| |

| |
 Coloured water (top) and perfluoroheptane (bottom). Perfluoroheptane is hydrophobic and is denser than water, so it sinks to the bottom and the animals pictured cannot penetrate it. | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
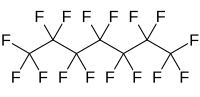
| Preferred IUPAC name Hexadecafluoroheptane | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.812 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7F16 |
| Molar mass | 388.051 g·mol |
| Appearance | clear liquid |
| Density | 1.706 g/cm |
| Boiling point | 80~82°C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Perfluoroheptane, C7F16, (usually referring to the straight chain molecule called n-perfluoroheptane) is a perfluorocarbon. It is hydrophobic (water-insoluble) and oleophobic (oil-insoluble). It is used in deacidification of paper as a medium carrying powdered magnesium oxide.
References
- ^ "Perfluoro-n-heptane Safety Data Sheet" (PDF). Exfluor Research Corporation. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- Pubchem (USG) page on perfluoroheptane
- Porck, Henk J. (1996). Mass Deacidification: An Update on Possibilities and Limitations (PDF). Washington D.C.: Commission on Preservation and Access. p. 16. ISBN 1887334521. Retrieved 2015-12-09.
This article about an organic halide is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |