| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Province of Vicenza" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Province of Vicenza
Provincia di Vicenza (Italian) Provincia de Vicensa (Venetian) | |
|---|---|
| Province | |
 Villa Cordellina Lombardi, the provincial seat Villa Cordellina Lombardi, the provincial seat | |
 Coat of arms Coat of arms | |
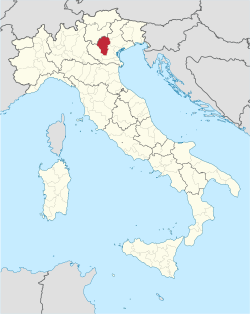 Map highlighting the location of the province of Vicenza in Italy Map highlighting the location of the province of Vicenza in Italy | |
| Country | |
| Region | |
| Capital(s) | Vicenza |
| Comuni | 119 |
| Government | |
| • President | Francesco Rucco |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,722.53 km (1,051.17 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 938,957 |
| • Density | 340/km (890/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | €27.697 billion (2015) |
| • Per capita | €31,890 (2015) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 36010-36078, 36100 |
| Telephone prefix | 0424, 0444, 0445 |
| Vehicle registration | VI |
| ISTAT | 024 |
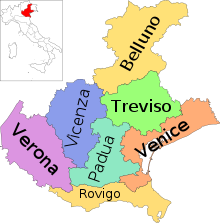
The province of Vicenza (Venetian: provincia de Vicensa; Italian: provincia di Vicenza) is a province in the Veneto region of Italy. Its capital city is Vicenza.
The province has an area of 2,722.53 km, and a total population of 865,082 (as of 2017). There are 113 comuni (municipalities) in the province. Towns in the province include Bassano del Grappa, Schio, Arzignano, Montecchio Maggiore, Thiene, Torri di Quartesolo, Noventa Vicentina, Marostica, Lonigo and Valdagno.
Population is unevenly spread throughout the province. More than 60% of the populace resides in densely industrialised areas in the eastern, western, and northern (known as Alto Vicentino) conurbations, as well as the area surrounding Bassano del Grappa. The remaining 40% reside in predominantly rural areas in the southern part of the province (the Colli Berici and Basso Vicentino) or the Asiago plateau.
Economic development in some areas is hindered by industrial and agricultural depression. Towns in the western section such as Valdagno and Montecchio Maggiore suffer from high unemployment, following a decline in steel and textile industries. The Colli Berici and Basso Vicentino remain overwhelmingly agricultural and present high levels of unemployment. The heavily industrial Alto Vicentino area alone accounts for half of the province's GDP.
Federico Faggin, an Italian physicist/electrical engineer principally responsible for the design of the first microprocessor, was born in Vicenza.
Comuni
There were 116 comuni (sg.: comune) in the province (dati: Istat 01/01/2018):
| Pos. | Comune di | Population (ab) |
Area (km) |
Density (ab/km) |
Altitude (m.s.l.m.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1º | Vicenza | 111.620 | 80,57 | 1.385 | 39 |
| 2º | Bassano del Grappa | 43.481 | 47,06 | 924 | 129 |
| 3º | Schio | 39.082 | 66,21 | 590 | 200 |
| 4º | Valdagno | 26.016 | 50,22 | 518 | 230 |
| 5º | Arzignano | 25.605 | 34,19 | 749 | 118 |
| 6º | Thiene | 24.309 | 19,70 | 1.234 | 147 |
| 7º | Montecchio Maggiore | 23.316 | 30,53 | 763 | 72 |
| 8º | Lonigo | 16.466 | 49,42 | 333 | 31 |
| 9º | Malo | 14.855 | 30,53 | 487 | 116 |
| 10º | Cassola | 14.771 | 12,74 | 1.159 | 92 |
- Agugliaro
- Albettone
- Alonte
- Altavilla Vicentina
- Altissimo
- Arcugnano
- Arsiero
- Arzignano
- Asiago
- Asigliano Veneto
- Barbarano Mossano
- Bassano del Grappa
- Bolzano Vicentino
- Breganze
- Brendola
- Bressanvido
- Brogliano
- Caldogno
- Caltrano
- Calvene
- Camisano Vicentino
- Campiglia dei Berici
- Carrè
- Cartigliano
- Cassola
- Castegnero
- Castelgomberto
- Chiampo
- Chiuppano
- Cogollo del Cengio
- Colceresa
- Cornedo Vicentino
- Costabissara
- Creazzo
- Crespadoro
- Dueville
- Enego
- Fara Vicentino
- Foza
- Gallio
- Gambellara
- Gambugliano
- Grisignano di Zocco
- Grumolo delle Abbadesse
- Isola Vicentina
- Laghi
- Lastebasse
- Longare
- Lonigo
- Lugo di Vicenza
- Lusiana Conco
- Malo
- Marano Vicentino
- Marostica
- Monte di Malo
- Montebello Vicentino
- Montecchio Maggiore
- Montecchio Precalcino
- Montegalda
- Montegaldella
- Monteviale
- Monticello Conte Otto
- Montorso Vicentino
- Mussolente
- Nanto
- Nogarole Vicentino
- Nove
- Noventa Vicentina
- Orgiano
- Pedemonte
- Pianezze
- Piovene Rocchette
- Pojana Maggiore
- Posina
- Pove del Grappa
- Pozzoleone
- Quinto Vicentino
- Recoaro Terme
- Roana
- Romano d'Ezzelino
- Rossano Veneto
- Rosà
- Rotzo
- Salcedo
- San Pietro Mussolino
- San Vito di Leguzzano
- Sandrigo
- Santorso
- Sarcedo
- Sarego
- Schiavon
- Schio
- Solagna
- Sossano
- Sovizzo
- Tezze sul Brenta
- Thiene
- Tonezza del Cimone
- Torrebelvicino
- Torri di Quartesolo
- Trissino
- Valbrenta
- Valdagno
- Valdastico
- Valli del Pasubio
- Val Liona
- Velo d'Astico
- Vicenza
- Villaga
- Villaverla
- Zanè
- Zermeghedo
- Zovencedo
- Zugliano
Economy
The industrial sector plays a primary role and over the last half century has supplanted the predominant agricultural sector: since the second post-war period, the province has in fact been one of the major interpreters of the remarkable economic and industrial development of the Northeast of Italy. The most important economic activities in the province are textile, tanning, marble extraction, ceramics, furniture, but above all jewelry.
Small and medium-sized enterprises predominate on the territory, making the province of Vicenza one of the most important on a national level, and which have developed, giving rise to mainly 4 industrial districts:
- The leather district in the Chiampo Valley, in Arzignano, Chiampo, Montorso Vicentino, Zermeghedo and Montebello Vicentino,
- The wool and yarn district in the towns of Schio and Valdagno (historically linked to the two large local industries, Lanerossi and Marzotto respectively)
- The goldsmith district in Vicenza, Trissino and Camisano Vicentino
- The electronics district in Vicenza
Other activities typically linked to the territory are:
- The distilleries in Bassano del Grappa, considered the world capital of grappa
- The furniture factories in Bassano del Grappa
- The production of ceramics in Nove and Vicenza
Quality of life
According to the European Environment Agency, in 2023 it was the 362nd most polluted city in Europe (out of a sample of 375 cities) and the third in Italy, after the provinces of Cremona and Padua.
See also
References
- Regions and Cities > Regional Statistics > Regional Economy > Regional Gross Domestic Product (Small regions TL3), OECD.Stats. Accessed on 16 November 2018.
- The Italian institute of statistics, Istat, see this link Archived 2007-08-07 at the Wayback Machine
- "European city air quality viewer".
External links
- Official website (in Italian)
| Provinces and places | 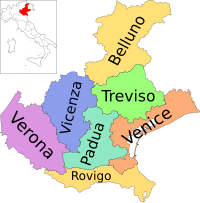 | |
|---|---|---|
| History | ||
| Politics and government | ||
| Education and culture | ||
| Categories | ||
45°33′N 11°33′E / 45.550°N 11.550°E / 45.550; 11.550
Categories: