| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (January 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. Please help improve it to make it understandable to non-experts, without removing the technical details. (January 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
In game theory, the price of stability (PoS) of a game is the ratio between the best objective function value of one of its equilibria and that of an optimal outcome. The PoS is relevant for games in which there is some objective authority that can influence the players a bit, and maybe help them converge to a good Nash equilibrium. When measuring how efficient a Nash equilibrium is in a specific game we often also talk about the price of anarchy (PoA), which is the ratio between the worst objective function value of one of its equilibria and that of an optimal outcome.
Examples
Another way of expressing PoS is:
In particular, if the optimal solution is a Nash equilibrium, then the PoS is 1.
In the following prisoner’s dilemma game, since there is a single equilibrium we have PoS = PoA = 1/2.
| Left | Right | |
|---|---|---|
| Top | (2,2) | (0,3) |
| Bottom | (3,0) | (1,1) |
On this example which is a version of the battle of sexes game, there are two equilibrium points, and , with values 3 and 15, respectively. The optimal value is 15. Thus, PoS = 1 while PoA = 1/5.
| Left | Right | |
|---|---|---|
| Top | (2,1) | (0,0) |
| Bottom | (0,0) | (5,10) |
Background and milestones
The price of stability was first studied by A. Schulz and N. Stier-Moses while the term was coined by E. Anshelevich et al. Schulz and Stier-Moses focused on equilibria in a selfish routing game in which edges have capacities. Anshelevich et al. studied network design games and showed that a pure strategy Nash equilibrium always exists and the price of stability of this game is at most the nth harmonic number in directed graphs. For undirected graphs Anshelevich and others presented a tight bound on the price of stability of 4/3 for a single source and two players case. Jian Li has proved that for undirected graphs with a distinguished destination to which all players must connect the price of stability of the Shapely network design game is where is the number of players. On the other hand, the price of anarchy is about in this game.
Network design games
Setup
Network design games have a very natural motivation for the Price of Stability. In these games, the Price of Anarchy can be much worse than the Price of Stability.
Consider the following game.
- players;
- Each player aims to connect to on a directed graph ;
- The strategies for a player are all paths from to in ;
- Each edge has a cost ;
- 'Fair cost allocation': When players choose edge , the cost is split equally among them;
- The player cost is
- The social cost is the sum of the player costs: .
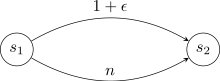
Price of anarchy
The price of anarchy can be . Consider the following network design game.
Consider two different equilibria in this game. If everyone shares the edge, the social cost is . This equilibrium is indeed optimal. Note, however, that everyone sharing the edge is a Nash equilibrium as well. Each agent has cost at equilibrium, and switching to the other edge raises his cost to .
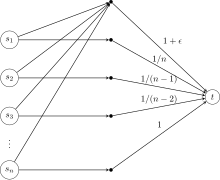
Lower bound on price of stability
Here is a pathological game in the same spirit for the Price of Stability, instead. Consider players, each originating from and trying to connect to . The cost of unlabeled edges is taken to be 0.
The optimal strategy is for everyone to share the edge, yielding total social cost . However, there is a unique Nash for this game. Note that when at the optimum, each player is paying , and player 1 can decrease his cost by switching to the edge. Once this has happened, it will be in player 2's interest to switch to the edge, and so on. Eventually, the agents will reach the Nash equilibrium of paying for their own edge. This allocation has social cost , where is the harmonic number, which is . Even though it is unbounded, the price of stability is exponentially better than the price of anarchy in this game.
Upper bound on price of stability
Note that by design, network design games are congestion games. Therefore, they admit a potential function .
Theorem. Suppose there exist constants and such that for every strategy ,
Then the price of stability is less than
Proof. The global minimum of is a Nash equilibrium, so
Now recall that the social cost was defined as the sum of costs over edges, so
We trivially have , and the computation above gives , so we may invoke the theorem for an upper bound on the price of stability.
See also
- Price of anarchy
- Competitive facility location game - a game with no price-of-stability.
References
- A.S. Schulz, N.E. Stier-Moses. On the performance of user equilibria in traffic networks. Proceedings of the 14th Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms (SODA), 2003.
- E. Anshelevich, E. Dasgupta, J. Kleinberg, E. Tardos, T. Wexler, T. Roughgarden. The Price of Stability for Network Design with Fair Cost Allocation. SIAM Journal on Computing, 38:4, 1602-1623, 2008. Conference version appeared in FOCS 2004.
- Vazirani, Vijay V.; Nisan, Noam; Roughgarden, Tim; Tardos, Éva (2007). Algorithmic Game Theory (PDF). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-87282-0.
- L. Agussurja and H. C. Lau. The Price of Stability in Selfish Scheduling Games. Web Intelligence and Agent Systems: An International Journal, 9:4, 2009.
- Jian Li. An upper bound on the price of stability for undirected Shapely network design games. Information Processing Letters 109 (15), 876-878, 2009.

 we have PoS = PoA = 1/2.
we have PoS = PoA = 1/2.
 and
and  where
where  is the number of players. On the other hand, the
is the number of players. On the other hand, the  aims to connect
aims to connect  to
to  on a directed graph
on a directed graph  ;
; for a player are all paths from
for a player are all paths from  ;
; ;
; players choose edge
players choose edge  , the cost
, the cost  is split equally among them;
is split equally among them;
 .
. Price of Anarchy
Price of Anarchy edge, the social cost is
edge, the social cost is  at equilibrium, and
switching to the other edge raises his cost to
at equilibrium, and
switching to the other edge raises his cost to  . The cost of unlabeled edges is taken to be 0.
. The cost of unlabeled edges is taken to be 0.
 , and player 1 can decrease his cost by switching to the
, and player 1 can decrease his cost by switching to the  edge. Once this has happened, it will be in player 2's interest to switch to the
edge. Once this has happened, it will be in player 2's interest to switch to the  edge, and so on. Eventually, the agents will reach the Nash equilibrium of paying for their own edge. This allocation has social cost
edge, and so on. Eventually, the agents will reach the Nash equilibrium of paying for their own edge. This allocation has social cost  , where
, where  is the
is the  . Even though it is unbounded, the price of stability is exponentially better than the price of anarchy in this game.
. Even though it is unbounded, the price of stability is exponentially better than the price of anarchy in this game.
 .
.
 and
and  such that for every strategy
such that for every strategy  ,
,


 of
of  is a Nash
equilibrium, so
is a Nash
equilibrium, so


 , and the computation above gives
, and the computation above gives  , so we may invoke the theorem for an upper bound on the price of stability.
, so we may invoke the theorem for an upper bound on the price of stability.