City in Israel
| Holon חוֹלוֹן | |
|---|---|
| City (from 1950) | |
| Hebrew transcription(s) | |
| • ISO 259 | Ḥolon |
     ] ] | |
 Flag Flag Coat of Arms Coat of Arms | |
  | |
| Coordinates: 32°01′N 34°46′E / 32.017°N 34.767°E / 32.017; 34.767 | |
| Country | |
| District | |
| Founded | 1936 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Shay Keinan (Likud) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 18,927 dunams (18.927 km or 7.308 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 197,957 |
| • Density | 10,000/km (27,000/sq mi) |
| Ethnicity | |
| • Jews and others | 99.8% |
| • Arabs | 0.2% |
| Name meaning | (Little) sand |
| Website | www |
Holon (Hebrew: חוֹלוֹן [χoˈlon] ) is a city in the Tel Aviv District of Israel, located south of Tel Aviv. Holon is part of the Tel Aviv metropolitan area. In 2022 it had a population of 197,957, making it the tenth most populous city in Israel. Holon has the second-largest industrial zone in Israel, after Haifa. Its jurisdiction is 19,200 dunams and its population is about 194,273 residents as of 2018 according to CBS data.
Etymology
The name of the city comes from the Hebrew word חוֹלוֹן holon, meaning "(little) sand". The name Holon also appears in the Bible: "And Holon with its suburbs, and Debir with its suburbs" (Book of Joshua 21:15).
History

Holon was founded in 1935 on sand dunes six kilometers (3.7 miles) from Tel Aviv. The Łódzia textile factory was established there by Jewish immigrants from Łódź, Poland, along with many other industrial enterprises. In February 1936, the cornerstone was laid for Kiryat Avoda, a Modernist building complex designed by architect Joseph Neufeld to solve the shortage of housing for municipal workers.
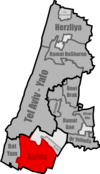
In the early months of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, Holon was on the front line, with constant shooting taking place on the border with the village of Tel A-Rish to its northwest—a suburb of Arab Jaffa—and clashes also in the direction of the town of Yazur to the east. An attack by the Holon-based Haganah militia units on Tel A-Rish was repulsed with considerable losses.
After the establishment of the state, Holon expanded to include Tel A-Rish (renamed Tel Giborim, "The Mound of the Heroes") and the orange groves of Yazur.
In February 2001, a Palestinian attack at a crowded bus stop in Holon killed eight Israelis and injured twenty-five. The image of Holon as a working-class dormitory community has changed over the years.

Through municipal efforts, the city has been rebranded as a child-friendly city. It offers family attractions such as the Yamit Water Park, the Israeli Children's Museum, and the Israel Museum of Caricature and Comics.

Historic landmarks in Holon slated for preservation include Derech Habitachon ("Safe Road"), paved during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War; water towers in the Moledet and Azor neighborhoods; Hosmasa, a building used by the Haganah; the pillbox guard post; Stroma Square, Mansbach health clinic, Hameshakem building, the Agrobank neighborhood and two schools – Bialik and Shenkar. A new neighborhood, Migdalim Bashdera, is under construction, with plans for 23 upscale residential towers, a new city hall, several cultural and commercial centers, some of them already built. A French urban planner was commissioned to design a north-south boulevard with pedestrian walks, bicycle paths, sports fields, parks and waterfalls. The last undeveloped land reserve remaining in Holon is the H-500 Holon plan, that consists of approximately 4,080 dunams in the south of the city, and is intended to consist of 13,700 dwelling units in total.
Local government
Mayors
- Haim Kugel [he] – 1940 to 1953
- Pinhas Eylon – 1953 to 1987
- Haim Sharon – 1987 to 1988
- Moshe Rom – 1988 to 1993
- Moti Sasson – 1993 to 2024
- Shay Keinan - 2024 to present
Culture

Holon hosts a variety of springtime events, including the Yemay Zemer (Days of Song) Festival during Passover and a Women's Festival in March, both at the Holon Theater. Holon is also one of the host cities for the Rhythmic Gymnastics Grand Prix Series in March. Israeli violinist Pinchas Zukerman runs a summer music camp in the city for young violinists. Since the election of Mayor Moti Sasson in 1993, many cultural projects have been inaugurated. Billing itself as a "children's city," Holon is home to the Holon Children's Museum and the Mediatheque youth theater. Holon also plays host each year to a street carnival in celebration of the Jewish holiday of Purim, the Adloyada. Thousands of children dress up in costumes and the streets close down for a parade featuring colorful floats.
In October 2013, Holon hosted major international designers who arrived for Holon Fashion Week (known as HoF13), among them milliner Stephen Jones and BioCouture founder Suzanne Lee. Cinematheque Holon hosts the only digital arts and media arts festival in Israel, Print Screen Festival. The festival was established 2010.
Museums and Arts Centers

- Design Museum Holon - the first Israeli museum of design. opened in 2010 near the "Médiathèque" and the Faculty of Design of Holon Institute of Technology.
- Holon Children's Museum - inaugurated in 2001, located in Peres Park in the southeast of the city.
- Israeli Center for Digital Art - inaugurated in 2001, promotes digital art in Israel.
- Israeli Museum of Caricature and Comics - inaugurated in 2007, a museum that presents works by Israeli artists on the subjects of comics and cartoons.
- Médiathèque (Holon) - inaugurated in 2004, one part of it is the largest and most sophisticated public library in Israel. The second part is a theater for young people.
- Historical Vehicle Museum - contains a rare collection of "Egged" historical buses, some of them from before the establishment of the state. All buses are restored to their authentic condition and are roadworthy. The museum is located on the grounds of the "Egged" Holon parking lot in the south of the city, in Kiryat Ben-Gurion.
- The Puppet Theater Center- The center contains the Museum of the Art of Puppetry, a performance hall and the School of the Art of Puppetry. The International Festival of Puppet Theater and Film, featuring puppet makers and artists from Israel and around the world, has been held annually in July since 1995 at the Puppet Theater Center in Holon.
Samaritan community

In 1954, the president of Israel, Yitzhak Ben-Zvi, helped to establish a Samaritan quarter on the outskirts of Holon. The quarter was named Neve Pinchas after Pinhas Ben-Abraham, the high priest of the Samaritan community.
Holon is one of only two cities in the world to have a Samaritan community, the other being the village of Kiryat Luza on Mount Gerizim above Nablus on the West Bank.
Transportation
Holon is served by Holon–Wolfson railway station and Holon Junction railway station of Israel Railways.
Education
The Collège-Lycée franco-israélien Raymond Leven is located in Mikve, Holon.
The Holon Institute of Technology was founded in 1969.
Sports
- Hapoel Holon (basketball) – premier league, national champion in 2008 and 2022, and state cup holder in 2009 and 2018
- Hapoel Tzafririm Holon F.C. (football)
- Holon yuvalim HC - multiple Ligat Ha'Al titles, usually the only representation of Israel in european competitions and a regular member of the European Cup
Notable people


- Moshik Afia, singer
- Chen Aharoni, singer
- Oz Almog, Israeli-Austrian artist & author
- Rafi Amit, poker player
- Avraam Benaroya, Greek-Jewish socialist leader, founder of the Communist Party of Greece
- David Ben Dayan, football player
- Omri Casspi, NBA basketball player
- Eli Cohen, Israeli Minister of Foreign Affairs
- Bat-Sheva Dagan, Holocaust survivor, teacher, psychologist, author
- Moti Daniel, basketball player
- David D'Or, countertenor & composer; Israel's 2001 Singer of the Year
- Ilona Feher, violinist
- Tal Hen, footballer
- Dana International, pop singer
- Tomer Kapon, film and television actor
- Hila Klein, YouTuber
- Eran Kolirin, cinema director & script writer
- Aryeh Krishek, novelist and biographer
- Chen Kugel, Israeli pathologist who did an autopsy on Yahya Sinwar
- Stephane Legar, singer, dancer, and runway model
- Moran Mazor, singer
- Sofia Mechetner, model, the face of Dior
- Avihu Medina, composer, arranger, songwriter, and singer
- Adir Miller, actor, screenwriter and comedian
- Moshe Mizrahi, basketball player
- Lior Narkis, singer
- Avi Nimni, footballer
- Oren Nissim, footballer
- Chen Reiss, opera singer
- Irina Risenzon, rhythmic gymnast
- Shira Rishony, Olympic judoka
- Peter Roth, rock singer & composer
- Ben Sahar, football player
- Moti Sasson, Mayor of Holon
- Hezi Shai, IDF tank commander
- Sofi Tsedaka, actress, singer, television presenter and politician
- Arie Vardi, pianist & teacher
- Rahel Vigdozchik, Olympic rhythmic gymnast
- Amos Yaron, IDF major general
- Avraham Yosef, rabbi and son of Ovadia Yosef
- Rami Yosifov, guitarist of Teapacks
- Oren Zeitouni, footballer
- Moses Hacmon, artist, Trisha Paytas' spouse
Twin towns – sister cities

Holon is twinned with:
 Andong, South Korea
Andong, South Korea Anshan, China
Anshan, China Cleveland, United States
Cleveland, United States Dayton, United States
Dayton, United States Hann. Münden, Germany
Hann. Münden, Germany Mitte (Berlin), Germany
Mitte (Berlin), Germany Suresnes, France
Suresnes, France
In Popular Folklore
Character Rahamim Ben-Salomon, from Abie Rotenberg's song "Sfashkenaz" is originally from Holon.
Gallery
-
 Convoy being assembled at Holon, 1948
Convoy being assembled at Holon, 1948
-
 Yanshul, symbol of the Holon Children's Museum
Yanshul, symbol of the Holon Children's Museum
-
 Holon 1942 1:20,000
Holon 1942 1:20,000
-
 Holon 1945 1:250,000
Holon 1945 1:250,000
References
- ^ "Regional Statistics". Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved March 21, 2024.
- Mandic, Asja; Roberts, Patrick (2012). Museum Education in Times of Radical Social Change: Journal of Museum Education 37:3 Thematic Issue. Taylor & Francis Group. p. 58. ISBN 978-1-61132-821-9. Archived from the original on May 29, 2021. Retrieved December 18, 2020.
- ""יישובים/חולון"". Archived from the original on May 29, 2021. Retrieved May 29, 2021.
- "The Story of Holon:Making Sand Dunes Sophisticated". Isrealli.org. Archived from the original on February 28, 2011. Retrieved January 20, 2011.
- ^ The Guide to Israel, Zeev Vilnay, Hamakor Press, Jerusalem, 1972, p.239
- Back to the future, The tree is still standing
- "Victims of Palestinian Violence and Terrorism since September 2000". Mfa.gov.il. Archived from the original on April 3, 2007. Retrieved April 25, 2014.
- ^ Bassok, Moti (November 29, 2013). "Working class Holon aims to attract affluent home buyers". Haaretz. Archived from the original on March 18, 2014. Retrieved April 25, 2014.
- Aderet, Ofer (June 9, 2011). "Holon seeking to preserve 18 historic sites". Haaretz. Archived from the original on May 19, 2014. Retrieved April 25, 2014.
- "The Holon H-500 Information Arena". Joseph Raiten. Archived from the original on December 28, 2016. Retrieved December 27, 2016.
- ^ "Haim Kugel". Holon City. Archived from the original on October 30, 2017. Retrieved June 8, 2015.
- "Pinhas Eylon". Holon City. Archived from the original on October 30, 2017. Retrieved June 8, 2015.
- "תוצאות הבחירות המקומיות 2024". TheMarker (in Hebrew). March 3, 2024. Retrieved May 7, 2024.
- "Festivals". Holon Municipality. Archived from the original on February 11, 2018. Retrieved May 8, 2013.
- "Israeli cultural scene explodes with dynamic music, fiction, art". J. Jweekly. June 5, 1998. Archived from the original on December 3, 2013. Retrieved April 25, 2014.
- "Post-championship Holon dreams of prosperity, tourism – Haaretz – Israel News". Haaretz. Archived from the original on February 21, 2009. Retrieved May 5, 2009.
- Purim parade in Holon Archived March 4, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Jerusalem Post
- Handwerker, Haim (September 10, 2013). "Holon Fashion Week attracts big industry names". Haaretz. Archived from the original on April 25, 2014. Retrieved April 25, 2014.
- "Print Screen 2019". printscreen2019. Archived from the original on November 30, 2020. Retrieved November 30, 2020.
- "Israel Puppet Center Holon". Archived from the original on February 6, 2023. Retrieved February 20, 2023.
- "The Festival of Puppet Theater and Film". Archived from the original on February 6, 2023. Retrieved February 20, 2023.
- "Samaritans". Jewishmag.com. Archived from the original on October 3, 2009. Retrieved May 5, 2009.
- "La localisation Archived January 22, 2015, at the Wayback Machine." Collège-Lycée franco-israélien Raymond Leven. Retrieved on January 22, 2015. "Agricultural School Mikve Israel Mikve israel street 1 5891000 Holon – ISRAEL" – Address in Hebrew Archived January 22, 2015, at the Wayback Machine: "בה"ס חקלאי מקווה ישראל 5891000 חולון"
- "International relations". holon.muni.il. Holon. Archived from the original on September 26, 2020. Retrieved February 24, 2020.
- "Cleveland's Sister Cities". city.cleveland.oh.us. City of Cleveland. Archived from the original on June 15, 2015. Retrieved February 24, 2020.
External links
- Holon Municipality official site (English)
- Friends of Holon Foundation (English)
- Design Museum Holon (English)
- Hapoel Holon Basketball Club official site (Hebrew)
- Holon's Story Gardens (1/2) Archived November 18, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- Holon's Story Gardens (2/2) Archived November 18, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- Youth week in Holon (Hebrew)
- City blog presents the best part of the Holon city (Hebrew)
- The Holon H-500 Information Arena (English and Hebrew)
| Tel Aviv District | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cities |  | |
| Local councils | ||
| ||
| Israeli cities | |
|---|---|
| 300,000+ | |
| 200,000–299,999 | |
| 100,000–199,999 | |
| 50,000–99,999 | |
| 15,000–49,999 |
|