been found to incorporate individual stones painted in yellows, reds, and oranges, using ochre pigment made of haematite mixed with animal fat, milk or eggs.
Ancient colored walls at Dendera, Egypt, which were exposed for years to the elements, still possess their brilliant color, as vivid as when they were painted about 2,000 years ago. The Egyptians mixed their colors with a gummy substance and applied them separately from each other without any blending or mixture. They appear to have used six colors: white, black, blue, red, yellow, and green. They first covered the area entirely with white, then traced the design in black, leaving out the lights of the ground color. They used minium for red, generally of a dark tinge.
The oldest known oil paintings are Buddhist murals created c. 650 AD. The works are located in cave-like rooms carved from the cliffs of Afghanistan's Bamiyan Valley, "using walnut and poppy seed oils." Pliny mentions some painted ceilings in his day in the town of Ardea, which had been made before the foundation of Rome. After the lapse of so many centuries, he expressed great surprise and admiration at their freshness.
In the 13th century, oil was used to detail tempera paintings. In the 14th century, Cennino Cennini described a painting technique utilizing tempera painting covered by light layers of oil. The slow-drying properties of organic oils were commonly known to early European painters. However, the difficulty in acquiring and working the materials meant that they were rarely used (and indeed, the slow drying was seen as a disadvantage). The paint was made with the yolk of eggs, and therefore, the substance would harden and adhere to the surface it was applied to. The pigment was made from plants, sand, and different soils. Most paints use either oil or water as a base (the diluent, solvent, or vehicle for the pigment).
The Flemish-trained or influenced Antonello da Messina, who Vasari wrongly credited with the introduction of oil paint to Italy, does seem to have improved the formula by adding litharge, or lead (II) oxide. A still extant example of 17th-century house oil painting is Ham House in Surrey, England, where a primer was used along with several undercoats and an elaborate decorative overcoat; the pigment and oil mixture would have been ground into a paste with a mortar and pestle. The painters did the process by hand, which exposed them to lead poisoning due to the white-lead powder.
In 1718, Marshall Smith invented a "Machine or Engine for the Grinding of Colors" in England. It is not known precisely how it operated, but it was a device that dramatically increased the efficiency of pigment grinding. Soon, a company called Emerton and Manby was advertising exceptionally low-priced paints that had been ground with labor-saving technology:

One Pound of Colour ground in a Horse-Mill will paint twelve Yards of Work, whereas Colour ground any other Way, will not do half that Quantity.
By the proper onset of the Industrial Revolution, in the mid-18th century, paint was being ground in steam-powered mills, and an alternative to lead-based pigments had been found in a white derivative of zinc oxide. Interior house painting increasingly became the norm as the 19th century progressed, both for decorative reasons and because the paint was effective in preventing the walls rotting from damp. Linseed oil was also increasingly used as an inexpensive binder.
In 1866, Sherwin-Williams in the United States opened as a large paint-maker and invented a paint that could be used from the tin without preparation.
It was only when the stimulus of World War II created a shortage of linseed oil in the supply market that artificial resins, or alkyds, were invented. Cheap and easy to make, they held the color well and lasted for a long time.
Types
Pigmented
Through the 20th century, paints used pigments, typically suspended in a liquid.
Structural
In the 21st century, "paints" that used structural color were created. Aluminum flakes dotted with smaller aluminum nanoparticles could be tuned to produce arbitrary colors by adjusting the nanoparticle sizes rather than picking/mixing minerals to do so. These paints weighed a tiny fraction of the weight of conventional paints, a particular advantage in air and road vehicles. They reflect heat from sunlight and do not break down outdoors. Preliminary experiments suggest it can reduce temperatures by 20 to 30 degrees Fahrenheit vs conventional paint. Its constituents are also less toxic.
Making the paint starts with a thin double-sided mirror. The researchers deposited metallic nanoparticles on both sides of the sheet. Large sheets were ground to produce small flakes.
Components
Vehicle
The vehicle is composed of binder; if it is necessary to thin it with a diluent like solvent or water, it is a combination of binder and diluent. In this case, once the paint has dried or cured very nearly all of the diluent has evaporated and only the binder is left on the coated surface. Thus, an important quantity in coatings formulation is the "vehicle solids", sometimes called the "resin solids" of the formula. This is the proportion of the wet coating weight that is binder, i.e., the polymer backbone of the film that will remain after drying or curing is complete. The volume of paint after it has dried, therefore only leaving the solids, is expressed as the volume solid.
Binder or film former
The binder is the film-forming component of paint. It is the only component that is always present among all the various types of formulations. Many binders must be thick enough to be applied and thinned. The type of thinner, if present, varies with the binder.
The binder imparts properties such as gloss, durability, flexibility, and toughness.
Binders include synthetic or natural resins such as alkyds, acrylics, vinyl-acrylics, vinyl acetate/ethylene (VAE), polyurethanes, polyesters, melamine resins, epoxy, silanes or siloxanes or oils.
Binders can be categorized according to the mechanisms for film formation. Thermoplastic mechanisms include drying and coalescence. Drying refers to simply evaporating the solvent or thinner to leave a coherent film behind. Coalescence refers to a mechanism that involves drying followed by actual interpenetration and fusion of formerly discrete particles. Thermoplastic film-forming mechanisms are sometimes described as "thermoplastic cure," but that is a misnomer because no chemical curing reactions are required to knit the film. On the other hand, thermosetting mechanisms are true curing mechanisms involving chemical reaction(s) among the polymers that make up the binder.
Thermoplastic Mechanisms
Some films are formed by simply cooling the binder. For example, encaustic or wax paints are liquid when warm, and harden upon cooling. In many cases, they re-soften or liquify if reheated.
Paints that dry by solvent evaporation and contain the solid binder dissolved in a solvent are known as lacquers. A solid film forms when the solvent evaporates. Because no chemical crosslinking is involved, the film can re-dissolve in solvent; lacquers are unsuitable for applications where chemical resistance is important. Classic nitrocellulose lacquers fall into this category, as do non-grain raising stains composed of dyes dissolved in solvent. Performance varies by formulation, but lacquers generally tend to have better UV resistance and lower corrosion resistance than comparable systems that cure by polymerization or coalescence.
The paint type known as Emulsion in the UK and Latex in the United States is a water-borne dispersion of sub-micrometer polymer particles. These terms in their respective countries cover all paints that use synthetic polymers such as acrylic, vinyl acrylic (PVA), styrene acrylic, etc. as binders. The term "latex" in the context of paint in the United States simply means an aqueous dispersion; latex rubber from the rubber tree is not an ingredient. These dispersions are prepared by emulsion polymerization. Such paints cure by a process called coalescence where first the water and then the trace, or coalescing, solvent, evaporate and draw together and soften the binder particles and fuse them together into irreversibly bound networked structures, so that the paint cannot redissolve in the solvent/water that originally carried it. The residual surfactants in paint, as well as hydrolytic effects with some polymers cause the paint to remain susceptible to softening and, over time, degradation by water. The general term of latex paint is usually used in the United States, while the term emulsion paint is used for the same products in the UK, and the term latex paint is not used at all.
Thermosetting Mechanisms
Paints that cure by polymerization are generally one- or two-package coatings that polymerize by way of a chemical reaction and cure into a cross-linked film. Depending on composition, they may need to dry first by evaporation of solvent. Classic two-package epoxies or polyurethanes would fall into this category.
The "drying oils", counter-intuitively, cure by a crosslinking reaction even if they are not put through an oven cycle and seem to dry in air. The film formation mechanism of the simplest examples involves the first evaporation of solvents followed by a reaction with oxygen from the environment over a period of days, weeks, and even months to create a crosslinked network. Classic alkyd enamels would fall into this category. Oxidative cure coatings are catalyzed by metal complex driers such as cobalt naphthenate though cobalt octoate is more common.
Recent environmental requirements restrict the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and alternative means of curing have been developed, generally for industrial purposes. UV curing paints, for example, enable formulation with very low amounts of solvent, or even none at all. This can be achieved because of the monomers and oligomers used in the coating have relatively very low molecular weight, and are therefore low enough in viscosity to enable good fluid flow without the need for additional thinner. If solvent is present in significant amounts, generally it is mostly evaporated first and then crosslinking is initiated by ultraviolet light. Similarly, powder coatings contain no solvent. Flow and cure are produced by the heating of the substrate after electrostatic application of the dry powder.
Combination mechanisms
So-called "catalyzed" lacquers" or "crosslinking latex" coatings are designed to form films by a combination of methods: classic drying plus a curing reaction that benefits from the catalyst. There are paints called plastisols/organosols, which are made by blending PVC granules with a plasticiser. These are stoved and the mix coalesces.
Diluent or solvent or thinner
The main purposes of the diluent are to dissolve the polymer and adjust the viscosity of the paint. It is volatile and does not become part of the paint film. It also controls flow and application properties, and in some cases can affect the stability of the paint while in liquid state. Its main function is as the carrier for the non-volatile components. To spread heavier oils (for example, linseed) as in oil-based interior house paint, a thinner oil is required. These volatile substances impart their properties temporarily—once the solvent has evaporated, the remaining paint is fixed to the surface.
This component is optional: some paints have no diluent.
Water is the main diluent for water-borne paints, even the co-solvent types.
Solvent-borne, also called oil-based, paints can have various combinations of organic solvents as the diluent, including aliphatics, aromatics, alcohols, ketones and white spirit. Specific examples are organic solvents such as petroleum distillate, esters, glycol ethers, and the like. Sometimes volatile low-molecular weight synthetic resins also serve as diluents.
Pigment, dye and filler
Main article: PigmentPigments are solid particles or flakes incorporated in the paint, usually to contribute color to the paint film. Pigments impart color by selective absorption of certain wavelengths of light and/or by scattering or reflecting light. The particle size of the pigment is critical to the light-scattering mechanism. The size of such particles can be measured with a Hegman gauge. Dyes, on the other hand, are dissolve in the paint and impart color only by the selective absorption mechanism. Paints can be formulated with only pigments, only dyes, both, or neither.
Pigments can also be used to give the paint special physical or optical properties, as opposed to imparting color, in which case they are called functional pigments. Fillers or extenders are an important class of the functional pigments. These are typically used to build film thickness and/or reduce the cost of the paint, or they can impart toughness and texture to the film. Fillers are usually cheap and inert materials, such as diatomaceous earth, talc, lime, barytes, clay, etc. Floor paints that must resist abrasion may contain fine quartz sand as a filler.
Sometimes, a single pigment can serve both decorative and functional purposes. For example some decorative pigments protect the substrate from the harmful effects of ultraviolet light by making the paint opaque to these wavelengths, i.e. by selectively absorbing them. These hiding pigments include titanium dioxide, phthalo blue, red iron oxide, and many others.
Some pigments are toxic, such as the lead pigments that are used in lead paint. Paint manufacturers began replacing white lead pigments with titanium white (titanium dioxide), before lead was banned in paint for residential use in 1978 by the US Consumer Product Safety Commission. The titanium dioxide used in most paints today is often coated with silica/alumina/zirconium for various reasons, such as better exterior durability, or better hiding performance (opacity) promoted by more optimal spacing within the paint film.
Micaceous iron oxide (MIO) is another alternative to lead for protection of steel, giving more protection against water and light damage than most paints. When MIO pigments are ground into fine particles, most cleave into shiny layers, which reflect light, thus minimising UV degradation and protecting the resin binder. Most pigments used in paint tend to be spherical, but lamellar pigments, such as glass flake and MIO have overlapping plates, which impede the path of water molecules. For optimum performance MIO should have a high content of thin flake-like particles resembling mica. ISO 10601 sets two levels of MIO content. MIO is often derived from a form of hematite.
Pigments can be classified as either natural or synthetic. Natural pigments are taken from the earth or plant sources and include colorants such as metal oxides or carbon black, or various clays, calcium carbonate, mica, silicas, and talcs. Synthetics include a host of colorants created in the lab as well as engineered molecules, calcined clays, blanc fixe, precipitated calcium carbonate, and synthetic pyrogenic silicas. The pigments and dyes that are used as colorants are classified by chemical type using the Color Index system, which is commercially significant.
Additives
Besides the three main categories of ingredients (binder, diluent, pigment), paint can have a wide variety of miscellaneous additives, which are usually added in small amounts, yet provide a significant effect on the product. Some examples include additives to modify texture , surface tension, improve flow properties, improve the finished appearance, increase wet edge, improve pigment stability, impart antifreeze properties, control foaming, control skinning, create acrylic pouring cells, etc. Other types of additives include catalysts, thickeners, stabilizers, emulsifiers, texturizers, adhesion promoters, UV stabilizers, flatteners (de-glossing agents), biocides to fight bacterial growth and the like.
Additives normally do not significantly alter the percentages of individual components in a formulation.
Color changing
Various technologies exist for making paints that change color. Thermochromic ink and coatings contain materials that change conformation when heat is applied or removed, and so they change color. Liquid crystals have been used in such paints, such as in the thermometer strips and tapes used in aquaria and novelty/promotional thermal cups and straws.
Photochromic materials are used to make eyeglasses and other products. Similar to thermochromic molecules, photochromic molecules change conformation when light energy is applied or removed, and so they change color.
Color-changing paints can also be made by adding halochromic compounds or other organic pigments. One patent cites use of these indicators for wall coating applications for light-colored paints. When the paint is wet it is pink in color but upon drying it regains its original white color. As cited in patent, this property of the paint enabled two or more coats to be applied on a wall properly and evenly. The previous coats having dried would be white whereas the new wet coat would be distinctly pink. Ashland Inc. introduced foundry refractory coatings with similar principle in 2005 for use in foundries.
Electrochromic paints change color in response to an applied electric current. Car manufacturer Nissan has been reportedly working on an electrochromic paint, based on particles of paramagnetic iron oxide. When subjected to an electromagnetic field the paramagnetic particles change spacing, modifying their color and reflective properties. The electromagnetic field would be formed using the conductive metal of the car body. Electrochromic paints can be applied to plastic substrates as well, using a different coating chemistry. The technology involves using special dyes that change conformation when an electric current is applied across the film itself. This new technology has been used to achieve glare protection at the touch of a button in passenger airplane windows.
Color can also change depending on viewing angle, using iridescence, for example, in ChromaFlair.
Art
Main article: Painting
Since the time of the Renaissance, siccative (drying) oil paints, primarily linseed oil, have been the most commonly used kind of paints in fine art applications; oil paint is still common today. However, in the 20th century, new water-borne paints such acrylic paints, entered the market with the development of acrylic and other latex paints. Milk paints (also called casein), where the medium is derived from the natural emulsion that is milk, were common in the 19th century and are still used. Used by the earliest western artists, Egg tempera (where the medium is an emulsion of raw egg yolk mixed with oil) remains in use as well, as are encaustic wax-based paints. Gouache is an opaque variant of watercolor, which is based around varying levels of translucency; both paints use gum arabic as the binder and water as a thinner. Gouache is also known as 'designer color' or 'body color'.
Poster paint is a distemper paint that has been used primarily in the creation of student works, or by children. There are varying brands of poster paint and depending on the brand, the quality will differ. More inexpensive brands will often crack or fade over time if they are left on a poster for an extended time.

Application
Paint can be applied as a solid, a gas, a gaseous suspension (aerosol) or a liquid. Techniques vary depending on the practical or artistic results desired.
As a solid (usually used in industrial and automotive applications), the paint is applied as a very fine powder, then baked at high temperature. This melts the powder and causes it to adhere to the surface. The reasons for doing this involve the chemistries of the paint, the surface itself, and perhaps even the chemistry of the substrate (the object being painted). This is called "powder coating" an object.
In a gas phase application, the coating composition is introduced (if gaseous), vaporized (if liquid) or sublimed (if solid) then deposited on a distant substrate, often under vacuum. These applications are classed broadly into physical vapor deposition methods like sputtering or vacuum deposition, in which solid or liquid starting materials produce a vapor that condenses on the substrate; or chemical vapor deposition methods, in which gaseous starting materials chemically react with the substrate to form a coating. These techniques are especially important in the electronics and optical industries.
As a gaseous suspension, liquid paint is aerosolized by the force of compressed air or by the action of high-pressure compression of the paint itself, and the paint is turned into small droplets that travel to the article to be painted. Alternate methods are airless spray, hot spray, hot airless spray, and any of these with an electrostatic spray included. There are numerous electrostatic methods available. The reasons for doing this include:
- The application mechanism is air and thus no solid object touches the object being painted;
- The distribution of the paint is uniform, so there are no sharp lines;
- It is possible to deliver very small amounts of paint;
- Painting multiple items at once quickly and efficiently;
- A chemical (typically a solvent) can be sprayed along with the paint to dissolve together both the delivered paint and the chemicals on the surface of the object being painted;
- Some chemical reactions in paint involve the orientation of the paint molecules.
- Expression
In a liquid application, paint can be applied by direct application using brushes, paint rollers, blades, scrapers, other instruments, or body parts such as fingers and thumbs.
Rollers generally have a handle that allows for different lengths of poles to be attached, allowing painting at different heights. Generally, roller application requires two coats for an even color. A roller with a thicker nap is used to apply paint on uneven surfaces. Edges are often finished with an angled brush.
- For a flat (matte) finish, a 1/2" nap roller would most likely be used
- For an eggshell finish, a 3/8" nap roller would most likely be used
- For a satin or pearl finish, a 3/8" nap roller would most likely be used
- For a semi-gloss or gloss finish, a 3/16" nap roller would most likely be used
After liquid paint is applied, there is an interval during which it can be blended with additional painted regions (at the "wet edge") called "open time". The open time of an oil or alkyd-based emulsion paint can be extended by adding white spirit, similar glycols such as Dowanol (propylene glycol ether) or open time prolongers. This can also facilitate the mixing of different wet paint layers for aesthetic effect. Latex and acrylic emulsions require the use of drying retardants suitable for water-based coatings. Depending on the quality and type of liquid paint used, the open time will vary. Oil paints for instance are renowned for their open time as oil paints allow for artists to blend the colors for extended periods of time without having to add any extending agents.
Dipping used to be the norm for objects such as filing cabinets, but this has been replaced by high-speed air turbine-driven bells with electrostatic spray. Car bodies are primed using cathodic elephoretic primer, which is applied by charging the body depositing a layer of primer. The unchanged residue is rinsed off and the primer stoved.
Many paints tend to separate when stored, the heavier components settling to the bottom, and require mixing before use. Some paint outlets have machines for mixing the paint by shaking the can vigorously for a few minutes.
The opacity and the film thickness of paint may be measured using a drawdown card.
Water-based paints tend to be the easiest to clean up after use; the brushes and rollers can be cleaned with soap and water.
Proper disposal of left over paint is a challenge. Sometimes it can be recycled: Old paint may be usable for a primer coat or an intermediate coat, and paints of similar chemistry can be mixed to make a larger amount of a uniform color.
To dispose of paint it can be dried and disposed of in the domestic waste stream, provided that it contains no prohibited substances (see container). Disposal of liquid paint usually requires special handling and should be treated as hazardous waste, and disposed of according to local regulations.
Product variants



- Primer is a preparatory coating put on materials before applying the paint itself. The primed surface ensures better adhesion of the paint, thereby increasing the durability of the paint and providing improved protection for the painted surface. Suitable primers also may block and seal stains, or hide a color that is to be painted over.
- Emulsion paints are water-based paints in which the paint material is dispersed in a liquid that consists mainly of water. For suitable purposes this has advantages in fast-drying, low toxicity, low cost, easier application, and easier cleaning of equipment, among other factors.
- Varnish and shellac are in effect paints without pigment; they provide a protective coating without substantially changing the color of the surface, though they can emphasise the colour of the material.
- Wood stain is a type of paint that is formulated to be very "thin", meaning low in viscosity, so that the pigment soaks into a material such as wood rather than remaining in a film on the surface. Stain is mainly dispersed pigment or dissolved dye plus binder material in a solvent. It is designed to add color without providing a surface coating.
- Lacquer is a solvent-based paint or varnish that produces an especially hard, durable finish. Usually it is a rapidly drying formulation.
- Enamel paint is formulated to give an especially hard, usually glossy, finish. Some enamel paints contain fine glass powder or metal flake instead of the color pigments in standard oil-based paints. Enamel paint sometimes is mixed with varnish or urethane to improve its shine and hardness.
- A glaze is an additive used with paint to slow drying time and increase translucency, as in faux painting and for some artistic effects.
- A roof coating is a fluid that sets as an elastic membrane that can stretch without harm. It provides UV protection to polyurethane foam and is widely used in roof restoration.
- Fingerpaints are formulations suitable for application with the fingers; they are popular for use by children in primary school activities.
- Inks are similar to paints, except that they are typically made using finely ground pigments or dyes, and are not designed to leave a thick film of binder. They are used largely for writing, printing, or calligraphy.
- Anti-graffiti coatings are used to defeat the marking of surfaces by graffiti artists or vandals. There are two categories of anti-graffiti coatings: sacrificial and non-bonding:
- Sacrificial coatings are clear coatings that allow the removal of graffiti, usually by washing the surface with high-pressure water that removes the graffiti together with the coating (hence the term "sacrificial"). After removal of the graffiti, the sacrificial coating must be re-applied for continued protection. Such sacrificial protective coatings are most commonly used on natural-looking masonry surfaces, such as statuary and marble walls, and on rougher surfaces that are difficult to clean.
- Non-bonding coatings are clear, high-performance coatings, usually catalyzed polyurethanes, that do not bond strongly to paints used for graffiti. Graffiti on such a surface can be removed with a solvent wash, without damaging either the underlying surface or the protective non-bonding coating. These coatings work best on smooth surfaces, and are especially useful on decorative surfaces such as mosaics or painted murals, which might be expected to suffer harm from high pressure sprays.
- Urine-repellent paint is a very hydrophobic (water-repellent) paint. It has been used by cities and other property owners to deter men from urinating against walls, as the urine splashes back on their shoes, instead of dripping down the wall.
- Anti-climb paint is a non-drying paint that appears normal but is extremely slippery. It is useful on drainpipes and ledges to deter burglars and vandals from climbing them, and is found in many public places. When a person attempts to climb objects coated with the paint, it rubs off onto the climber, as well as making it hard for them to climb.
- Anti-fouling paint, or bottom paint, prevents barnacles and other marine organisms from adhering to the hulls of ships.
- Insulative paint or insulating paint, reduces the rate of thermal transfer through a surface it's applied to. One type of formulation is based on the addition of hollow microspheres to any suitable type of paint.
- Anti-slip paint contains chemicals or grit to increase the friction of a surface so as to decrease the risk of slipping, particularly in wet conditions.
- Road marking paint is specially used to marking and painting road traffic signs and lines, to form a durable coating film on the road surface. It must be fast-drying, provide a thick coating, and resist wear and slipping, especially in wet conditions.
- Luminous paint or luminescent paint is paint that exhibits luminescence. In other words, it gives off visible light through fluorescence, phosphorescence, or radioluminescence.
- Chalk paint is a decorative paint used for home decor to achieve looks such as shabby chic or vintage with home decor.
Finish types
- Flat Finish paint is generally used on ceilings or walls that are in bad shape. This finish is useful for hiding imperfections in walls and it is economical in effectively covering large areas. However, this finish is not easily washable and is subject to staining.
- Matte Finish is generally similar to flat finish, but such paints commonly offer superior washability and coverage. (See Gloss and matte paint.)
- Eggshell Finish has some sheen, supposedly like that of the shell on an egg. This finish provides great washability but is not very effective at hiding imperfections on walls and similar surfaces. The eggshell finish is valued for bathrooms because it is washable and water-repellent, so it tends not to peel in a wet environment.
- Pearl (Satin) Finish is very durable in terms of washability and resistance to moisture, even in comparison to an eggshell finish. It protects walls from dirt, moisture, and stains. Accordingly, it is exceptionally valuable for bathrooms, furniture, and kitchens, but it is shinier than eggshell, so it is even more prone to show imperfections. It has a soft, velvety appearance that is perfect for creating a luxurious feel in any room. Satin paint is also very durable and easy to clean, making it ideal for high-traffic areas like kitchens and bathrooms.
- Semi-Gloss Finish typically is used on trim to emphasize detail and elegance, and to show off woodwork, such as on doors and furniture. It provides a shiny surface and provides good protection from moisture and stains on walls. Its gloss does however emphasize imperfections on the walls and similar surfaces. It is popular in schools and factories where washability and durability are the main considerations.
- High-gloss paint is a highly glossy form of paint that is light reflecting and has a mirror-like look. It pairs well with other finishes. While it is highly durable and easy to clean, high gloss paint is known for obvious visibility of imperfections like scratches and dents.
Failure
The main reasons for paint failure after application on the surface are the applicator and improper treatment of the surface.
Defects or degradation can be attributed to:
- Dilution
- This usually occurs when the dilution of the paint is not done as per manufacturers recommendation. There can be a case of over dilution and under dilution, as well as dilution with the incorrect diluent.
- Contamination
- Foreign contaminants can cause various film defects.
- Peeling/Blistering
- Most commonly due to improper surface treatment before application and inherent moisture/dampness being present in the substrate. The degree of blistering can be assessed according to ISO 4628 Part 2 or ASTM Method D714 (Standard Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Blistering of Paints).
- Chalking
- Chalking is the progressive powdering of the paint film on the painted surface. The primary reason for the problem is polymer degradation of the paint matrix due to exposure of UV radiation in sunshine and condensation from dew. The degree of chalking varies as epoxies react quickly while acrylics and polyurethanes can remain unchanged for long periods. The degree of chalking can be assessed according to International Standard ISO 4628 Part 6 or 7 or American Society of Testing and Materials(ASTM) Method D4214 (Standard Test Methods for Evaluating the Degree of Chalking of Exterior Paint Films).
- Cracking
- Cracking of paint film is due to the unequal expansion or contraction of paint coats. It usually happens when the coats of the paint are not allowed to cure/dry completely before the next coat is applied. The degree of cracking can be assessed according to International Standard ISO 4628 Part 4 or ASTM Method D661 (Standard Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Cracking of Exterior Paints). Cracking can also occur when the paint is applied to a surface that is incompatible or unstable. For instance, clay that hasn't dried completely when painted will cause the paint to crack due to the residual moisture in the clay.
- Erosion
- Erosion is very quick chalking. It occurs due to external agents like air, water etc. It can be evaluated using ASTM Method ASTM D662 (Standard Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Erosion of Exterior Paints). The generation of acid by fungal species can be a significant component of erosion of painted surfaces. The fungus Aureobasidium pullulans is known for damaging wall paints.
Dangers
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in paint are considered harmful to the environment and especially for people who work with them on a regular basis. Exposure to VOCs has been related to organic solvent syndrome, although this relation has been somewhat controversial. The controversial solvent 2-butoxyethanol is also used in paint production. Jurisdictions such as Canada, China, the EU, India, the United States, and South Korea have definitions for VOCs in place, along with regulations to limit the use of VOCs in consumer products such as paint.
In the US, environmental regulations, consumer demand, and advances in technology led to the development of low-VOC and zero-VOC paints and finishes. These new paints are widely available and meet or exceed the old high-VOC products in performance and cost-effectiveness while having significantly less impact on human and environmental health.
Globally, the most widely accepted standard for acceptable levels of VOC in paint is Green Seal’s GS-11 Standards from the US which defines different VOC levels acceptable for different types of paint based on use case and performance requirements.
A polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) was reported (published in 2009) in air samples collected in Chicago, Philadelphia, the Arctic, and several sites around the Great Lakes. PCB is a global pollutant and was measured in the wastewater effluent from paint production. The widespread distribution of PCB suggests volatilization of this compound from surfaces, roofs etc. PCB is present in consumer goods including newspapers, magazines, and cardboard boxes, which usually contain color pigments. Therefore, a hypothesis exists that PCB congeners are present as byproduct in some current commercial pigments.
Research is ongoing to remove heavy metals from paint formulations completely.
Environmental impact of plastics in paints
The ongoing scrutiny of the environmental impact of plastics in paint production is reminiscent of previous investigations into the use of lead in paints. This assessment is driven by accumulating evidence that underscores the role of paint as a significant contributor to microplastic pollution. In 2019, of the 44.4 million tons of globally produced paint, 95 percent was plastic-based. Further, a 2022 study by Environmental Action revealed that approximately 58 percent of the microplastics found in oceans and waterways could be traced back to paint.
Efforts to mitigate this environmental issue have spurred the development and exploration of alternatives to plastic-based paints, such as those derived from linseed, walnut, milk, and limewash. However, their cost is a significant deterrent to the widespread adoption of these environmentally-friendly alternatives. As of 2023, a gallon of plastic-based paint may cost around $20 to $30, however the price for specialized paint, such as graphene and lime, ranges from $34 to $114 per gallon, underlining the financial challenges associated with transitioning from plastic-based paints.
See also
- Adhesive
- Aerosol paint
- Anti-graffiti coating
- Bresle method
- Brush
- Coating
- Density cup
- Distressing
- Environmental issues with paint
- Faux painting
- Painting
- Formulations
- Fresco
- Gloss and matte paint
- Interior radiation control coating
- Lacquer
- List of art media
- NACE International
- Paint adhesion testing
- Paint recycling
- Paint (software)
- Paint stripper
- Powder coating
- Primer
- Road surface marking
- Roof coating
- Soy paint
- Stain-blocking primer
References
- Taggart, Emma (2022-12-14). "Unearth the Colorful History of Paint: From Natural Pigments to Synthetic Hues". My Modern Met. Retrieved 2023-09-23.
- Marchant, Jo (January 2016). "A Journey to the Oldest Cave Paintings in the World". Smithsonian Magazine.
- "Painting 101: Oil or Latex?". HGTV.
- "What's the Ideal Outdoor Temperature Range for Using Exterior Paint?". 29 April 2022.
- Craughwell, Thomas J. (2012). 30,000 years of inventions. New York: Tess Press. ISBN 9781603763240. OCLC 801100207.
- Hillary Mayell (March 31, 2004). "Is Bead Find Proof Modern Thought Began in Africa?". National Geographic News. p. 2. Archived from the original on March 16, 2006. Retrieved May 20, 2016.
Work published in 2001 described 28 bone tools and thousands of pieces of ocher—a mineral used to create paint for body decoration and cave painting—dated at roughly 70,000 years old found in Blombos Cave in South Africa. Two pieces of ocher appear to be marked with abstract lines that could be viewed as artistic expression.
- ^ "Stone Age painting kits found in cave". The Guardian. October 13, 2011. Retrieved May 20, 2016.
- Stephanie Pappa (October 13, 2011). "Oldest Human Paint-Making Studio Discovered in Cave". Live Science. Retrieved October 14, 2011.
- "Painted walls in Orkney 5,000 years old". BBC News. 26 July 2010. Retrieved 10 March 2021.
- "Painted walls". The Ness of Brodgar Excavation. 2011-08-05. Retrieved 2021-03-10.
- Christiansen, Thomas; Cotte, Marine; de Nolf, Wout; Reyes-Herrera, Juan; de Meyer, Steven; Vanmeert, Frederik; Salvadó, Nati; Gonzalez, Victor; Lindelof, Poul Erik; Mortensen, Kell; Ryholt, Kim; Janssens, Koen; Larsen, Sine (October 26, 2020). Faber, Katherine (ed.). "Insights into the Composition of Ancient Egyptian Red and Black Inks on Papyri Achieved by Synchrotron-Based Microanalyses". PNAS. doi:10.1073/pnas.2004534117. hdl:2117/335402. Retrieved 2024-07-10.
- "Oldest Oil Paintings Found in Afghanistan" Archived June 3, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Rosella Lorenzi, Discovery News. Feb. 19, 2008.
- Theophilus Presbyter Book I ch. 25
- Barbera, Giocchino (2005). Antonello da Messina, Sicily's Renaissance Master (exhibition catalogue). New York: Metropolitan Museum of Art Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-11648-9 (online), p. 14
- Ploeger, Rebecca (2013). "Characterization and Stability Issues of Artists' Alkyd Paints" (PDF). New Insights into the Cleaning of Paintings: Proceedings from the Cleaning 2010 International Conference, Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, and Museum Conservation Institute. 3: 89–91.
- ^ Levy, Max G. "This Is the Lightest Paint in the World". Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. Retrieved 2023-03-24.
- ^ Wicks, Zeno W. Jr.; Jones, Frank N.; Pappas, S. Peter; Wicks, Doublas A. (2004). Organic Coatings: Science and Technology (3rd ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-471-69806-7.
- Lambourne, R; Strivens, T A (1999). Paint and Surface Coatings: Theory and Practice (2nd ed.). Abington, Cambridge, England: Woodhead Publishing Limited. p. 6. ISBN 1-85573-348-X.
- "Vermeer's Palette: The Anatomy of Pigment and Binder". www.essentialvermeer.com. Retrieved 2015-10-21.
- Baird, Colin; Cann, Michael (2005). CourseSmart International E-Book for Environmental Chemistry. W. H. Freeman. ISBN 9780716748779.
- Baghdachi, J. "Polymer Systems and Film Formation Mechanisms in High Solids, Powder and UV Cure Systems" (PDF). Society of Wood Science and Technology. Retrieved 2016-01-13.
- "Water-based Alchemy". Archived from the original on August 29, 2012. Retrieved August 11, 2012.
- Gite, V. V., et al. "Polyurethane coatings using trimer of isophorone diisocyanate." (2004).
- Berendsen, A. M., & Berendsen, A. M. (1989). Marine painting manual. London: Graham & Trotman. ISBN 1-85333-286-0 p. 114.
- "Powder Coating 101". Retrieved April 26, 2024.
- "Definitions of a Dye and a Pigment". April 26, 2024.
- "Four Important Functional Pigments". April 26, 2024.
- Gürses, Ahmet; Açıkyıldız, Metin; Güneş, Kübra; Gürses, M. Sadi (2016-05-04). Dyes and Pigments. Springer. ISBN 9783319338927.
- "Archives". Los Angeles Times. 14 October 2011.
- "MIO Coatings – What Are They?" (PDF). Dulux Protective Coatings. 2009.
- "ISO 10601:2007". Micaceous iron oxide pigments. International Organization for Standardization.
- "CICN Groups and Sub-Groups". April 26, 2024.
- frpdesigns.com Archived 2010-02-11 at the Wayback Machine, "Formulations, Fundamentals, Manipulation, Calculation and Data Management" p. 61.
- Bramley, Christopher Sinjin. "Colour changing paint" (PDF). European Patent Application EP1400574. European Patent Office.
- "Dramatic color change featured". New Materials International. Archived from the original on 2012-04-25. Retrieved 2011-11-03.
- Horvath, Lee. "Coatings Go Beyond Appearance to Provide Quality Control". Foundry Technology. Foundry Management & Technology.
- "DailyTech - Nissan Develops Color Changing Paint for Vehicles". Archived from the original on 2011-07-08. Retrieved 2008-03-19.
- "PVD vs CVD: Differences in Thin Film Deposition Techniques". Retrieved April 26, 2024.
- "Selecting the Right Paint Roller". Aubuchon Hardware. Archived from the original on 2012-04-20. Retrieved 2012-05-06.
- ""Safe Use, Storage and Disposal of Paint"". Archived from the original on 2007-02-24. Retrieved 2006-11-01.
- ""Storage and Disposal of Paint Facts"". Archived from the original on November 18, 2007.
- Huggler, Justin (2015-03-04). "Hamburg fights back against urination on streets with walls that 'pee back'". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 2020-04-02.
- Johnson, Lizzie (2015-07-31). "S.F.'s new urine-resistant walls seem to be keeping things dry". SFGate. Retrieved 2020-04-02.
- "'Anti-pee' walls will splash offenders". BBC News. 2015-12-17. Retrieved 2020-04-02.
- "road marking paint". Archived from the original on 2015-02-15. Retrieved 2014-09-15.
- "What is a Satin Finish? Stunning Uses in Your Home". 27 May 2022.
- "Paint Finish and Sheen Information; Info on Satin, Eggshell, Matte, and Other Paint Finishes." Professional Painting Contractor. Professional Painters, 2011. Web. 07 Apr. 2012. <http://www.painter-pros.com/finishes.php Archived 2012-09-06 at archive.today>.
- Mendelsohn, Hadley (2019-03-13). "Designers Are Going Nuts Over This Super Glossy Paint". House Beautiful. Retrieved 2019-04-11.
- Bayliss, D.A.; Deacon, D.H. (2002). Steelwork corrosion control (2nd ed.). London: Spon. pp. 13.6.6 Chalking. ISBN 978-0-415-26101-2.
- Xiaohui Wang; Ling Wang (2006). "Measures and Test Techniques for Fungus Resistance to Aircraft Materials and Equipment" (PDF).
- John W. Taylor; Joey Spatafora; Mary Berbee (1996). "Ascomycota".
- SPURGEON A (2006). "Watching Paint Dry: Organic Solvent Syndrome in late-Twentieth-Century Britain". Medical History. 50 (2): 167–188. doi:10.1017/s002572730000973x. PMC 1472097. PMID 16711296.
- "Ethylene Glycol Mono-N-Butyl Ether". National Library of Medicine HSDB. Retrieved 2014-03-14.
- "South Korea expands VOC controls and tightens limits in paint". chemicalwatch.com. Retrieved 2021-03-27.
- "Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) and Consumer Products Regulations". www.chemsafetypro.com. Retrieved 2021-03-27.
- Chang, John C. S.; Fortmann, Roy; Roache, Nancy; Lao, Huei-Chen (1999). "Evaluation of Low-VOC Latex Paints". Indoor Air. 9 (4): 253–258. Bibcode:1999InAir...9..253C. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0668.1999.00004.x. ISSN 0905-6947. PMID 10649858.
- Hu, D; Hornbuckle, KC (2010). "Inadvertent polychlorinated biphenyls in commercial paint pigments". Environ Sci Technol. 44 (8): 2822–7. Bibcode:2010EnST...44.2822H. doi:10.1021/es902413k. PMC 2853905. PMID 19957996.
- Puthran, Dayanand; Patil, Dilip (2023-01-01). "Usage of heavy metal-free compounds in surface coatings". Journal of Coatings Technology and Research. 20 (1): 87–112. doi:10.1007/s11998-022-00648-4. ISSN 1935-3804. S2CID 251771272.
- Rudgard, Olivia (2023-07-19). "Your Basic House Paints Have an Environmental Plastic Problem". Bloomberg News. Retrieved 2023-07-20.
Further reading
- Bently, J.; Turner, G.P.A. (1997). Introduction to Paint Chemistry and Principles of Paint Technology. Unk. ISBN 0-412-72320-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Talbert, Rodger (2007). Paint Technology Handbook. Grand Rapids, Michigan, USA. ISBN 978-1-57444-703-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Woodbridge, Paul R., ed. (1991). Principles of Paint Formulation. Unk. ISBN 0-412-02951-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)


