
| Geometry | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Projecting a sphere to a plane Projecting a sphere to a plane | ||||||||||
| Branches | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Zero-dimensional | ||||||||||
| One-dimensional | ||||||||||
Two-dimensional
|
||||||||||
| Three-dimensional | ||||||||||
| Four- / other-dimensional | ||||||||||
| Geometers | ||||||||||
by name
|
||||||||||
by period
|
||||||||||
In geometry, the circumference (from Latin circumferens, meaning "carrying around") is the perimeter of a circle or ellipse. The circumference is the arc length of the circle, as if it were opened up and straightened out to a line segment. More generally, the perimeter is the curve length around any closed figure. Circumference may also refer to the circle itself, that is, the locus corresponding to the edge of a disk. The circumference of a sphere is the circumference, or length, of any one of its great circles.
Circle
The circumference of a circle is the distance around it, but if, as in many elementary treatments, distance is defined in terms of straight lines, this cannot be used as a definition. Under these circumstances, the circumference of a circle may be defined as the limit of the perimeters of inscribed regular polygons as the number of sides increases without bound. The term circumference is used when measuring physical objects, as well as when considering abstract geometric forms.
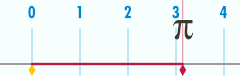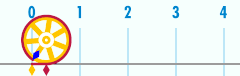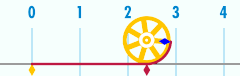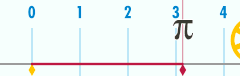

Relationship with π
The circumference of a circle is related to one of the most important mathematical constants. This constant, pi, is represented by the Greek letter Its first few decimal digits are 3.141592653589793... Pi is defined as the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter
Or, equivalently, as the ratio of the circumference to twice the radius. The above formula can be rearranged to solve for the circumference:
The ratio of the circle's circumference to its radius is equivalent to . This is also the number of radians in one turn. The use of the mathematical constant π is ubiquitous in mathematics, engineering, and science.
In Measurement of a Circle written circa 250 BCE, Archimedes showed that this ratio (written as since he did not use the name π) was greater than 310/71 but less than 31/7 by calculating the perimeters of an inscribed and a circumscribed regular polygon of 96 sides. This method for approximating π was used for centuries, obtaining more accuracy by using polygons of larger and larger number of sides. The last such calculation was performed in 1630 by Christoph Grienberger who used polygons with 10 sides.
Ellipse

Some authors use circumference to denote the perimeter of an ellipse. There is no general formula for the circumference of an ellipse in terms of the semi-major and semi-minor axes of the ellipse that uses only elementary functions. However, there are approximate formulas in terms of these parameters. One such approximation, due to Euler (1773), for the canonical ellipse, is Some lower and upper bounds on the circumference of the canonical ellipse with are:
Here the upper bound is the circumference of a circumscribed concentric circle passing through the endpoints of the ellipse's major axis, and the lower bound is the perimeter of an inscribed rhombus with vertices at the endpoints of the major and minor axes.
The circumference of an ellipse can be expressed exactly in terms of the complete elliptic integral of the second kind. More precisely, where is the length of the semi-major axis and is the eccentricity
See also
- Arc length – Distance along a curve
- Area – Size of a two-dimensional surface
- Circumgon – Geometric figure which circumscribes a circle
- Isoperimetric inequality – Geometric inequality applicable to any closed curve
- Perimeter-equivalent radius – Radius of a circle or sphere equivalent to a non-circular or non-spherical objectPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
Notes
- The Greek letter 𝜏 (tau) is sometimes used to represent this constant. This notation is accepted in several online calculators and many programming languages.
References
- Bennett, Jeffrey; Briggs, William (2005), Using and Understanding Mathematics / A Quantitative Reasoning Approach (3rd ed.), Addison-Wesley, p. 580, ISBN 978-0-321-22773-7
- Jacobs, Harold R. (1974), Geometry, W. H. Freeman and Co., p. 565, ISBN 0-7167-0456-0
- Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A000796". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.
- "Mathematics Essentials Lesson: Circumference of Circles". openhighschoolcourses.org. Retrieved 2024-12-02.
- "Supported Functions". help.desmos.com. Archived from the original on 2023-03-26. Retrieved 2024-10-21.
- "math — Mathematical functions". Python 3.7.0 documentation. Archived from the original on 2019-07-29. Retrieved 2019-08-05.
- "Math class". Java 19 documentation.
- "std::f64::consts::TAU - Rust". doc.rust-lang.org. Archived from the original on 2023-07-18. Retrieved 2024-10-21.
- Katz, Victor J. (1998), A History of Mathematics / An Introduction (2nd ed.), Addison-Wesley Longman, p. 109, ISBN 978-0-321-01618-8
- Jameson, G.J.O. (2014). "Inequalities for the perimeter of an ellipse". Mathematical Gazette. 98 (499): 227–234. doi:10.2307/3621497. JSTOR 3621497. S2CID 126427943.
- Almkvist, Gert; Berndt, Bruce (1988), "Gauss, Landen, Ramanujan, the arithmetic-geometric mean, ellipses, π, and the Ladies Diary", American Mathematical Monthly, 95 (7): 585–608, doi:10.2307/2323302, JSTOR 2323302, MR 0966232, S2CID 119810884


 to its
to its 


 . This is also the number of
. This is also the number of  since he did not use the name π) was greater than 310/71 but less than 31/7 by calculating the perimeters of an inscribed and a circumscribed regular polygon of 96 sides. This method for approximating π was used for centuries, obtaining more accuracy by using polygons of larger and larger number of sides. The last such calculation was performed in 1630 by
since he did not use the name π) was greater than 310/71 but less than 31/7 by calculating the perimeters of an inscribed and a circumscribed regular polygon of 96 sides. This method for approximating π was used for centuries, obtaining more accuracy by using polygons of larger and larger number of sides. The last such calculation was performed in 1630 by  is
is
 Some lower and upper bounds on the circumference of the canonical ellipse with
Some lower and upper bounds on the circumference of the canonical ellipse with  are:
are:



 is the circumference of a
is the circumference of a  is the
is the  where
where  is the length of the semi-major axis and
is the length of the semi-major axis and  is the eccentricity
is the eccentricity 