A propositional directed acyclic graph (PDAG) is a data structure that is used to represent a Boolean function. A Boolean function can be represented as a rooted, directed acyclic graph of the following form:
- Leaves are labeled with (true), (false), or a Boolean variable.
- Non-leaves are (logical and), (logical or) and (logical not).
- - and -nodes have at least one child.
- -nodes have exactly one child.
Leaves labeled with () represent the constant Boolean function which always evaluates to 1 (0). A leaf labeled with a Boolean variable is interpreted as the assignment , i.e. it represents the Boolean function which evaluates to 1 if and only if . The Boolean function represented by a -node is the one that evaluates to 1, if and only if the Boolean function of all its children evaluate to 1. Similarly, a -node represents the Boolean function that evaluates to 1, if and only if the Boolean function of at least one child evaluates to 1. Finally, a -node represents the complementary Boolean function its child, i.e. the one that evaluates to 1, if and only if the Boolean function of its child evaluates to 0.
PDAG, BDD, and NNF
Every binary decision diagram (BDD) and every negation normal form (NNF) are also a PDAG with some particular properties. The following pictures represent the Boolean function :
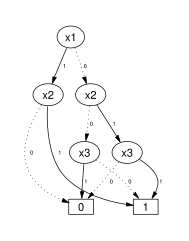 |
 |
 |
See also
References
- M. Wachter & R. Haenni, "Propositional DAGs: a New Graph-Based Language for Representing Boolean Functions", KR'06, 10th International Conference on Principles of Knowledge Representation and Reasoning, Lake District, UK, 2006.
- M. Wachter & R. Haenni, "Probabilistic Equivalence Checking with Propositional DAGs", Technical Report iam-2006-001, Institute of Computer Science and Applied Mathematics, University of Bern, Switzerland, 2006.
- M. Wachter, R. Haenni & J. Jonczy, "Reliability and Diagnostics of Modular Systems: a New Probabilistic Approach", DX'06, 18th International Workshop on Principles of Diagnosis, Peñaranda de Duero, Burgos, Spain, 2006.
| Diagrams in logic | ||
|---|---|---|
 (true),
(true),  (false), or a Boolean variable.
(false), or a Boolean variable. (logical and),
(logical and),  (logical or) and
(logical or) and  (logical not).
(logical not). is interpreted as the assignment
is interpreted as the assignment  , i.e. it represents the Boolean function which evaluates to 1 if and only if
, i.e. it represents the Boolean function which evaluates to 1 if and only if  :
: