Medical condition
| Rosacea | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Acne rosacea |
 | |
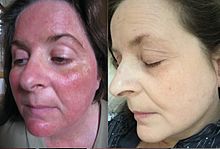
| Rosacea over the cheeks and nose | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Facial redness, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels |
| Complications | Rhinophyma |
| Usual onset | 30–50 years old |
| Duration | Long term |
| Types | Erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous, ocular |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risk factors | Family history |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms |
| Differential diagnosis | Acne, perioral dermatitis, seborrhoeic dermatitis, dermatomyositis, lupus |
| Medication | Antibiotics either by mouth or applied to the skin |
| Frequency | ~5% |
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, enlarged nose may occur in severe disease, a condition known as rhinophyma.
The cause of rosacea is unknown. Risk factors are believed to include a family history of the condition. Factors that may potentially worsen the condition include heat, exercise, sunlight, cold, spicy food, alcohol, menopause, psychological stress, or steroid cream on the face. Diagnosis is based on symptoms.
While not curable, treatment usually improves symptoms. Treatment is typically with metronidazole, doxycycline, minocycline, or tetracycline. When the eyes are affected, azithromycin eye drops may help. Other treatments with tentative benefit include brimonidine cream, ivermectin cream, and isotretinoin. Dermabrasion or laser surgery may also be used. The use of sunscreen is typically recommended.
Rosacea affects between 1% and 10% of people. Those affected are most often 30 to 50 years old and female. Fair-skinned people seem to be more commonly affected. The condition was described in The Canterbury Tales in the 1300s, and possibly as early as the 200s BC by Theocritus.
Signs and symptoms

Rosacea typically begins with reddening (flushing) of the skin in symmetrical patches near the center of the face. Common signs can depend on age and sex: flushing and red swollen patches are common in the young, small and visible dilated blood vessels in older individuals, and swelling of the nose is common in men. Other signs include lumps on the skin (papules or pustules) and swelling of the face. Many people experience stinging or burning pain and rarely itching.
Skin problems tend to be aggravated by particular trigger factors, that differ for different people. Common triggers are ultraviolet light, heat, cold, or certain foods or beverages.
Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea
Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea rosacea (also known as "vascular rosacea") is characterized by prominent history of prolonged (over 10 minutes) flushing reaction to various stimuli, such as emotional stress, hot drinks, alcohol, spicy foods, exercise, cold or hot weather, or hot baths and showers.
Glandular rosacea
In glandular rosacea, men with thick sebaceous skin predominate, a disease in which the papules are edematous, and the pustules are often 0.5 to 1.0 cm in size, with nodulocystic lesions often present.
Cause
The exact cause of rosacea is unknown. Triggers that cause episodes of flushing and blushing play a part in its development. Exposure to temperature extremes, strenuous exercise, heat from sunlight, severe sunburn, stress, anxiety, cold wind, and moving to a warm or hot environment from a cold one, such as heated shops and offices during the winter, can each cause the face to become flushed. Certain foods and drinks can also trigger flushing, such as alcohol, foods and beverages containing caffeine (especially hot tea and coffee), foods high in histamines, and spicy foods.
Medications and topical irritants have also been known to trigger rosacea flares. Some acne and wrinkle treatments reported to cause rosacea include microdermabrasion and chemical peels, as well as high dosages of isotretinoin, benzoyl peroxide, and tretinoin.
Steroid-induced rosacea is caused by the use of topical steroids. These steroids are often prescribed for seborrheic dermatitis. Dosage should be slowly decreased and not immediately stopped to avoid a flare-up.
Cathelicidins
In 2007, Richard Gallo and colleagues noticed that patients with rosacea had high levels of cathelicidin, an antimicrobial peptide, and elevated levels of stratum corneum tryptic enzymes (SCTEs). Antibiotics have been used in the past to treat rosacea, but they may only work because they inhibit some SCTEs.
Demodex folliculitis and Demodex mites
Studies of rosacea and Demodex mites have revealed that some people with rosacea have increased numbers of the mite, especially those with steroid-induced rosacea. Demodex folliculitis (demodicidosis, also known as "mange" in animals) is a condition that may have a "rosacea-like" appearance.
A 2007, National Rosacea Society-funded study demonstrated that Demodex folliculorum mites may be a cause or exacerbating factor in rosacea. The researchers identified Bacillus oleronius as a distinct bacterium associated with Demodex mites. When analyzing blood samples using a peripheral blood mononuclear cell proliferation assay, they discovered that B. oleronius stimulated an immune system response in 79 percent of 22 patients with subtype 2 (papulopustular) rosacea, compared with only 29% of 17 subjects without the disorder. They concluded, "The immune response results in inflammation, as evident in the papules (bumps) and pustules (pimples) of subtype 2 rosacea. This suggests that the B. oleronius bacteria found in the mites could be responsible for the inflammation associated with the condition."
Intestinal bacteria
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) was demonstrated to have greater prevalence in rosacea patients and treating it with locally acting antibiotics led to rosacea lesion improvement in two studies. Conversely in rosacea patients who were SIBO negative, antibiotic therapy had no effect. The effectiveness of treating SIBO in rosacea patients may suggest that gut bacteria play a role in the pathogenesis of rosacea lesions.
Diagnosis
Most people with rosacea have only mild redness and are never formally diagnosed or treated. No test for rosacea is known. In many cases, simple visual inspection by a trained health-care professional is sufficient for diagnosis. In other cases, particularly when pimples or redness on less-common parts of the face is present, a trial of common treatments is useful for confirming a suspected diagnosis. The disorder can be confused or co-exist with acne vulgaris or seborrheic dermatitis. The presence of a rash on the scalp or ears suggests a different or co-existing diagnosis because rosacea is primarily a facial diagnosis, although it may occasionally appear in these other areas.
Classification

Four rosacea subtypes exist, and a patient may have more than one subtype:
- Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea exhibits permanent redness (erythema) with a tendency to flush and blush easily. Also small, widened blood vessels visible near the surface of the skin (telangiectasias) and possibly intense burning, stinging, and itching are common. People with this type often have sensitive skin. Skin can also become very dry and flaky. In addition to the face, signs can also appear on the ears, neck, chest, upper back, and scalp.
- Papulopustular rosacea presents with some permanent redness with red bumps (papules); some pus-filled pustules can last 1–4 days or longer. This subtype is often confused with acne.
- Phymatous rosacea is most commonly associated with rhinophyma, an enlargement of the nose. Signs include thickening skin, irregular surface nodularities, and enlargement. Phymatous rosacea can also affect the chin (gnathophyma), forehead (metophyma), cheeks, eyelids (blepharophyma), and ears (otophyma). Telangiectasias may be present.
- In ocular rosacea, affected eyes and eyelids may appear red due to telangiectasias and inflammation, and may feel dry, irritated, or gritty. Other symptoms include foreign-body sensations, itching, burning, stinging, and sensitivity to light. Eyes can become more susceptible to infection. About half of the people with subtypes 1–3 also have eye symptoms. Keratitis is a rare complication which is characterized by blurry vision and vision loss as the cornea is affected.
Variants
Variants of rosacea include:
- Pyoderma faciale, also known as rosacea fulminans, is a conglobate, nodular disease that arises abruptly on the face.
- Rosacea conglobata is a severe rosacea that can mimic acne conglobata, with hemorrhagic nodular abscesses and indurated plaques.
- Phymatous rosacea is a cutaneous condition characterized by overgrowth of sebaceous glands. Phyma is Greek for swelling, mass, or bulb, and these can occur on the face and ears.
Treatment
The type of rosacea that a person has will indicate the choice of treatment. Mild cases are often not treated at all, or are simply covered up with normal cosmetics.
Therapy for the treatment of rosacea is not curative, and is best measured in terms of reduction in the amount of facial redness and inflammatory lesions, a decrease in the number, duration, and intensity of flares, and concomitant symptoms of itching, burning, and tenderness. The two primary modalities of rosacea treatment are topical and oral antibiotic agents. Laser therapy has also been classified as a form of treatment. While medications often produce a temporary remission of redness within a few weeks, the redness typically returns shortly after treatment is suspended. Long-term treatment, usually 1–2 years, may result in permanent control of the condition for some patients. Lifelong treatment is often necessary, although some cases resolve after a while and go into a permanent remission. Other cases, if left untreated, worsen over time. Some people have also reported better results after changing diet. This is not confirmed by medical studies, even though some studies relate the histamine production to outbreak of rosacea.
Behavior
Certain behavioral changes may improve the symptoms of rosacea or help to prevent exacerbations. Keeping a symptoms diary to document potential symptom triggers and avoiding those triggers is recommended. Common exacerbating triggers include ultraviolet light and irritant cosmetics, therefore it is recommended that those with rosacea wear sunscreen (with a sun factor protection (SPF) of 30 or greater) and avoid cosmetics. If using cosmetics or makeup is desired, then oil free foundation and concealer should be used. Skin astringents, products that can dry the skin and impair the skin barrier, including products with alcohol, menthol, peppermint, camphor, or eucalyptus oil, should generally be avoided. People should avoid using exfoliating skin scrubs, cosmetics or soaps containing sodium laureth sulfate, or waterproof makeup to the affected area as these products can compromise the skin barrier protection and be difficult to remove. Using soap-free cleansers and non-oily moisturizers are preferred if used on the affected area. Many skin care products have been specifically formulated for those with sensitive skin or for those with conditions such as rosacea. Ocular rosacea may be treated with daily gentle eyelid washing using warm water, and artificial tears to lubricate the eye.
Managing pre-trigger events such as prolonged exposure to cool environments can directly influence warm-room flushing.
Medications
Medications with good evidence include topical metronidazole, ivermectin and azelaic acid. Good evidence medications taken by mouth include brimonidine, and doxycycline and isotretinoin. Lesser evidence supports tetracycline by mouth. Isotretinoin and tetracycline antibiotics, which may be used in more severe cases of inflammatory rosacea, are absolutely contraindicated in women who are pregnant, may become pregnant or lactating as they are highly teratogenic (associated with birth defects). Contraception is required for women of child bearing age who are using these medications.
Metronidazole is thought to act through anti-inflammatory mechanisms, while azelaic acid is thought to decrease cathelicidin production. Oral antibiotics of the tetracycline class such as doxycycline, minocycline, and oxytetracycline are also commonly used and thought to reduce papulopustular lesions through anti-inflammatory actions rather than through their antibacterial capabilities.
Topical minocycline applied as a foam is a newer treatment option for rosacea that the FDA has approved. Minocycline shows a targeted approach for managing inflammatory lesions of rosacea while minimizing systemic side effects commonly associated with oral antibiotic use. It is available in foam formulation and is applied to the affected areas once daily. Minocycline belongs to the tetracycline family of antibiotics and exhibits antimicrobial properties and anti-inflammatory activity, similar to other members of this class, such as doxycycline. Topical minocycline reduces inflammatory lesions associated with rosacea; however, rare adverse events such as folliculitis have been reported.
Topical metronidazole is a commonly used treatment for rosacea; it is available in various formulations such as creams, gels, or lotions and applied to clean, dry skin once or twice daily. Topical metronidazole has been shown to effectively reduce inflammatory lesions and perilesional erythema associated with rosacea by inhibiting both microbial growth and pro-inflammatory mediators generated by neutrophils. Benefits of topical metronidazole include its effectiveness in reducing symptoms, extensive clinical experience supporting its use, and generally good tolerability with minimal systemic side effects; still, some patients may experience mild local irritation upon initial use, and it may have limited impact on persistent facial redness (erythema).
Topical azelaic acid is available in gel or cream formulations; it exerts its effects by reducing inflammation through its activity on the cathelicidin pathway, which is upregulated in rosacea-affected skin; it also reduces inflammatory lesions and improves overall symptoms of rosacea; it has been well-studied and shown to be effective in clinical trials; still, some patients may experience mild local irritation during the first few weeks of use.
Using alpha-hydroxy acid peels may help relieve redness caused by irritation, and reduce papules and pustules associated with rosacea.
Oral Beta-blockers are often used for those with flushing due to rosacea. These include nadolol, propranolol or carvedilol. The possible adverse reactions of the oral beta-blockers include low blood pressure, low heart rate or dizziness. The oral α-2 adrenergic receptor agonist clonidine can also be used for flushing symptoms. The flushing and blushing that typically accompany rosacea may also be treated with the topical application of alpha agonists such as brimonidine which has vasoconstrictor activity and achieves maximal symptom improvement 3–6 hours after application, other topicals used for flushing or erythema include oxymetazoline or xylometazoline.
Topical ivermectin is a treatment option for rosacea that targets Demodex mites, which are associated with inflammation in the skin of patients with rosacea; the cream is applied once daily to clean, dry skin. Topical ivermectin has been shown to reduce Demodex mite density and improve cutaneous inflammatory markers in clinical studies; overall, it decreases Demodex mite density and improves the symptoms of inflammation associated with rosacea; however, some patients may experience transient burning or itching upon application. Topical ivermectin offers a targeted approach for managing rosacea by addressing the role of Demodex mites in the disease process. A review found that ivermectin was more effective than alternatives for treatment of papulopustular acne rosacea. An ivermectin cream has been approved by the FDA, as well as in Europe, for the treatment of inflammatory lesions of rosacea. The treatment is based upon the hypothesis that parasitic mites of the genus Demodex play a role in rosacea. In a clinical study, ivermectin reduced lesions by 83% over 4 months, as compared to 74% under a metronidazole standard therapy. Quassia amara extract at 4% demonstrated to have clinical efficacy for rosacea. When compared to metronidazole 0.75% as usual care in a randomized, double-blinded clinical trial, Quassia amara extract at 4% demonstrated earlier onset of action, including improvement in telangiectasia, flushing, and papules. Quassia amara showed a sustained reduction of symptoms at 42 days of treatment.
Cyclosporin eye drops have been shown to reduce symptoms in those with ocular rosacea. Cyclosporin should not be used in those with an active ocular infection. Other options include topical metronidazole cream or topical fusidic acid applied to the eyelids, or oral doxycycline in more severe cases of ocular rosacea. If papules and pustules persist, then sometimes isotretinoin can be prescribed.
Systemic doxycycline modified-release capsules are commonly used for the treatment of rosacea. The capsules are taken orally once daily, usually in a low dose, to achieve anti-inflammatory effects. Doxycycline acts by inhibiting inflammation and reducing the production of reactive oxygen species associated with rosacea symptoms. The benefits of systemic doxycycline include its effectiveness in reducing inflammatory lesions, improving erythema, and controlling symptoms related to ocular involvement in rosacea patients; it is also well-tolerated at lower doses compared to traditional higher-dose regimens used for other indications. However, potential cons include gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea or abdominal pain, photosensitivity reactions that require sun protection measures during treatment, and rare instances of antibiotic-associated diarrhea or bacterial resistance development with long-term use.
Encapsulated benzoyl peroxide (E-BPO) cream, a newly FDA-approved topical agent for inflammatory lesions of rosacea, utilizes porous silica microcapsule technology to slow the absorption of benzoyl peroxide and diminish potential irritation.
Laser
Evidence for the use of laser and intense pulsed-light therapy in rosacea is poor.
Outcomes
The highly visible nature of rosacea symptoms are often psychologically challenging for those affected. People with rosacea can experience issues with self-esteem, socializing, and changes to their thoughts, feelings, and coping mechanisms.
Epidemiology
Rosacea affects around 5% of people worldwide. Incidence varies by ethnicity, and is particularly prevalent in those with Celtic heritage. Men and women are equally likely to develop rosacea.
See also
References
- Sand M, Sand D, Thrandorf C, Paech V, Altmeyer P, Bechara FG (4 June 2010). "Cutaneous lesions of the nose". Head & Face Medicine. 6: 7. doi:10.1186/1746-160X-6-7. PMC 2903548. PMID 20525327.
- ^ Tüzün Y, Wolf R, Kutlubay Z, Karakuş O, Engin B (February 2014). "Rosacea and rhinophyma". Clinics in Dermatology. 32 (1): 35–46. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.05.024. PMID 24314376.
- ^ "Questions and Answers about Rosacea". www.niams.nih.gov. April 2016. Archived from the original on 13 May 2017. Retrieved 5 June 2017.
- ^ van Zuuren EJ, Fedorowicz Z (September 2015). "Interventions for rosacea: abridged updated Cochrane systematic review including GRADE assessments". The British Journal of Dermatology. 173 (3): 651–62. doi:10.1111/bjd.13956. PMID 26099423. S2CID 41303286.
- "Rosacea First choice treatments". Prescrire International. 182: 126–128. May 2017. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
- Rainer BM, Kang S, Chien AL (2017). "Rosacea: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment". Dermatoendocrinol. 9 (1): e1361574. doi:10.1080/19381980.2017.1361574. PMC 5821167. PMID 29484096.
- Zouboulis CC, Katsambas AD, Kligman AM (2014). Pathogenesis and Treatment of Acne and Rosacea. Springer. p. XXV. ISBN 978-3-540-69375-8. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
- Schachner LA, Hansen RC (2011). Pediatric Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 827. ISBN 978-0-7234-3665-2. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
- name="JAmAcadDermatol2004-Wilkin">Wilkin J, Dahl M, Detmar M, Drake L, Liang MH, Odom R, Powell F (2004). "Standard grading system for rosacea: report of the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee on the classification and staging of rosacea" (PDF). J Am Acad Dermatol. 50 (6): 907–12. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.01.048. PMID 15153893. Archived from the original (PDF reprint) on 27 February 2007.
- ^ Buddenkotte J, Steinhoff M (2018). "Recent advances in understanding and managing rosacea". F1000Res. 7: 1885. doi:10.12688/f1000research.16537.1. PMC 6281021. PMID 30631431.
- ^ Rapini, Ronald P., Bolognia, Jean L., Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ^ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. Page 245. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Del Rosso JQ (October 2014). "Management of cutaneous rosacea: emphasis on new medical therapies". Expert Opin Pharmacother. 15 (14): 2029–38. doi:10.1517/14656566.2014.945423. PMID 25186025.
- "Rosacea". DermNet, New Zealand Dermatological Society. Archived from the original on 7 December 2010. Retrieved 3 February 2011.
- ^ Kenshi Yamasaki, Anna Di Nardo, Antonella Bardan, Masamoto Murakami, Takaaki Ohtake, Alvin Coda, Robert A Dorschner, Chrystelle Bonnart, Pascal Descargues, Alain Hovnanian, Vera B Morhenn, Richard L Gallo (August 2007). "Increased serine protease activity and cathelicidin promotes skin inflammation in rosacea". Nature Medicine. 13 (8): 975–80. doi:10.1038/nm1616. PMID 17676051. S2CID 23470611.
- Baima B, Sticherling M (2002). "Demodicidosis revisited". Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 82 (1): 3–6. doi:10.1080/000155502753600795. PMID 12013194.
- ^ Lacey N, Delaney S, Kavanagh K, Powell FC (2007). "Mite-related bacterial antigens stimulate inflammatory cells in rosacea" (PDF). British Journal of Dermatology. 157 (3): 474–481. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08028.x. PMID 17596156. S2CID 8057780.
- Elizabeth Lazaridou, Christina Giannopoulou, Christina Fotiadou, Eustratios Vakirlis, Anastasia Trigoni, Demetris Ioannides (November 2010). "The potential role of microorganisms in the development of rosacea". JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft. 9 (1): 21–25. doi:10.1111/j.1610-0387.2010.07513.x. PMID 21059171. S2CID 23494211.
- Celiker H, Toker E, Ergun T, Cinel L (2017). "An unusual presentation of ocular rosacea". Arquivos Brasileiros de Oftalmologia. 80 (6): 396–398. doi:10.5935/0004-2749.20170097. hdl:11424/241569. ISSN 0004-2749. PMID 29267579.
- Wilkin J, Dahl M, Detmar M, Drake L, Liang MH, Odom R, Powell F (2004). "Standard grading system for rosacea: report of the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee on the classification and staging of rosacea" (PDF). J Am Acad Dermatol. 50 (6): 907–12. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.01.048. PMID 15153893. Archived from the original (PDF reprint) on 27 February 2007.
- Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. ISBN 1-4160-3185-5.
- "What Rosacea Looks Like". Archived from the original on 4 February 2013. Retrieved 30 January 2013.
- Jansen T, Plewig G (1998). "Clinical and histological variants of rhinophyma, including nonsurgical treatment modalities". Facial Plast Surg. 14 (4): 241–53. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1064456. PMID 11816064. S2CID 962065.
- ^ Vieira AC, Mannis MJ (December 2013). "Ocular rosacea: common and commonly missed". J Am Acad Dermatol. 69 (6 (Suppl 1)): S36–41. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.04.042. PMID 24229635.
- ^ van Zuuren EJ (2 November 2017). "Rosacea". New England Journal of Medicine. 377 (18): 1754–1764. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1506630. PMID 29091565.
- ^ Freedberg, et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.
- van Zuuren EJ, Fedorowicz Z, Tan J, van der Linden M, Arents B, Carter B, Charland L (July 2019). "Interventions for rosacea based on the phenotype approach: an updated systematic review including GRADE assessments". The British Journal of Dermatology. 181 (1): 65–79. doi:10.1111/bjd.17590. PMC 6850438. PMID 30585305.
- ^ Noah Scheinfeld, Thomas Berk (January 2010). "A Review of the Diagnosis and Treatment of Rosacea". Postgraduate Medicine. 122 (1): 139–43. doi:10.3810/pgm.2010.01.2107. PMID 20107297. S2CID 22914205. Archived from the original on 5 January 2011.
- ^ Culp B, Scheinfeld N (January 2009). "Rosacea: a review". P&T. 34 (1): 38–45. PMC 2700634. PMID 19562004.
- Huynh TT (2013). "Burden of Disease: The Psychosocial Impact of Rosacea on a Patient's Quality of Life". American Health & Drug Benefits. 6 (6): 348–354. ISSN 1942-2962. PMC 4031723. PMID 24991368.
- Searle T, Ali FR, Carolides S, Al-Niaimi F (2021). "Rosacea and Diet: What is New in 2021?". The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology. 14 (12): 49–54. ISSN 1941-2789. PMC 8794493. PMID 35096255.
- Dahl, Colin (2008). A Practical Understanding of Rosacea – part one. Australian Sciences. Archived from the original on 21 March 2008. Retrieved 27 August 2008.
- ^ Desai SR, Baldwin H, Del Rosso JQ, Gallo RL, Bhatia N, Harper JC, York JP, Gold LS (February 2024). "Microencapsulated Benzoyl Peroxide for Rosacea in Context: A Review of the Current Treatment Landscape". Drugs. 84 (3): 275–284. doi:10.1007/s40265-024-02003-w. PMC 10982091. PMID 38418773.
- ^ van Zuuren EJ, Fedorowicz Z, Carter B, van der Linden MM, Charland L (28 April 2015). "Interventions for rosacea". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4 (4): CD003262. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003262.pub5. PMC 6481562. PMID 25919144.
- Tung RC, Bergfeld WF, Vidimos AT, Remzi BK (2000). "alpha-Hydroxy acid-based cosmetic procedures. Guidelines for patient management". American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 1 (2): 81–8. doi:10.2165/00128071-200001020-00002. PMID 11702315. S2CID 58337540.
- Husein-ElAhmed H, Steinhoff M (January 2020). "Efficacy of topical ivermectin and impact on quality of life in patients with papulopustular rosacea: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Dermatol Ther. 33 (1): e13203. doi:10.1111/dth.13203. PMID 31863543. S2CID 209433363.
- Siddiqui K, Stein Gold L, Gill J (2016). "The efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ivermectin compared with current topical treatments for the inflammatory lesions of rosacea: a network meta-analysis". SpringerPlus. 5 (1): 1151. doi:10.1186/s40064-016-2819-8. PMC 4956638. PMID 27504249.
- Moran EM, Foley R, Powell FC (2017). "Demodex and rosacea revisited". Clin. Dermatol. 35 (2): 195–200. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2016.10.014. PMID 28274359.
- "Galderma Receives FDA Approval of Soolantra (Ivermectin) Cream for Rosacea". drugs.com. Archived from the original on 22 January 2015."
- Ferrari A, Diehl C (January 2012). "Evaluation of the Efficacy and Tolerance of a Topical Gel With 4% Quassia Extract in the Treatment of Rosacea". The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 52 (1): 84–88. doi:10.1177/0091270010391533. PMID 21343346. S2CID 29876609.
- Diehl C, Ferrari A (2017). "Superiority of Quassia Amara 4% Cream over Metronidazole 0.75% Cream in the Treatment of Rosacea: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Trial". Journal of Clinical and Cosmetic Dermatology. 1 (3). doi:10.16966/2576-2826.117.
- Hoting E, Paul E, Plewig G (December 1986). "Treatment of rosacea with isotretinoin". Int J Dermatol. 25 (10): 660–3. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1986.tb04533.x. PMID 2948928. S2CID 22421145.
- van Zuuren EJ, Fedorowicz Z, Carter B, van der Linden MM, Charland L (28 April 2015). "Interventions for rosacea". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015 (4): CD003262. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003262.pub5. PMC 6481562. PMID 25919144.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Rosacea photo library at Dermnet Archived 26 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- Questions and Answers about Rosacea, from the US National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
| Diseases of the skin and appendages by morphology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growths |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rashes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellaneous disorders |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||