
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (1E)-N,N′-Bis(4-ethoxyphenyl)ethanimidamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C18H22N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 298.386 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Phenacaine, also known as holocaine, is a local anesthetic. It is approved for ophthalmic use.
Synthesis
The synthesis of phenacaine begins with the condensation of p-phenetidine (1) with triethyl orthoacetate (2) to afford the imino ether (a Pinner salt, 3). Reaction of that intermediate with a second equivalent of the aniline results (4) in a net displacement of ethanol, probably by an addition-elimination scheme, producing the amidine, phenacaine (5).
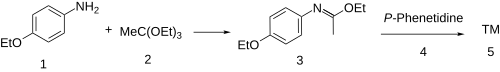
In the patented synthesis, phenacetin was used as precursor. Treatment with phosphorus trichloride (PCl3) gave the enol chloride, and reaction of this intermediate with p-phenetidine then completed the synthesis of phenacaine.
References
- "Holocaine Hydrochloride".
- Merck Index, 1985
- DeWolfe, Robert H. (1962). "Reactions of Aromatic Amines with Aliphatic Ortho Esters. A Convenient Synthesis of Alkyl N-Arylimidic Esters". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 27 (2): 490–493. doi:10.1021/jo01049a036.
- DE 79868, Ernst Taeuber, issued 1894
| Local anesthetics (primarily sodium channel blockers) (N01B) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esters by acid |
| ||||||
| Amides | |||||||
| Combinations | |||||||
| |||||||
This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |