
In Euclidean geometry, Ptolemy's theorem is a relation between the four sides and two diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral (a quadrilateral whose vertices lie on a common circle). The theorem is named after the Greek astronomer and mathematician Ptolemy (Claudius Ptolemaeus). Ptolemy used the theorem as an aid to creating his table of chords, a trigonometric table that he applied to astronomy.
If the vertices of the cyclic quadrilateral are A, B, C, and D in order, then the theorem states that:
This relation may be verbally expressed as follows:
- If a quadrilateral is cyclic then the product of the lengths of its diagonals is equal to the sum of the products of the lengths of the pairs of opposite sides.
Moreover, the converse of Ptolemy's theorem is also true:
- In a quadrilateral, if the sum of the products of the lengths of its two pairs of opposite sides is equal to the product of the lengths of its diagonals, then the quadrilateral can be inscribed in a circle i.e. it is a cyclic quadrilateral.
Corollaries on inscribed polygons
Equilateral triangle

Ptolemy's Theorem yields as a corollary a pretty theorem regarding an equilateral triangle inscribed in a circle.
Given An equilateral triangle inscribed on a circle and a point on the circle.
The distance from the point to the most distant vertex of the triangle is the sum of the distances from the point to the two nearer vertices.
Proof: Follows immediately from Ptolemy's theorem:
Square
Any square can be inscribed in a circle whose center is the center of the square. If the common length of its four sides is equal to then the length of the diagonal is equal to according to the Pythagorean theorem, and Ptolemy's relation obviously holds.
Rectangle

More generally, if the quadrilateral is a rectangle with sides a and b and diagonal d then Ptolemy's theorem reduces to the Pythagorean theorem. In this case the center of the circle coincides with the point of intersection of the diagonals. The product of the diagonals is then d, the right hand side of Ptolemy's relation is the sum a + b.
Copernicus – who used Ptolemy's theorem extensively in his trigonometrical work – refers to this result as a 'Porism' or self-evident corollary:
- Furthermore it is clear (manifestum est) that when the chord subtending an arc has been given, that chord too can be found which subtends the rest of the semicircle.
Pentagon

A more interesting example is the relation between the length a of the side and the (common) length b of the 5 chords in a regular pentagon. By completing the square, the relation yields the golden ratio:
Side of decagon

If now diameter AF is drawn bisecting DC so that DF and CF are sides c of an inscribed decagon, Ptolemy's Theorem can again be applied – this time to cyclic quadrilateral ADFC with diameter d as one of its diagonals:
- where is the golden ratio.
whence the side of the inscribed decagon is obtained in terms of the circle diameter. Pythagoras's theorem applied to right triangle AFD then yields "b" in terms of the diameter and "a" the side of the pentagon is thereafter calculated as
As Copernicus (following Ptolemy) wrote,
- "The diameter of a circle being given, the sides of the triangle, tetragon, pentagon, hexagon and decagon, which the same circle circumscribes, are also given."
Proofs
Further information: Proofs of trigonometric identitiesVisual proof
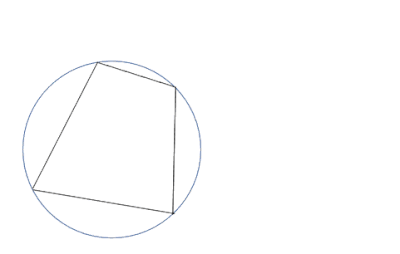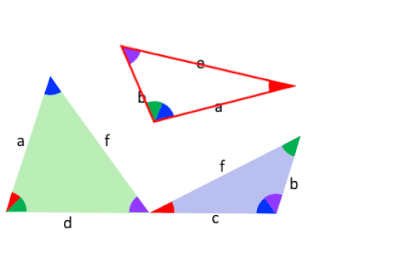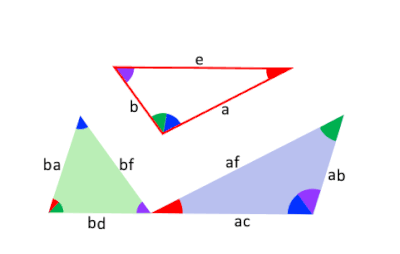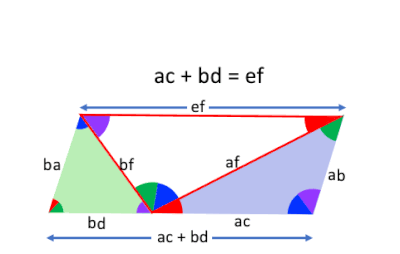
The animation here shows a visual demonstration of Ptolemy's theorem, based on Derrick & Herstein (2012).
Proof by similarity of triangles

Let ABCD be a cyclic quadrilateral. On the chord BC, the inscribed angles ∠BAC = ∠BDC, and on AB, ∠ADB = ∠ACB. Construct K on AC such that ∠ABK = ∠CBD; since ∠ABK + ∠CBK = ∠ABC = ∠CBD + ∠ABD, ∠CBK = ∠ABD.
Now, by common angles △ABK is similar to △DBC, and likewise △ABD is similar to △KBC. Thus AK/AB = CD/BD, and CK/BC = DA/BD; equivalently, AK⋅BD = AB⋅CD, and CK⋅BD = BC⋅DA. By adding two equalities we have AK⋅BD + CK⋅BD = AB⋅CD + BC⋅DA, and factorizing this gives (AK+CK)·BD = AB⋅CD + BC⋅DA. But AK+CK = AC, so AC⋅BD = AB⋅CD + BC⋅DA, Q.E.D.
The proof as written is only valid for simple cyclic quadrilaterals. If the quadrilateral is self-crossing then K will be located outside the line segment AC. But in this case, AK−CK = ±AC, giving the expected result.
Proof by trigonometric identities
Let the inscribed angles subtended by , and be, respectively, , and , and the radius of the circle be , then we have , , , , and , and the original equality to be proved is transformed to
from which the factor has disappeared by dividing both sides of the equation by it.
Now by using the sum formulae, and , it is trivial to show that both sides of the above equation are equal to
Q.E.D.
Here is another, perhaps more transparent, proof using rudimentary trigonometry. Define a new quadrilateral inscribed in the same circle, where are the same as in , and located at a new point on the same circle, defined by , . (Picture triangle flipped, so that vertex moves to vertex and vertex moves to vertex . Vertex will now be located at a new point D’ on the circle.) Then, has the same edges lengths, and consequently the same inscribed angles subtended by the corresponding edges, as , only in a different order. That is, , and , for, respectively, and . Also, and have the same area. Then,
Q.E.D.
Proof by inversion

Choose an auxiliary circle of radius centered at D with respect to which the circumcircle of ABCD is inverted into a line (see figure). Then Then and can be expressed as , and respectively. Multiplying each term by and using yields Ptolemy's equality.
Q.E.D.
Note that if the quadrilateral is not cyclic then A', B' and C' form a triangle and hence A'B'+B'C' > A'C', giving us a very simple proof of Ptolemy's Inequality which is presented below.
Proof using complex numbers
Embed ABCD in the complex plane by identifying as four distinct complex numbers . Define the cross-ratio
- .
Then
with equality if and only if the cross-ratio is a positive real number. This proves Ptolemy's inequality generally, as it remains only to show that lie consecutively arranged on a circle (possibly of infinite radius, i.e. a line) in if and only if .
From the polar form of a complex number , it follows
with the last equality holding if and only if ABCD is cyclic, since a quadrilateral is cyclic if and only if opposite angles sum to .
Q.E.D.
Note that this proof is equivalently made by observing that the cyclicity of ABCD, i.e. the supplementarity and , is equivalent to the condition
- ;
in particular there is a rotation of in which this is 0 (i.e. all three products are positive real numbers), and by which Ptolemy's theorem
is then directly established from the simple algebraic identity
Corollaries


In the case of a circle of unit diameter the sides of any cyclic quadrilateral ABCD are numerically equal to the sines of the angles and which they subtend. Similarly the diagonals are equal to the sine of the sum of whichever pair of angles they subtend. We may then write Ptolemy's Theorem in the following trigonometric form:
Applying certain conditions to the subtended angles and it is possible to derive a number of important corollaries using the above as our starting point. In what follows it is important to bear in mind that the sum of angles .
Corollary 1. Pythagoras's theorem
Let and . Then (since opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary). Then:
Corollary 2. The law of cosines

Let . The rectangle of corollary 1 is now a symmetrical trapezium with equal diagonals and a pair of equal sides. The parallel sides differ in length by units where:
It will be easier in this case to revert to the standard statement of Ptolemy's theorem:
The cosine rule for triangle ABC.
Corollary 3. Compound angle sine (+)
Let
Then
Therefore,
Formula for compound angle sine (+).
Corollary 4. Compound angle sine (−)
Let . Then . Hence,
Formula for compound angle sine (−).
This derivation corresponds to the Third Theorem as chronicled by Copernicus following Ptolemy in Almagest. In particular if the sides of a pentagon (subtending 36° at the circumference) and of a hexagon (subtending 30° at the circumference) are given, a chord subtending 6° may be calculated. This was a critical step in the ancient method of calculating tables of chords.
Corollary 5. Compound angle cosine (+)
This corollary is the core of the Fifth Theorem as chronicled by Copernicus following Ptolemy in Almagest.
Let . Then . Hence
Formula for compound angle cosine (+)
Despite lacking the dexterity of our modern trigonometric notation, it should be clear from the above corollaries that in Ptolemy's theorem (or more simply the Second Theorem) the ancient world had at its disposal an extremely flexible and powerful trigonometric tool which enabled the cognoscenti of those times to draw up accurate tables of chords (corresponding to tables of sines) and to use these in their attempts to understand and map the cosmos as they saw it. Since tables of chords were drawn up by Hipparchus three centuries before Ptolemy, we must assume he knew of the 'Second Theorem' and its derivatives. Following the trail of ancient astronomers, history records the star catalogue of Timocharis of Alexandria. If, as seems likely, the compilation of such catalogues required an understanding of the 'Second Theorem' then the true origins of the latter disappear thereafter into the mists of antiquity but it cannot be unreasonable to presume that the astronomers, architects and construction engineers of ancient Egypt may have had some knowledge of it.
Ptolemy's inequality
Main article: Ptolemy's inequality
The equation in Ptolemy's theorem is never true with non-cyclic quadrilaterals. Ptolemy's inequality is an extension of this fact, and it is a more general form of Ptolemy's theorem. It states that, given a quadrilateral ABCD, then
where equality holds if and only if the quadrilateral is cyclic. This special case is equivalent to Ptolemy's theorem.
Related theorem about the ratio of the diagonals
Ptolemy's theorem gives the product of the diagonals (of a cyclic quadrilateral) knowing the sides, the following theorem yields the same for the ratio of the diagonals.
Proof: It is known that the area of a triangle inscribed in a circle of radius is:
Writing the area of the quadrilateral as sum of two triangles sharing the same circumscribing circle, we obtain two relations for each decomposition.
Equating, we obtain the announced formula.
Consequence: Knowing both the product and the ratio of the diagonals, we deduce their immediate expressions:
See also
Notes
- C. Ptolemy, Almagest, Book 1, Chapter 10.
- Wilson, Jim. "Ptolemy's Theorem." link verified 2009-04-08
- De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium: Page 37. See last two lines of this page. Copernicus refers to Ptolemy's theorem as "Theorema Secundum".
- Proposition 8 in Book XIII of Euclid's Elements proves by similar triangles the same result: namely that length a (the side of the pentagon) divides length b (joining alternate vertices of the pentagon) in "mean and extreme ratio".
- And in analogous fashion Proposition 9 in Book XIII of Euclid's Elements proves by similar triangles that length c (the side of the decagon) divides the radius in "mean and extreme ratio".
- An interesting article on the construction of a regular pentagon and determination of side length can be found at the following reference
- De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium: Liber Primus: Theorema Primum
- W. Derrick, J. Herstein (2012) Proof Without Words: Ptolemy's Theorem, The College Mathematics Journal, v.43, n.5, p. 386.
- Alsina, Claudi; Nelsen, Roger B. (2010), Charming Proofs: A Journey Into Elegant Mathematics, Dolciani Mathematical Expositions, vol. 42, Mathematical Association of America, p. 112, ISBN 9780883853481.
- In De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium, Copernicus does not refer to Pythagoras's theorem by name but uses the term 'Porism' – a word which in this particular context would appear to denote an observation on – or obvious consequence of – another existing theorem. The 'Porism' can be viewed on pages 36 and 37 of DROC (Harvard electronic copy)
- ^ "Sine, Cosine, and Ptolemy's Theorem".
- To understand the Third Theorem, compare the Copernican diagram shown on page 39 of the Harvard copy of De Revolutionibus to that for the derivation of sin(A-B) found in the above cut-the-knot web page
- Claudi Alsina, Roger B. Nelsen: Charming Proofs: A Journey Into Elegant Mathematics. MAA, 2010, ISBN 9780883853481, pp. 112–113
References
- Coxeter, H. S. M. and S. L. Greitzer (1967) "Ptolemy's Theorem and its Extensions." §2.6 in Geometry Revisited, Mathematical Association of America pp. 42–43.
- Copernicus (1543) De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium, English translation found in On the Shoulders of Giants (2002) edited by Stephen Hawking, Penguin Books ISBN 0-14-101571-3
- Amarasinghe, G. W. I. S. (2013) A Concise Elementary Proof for the Ptolemy's Theorem, Global Journal of Advanced Research on Classical and Modern Geometries (GJARCMG) 2(1): 20–25 (pdf).
External links
- Proof of Ptolemy's Theorem for Cyclic Quadrilateral
- MathPages – On Ptolemy's Theorem
- Elert, Glenn (1994). "Ptolemy's Table of Chords". E-World.
- Ptolemy's Theorem at cut-the-knot
- Compound angle proof at cut-the-knot
- Ptolemy's Theorem Archived 2011-07-24 at the Wayback Machine on PlanetMath
- Ptolemy Inequality on MathWorld
- De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium at Harvard.
- Deep Secrets: The Great Pyramid, the Golden Ratio and the Royal Cubit
- Ptolemy's Theorem by Jay Warendorff, The Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
- Book XIII of Euclid's Elements
- A Miraculous Proof (Ptolemy's Theorem) by Zvezdelina Stankova, on Numberphile.



 then the length of the diagonal is equal to
then the length of the diagonal is equal to  according to the
according to the 

 where
where  is the golden ratio.
is the golden ratio.

 ,
,  and
and  be, respectively,
be, respectively,  ,
,  and
and  , and the radius of the circle be
, and the radius of the circle be  , then we have
, then we have  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  , and the original equality to be proved is transformed to
, and the original equality to be proved is transformed to

 has disappeared by dividing both sides of the equation by it.
has disappeared by dividing both sides of the equation by it.
 and
and  , it is trivial to show that both sides of the above equation are equal to
, it is trivial to show that both sides of the above equation are equal to

 inscribed in the same circle, where
inscribed in the same circle, where  are the same
as in
are the same
as in  , and
, and  located at a new point on the same circle, defined by
located at a new point on the same circle, defined by  ,
,
 . (Picture triangle
. (Picture triangle  flipped, so that vertex
flipped, so that vertex  moves to vertex
moves to vertex  and vertex
and vertex  will now be located at a new point D’ on the circle.)
Then,
will now be located at a new point D’ on the circle.)
Then,  and
and  .
Also,
.
Also, 
 of radius
of radius  centered at D with respect to which the circumcircle of ABCD is
centered at D with respect to which the circumcircle of ABCD is  Then
Then  and
and  can be expressed as
can be expressed as
 ,
,  and
and  respectively. Multiplying each term by
respectively. Multiplying each term by  and using
and using  yields Ptolemy's equality.
yields Ptolemy's equality.
 by identifying
by identifying  as four distinct
as four distinct  . Define the
. Define the  .
.
 is a positive real number. This proves
is a positive real number. This proves  lie consecutively arranged
on a circle (possibly of infinite radius, i.e. a line) in
lie consecutively arranged
on a circle (possibly of infinite radius, i.e. a line) in  .
.
 , it follows
, it follows

 .
.
 and
and  , is equivalent to the condition
, is equivalent to the condition
 ;
; is 0 (i.e. all three products are positive real numbers), and by which Ptolemy's theorem
is 0 (i.e. all three products are positive real numbers), and by which Ptolemy's theorem



 of any cyclic quadrilateral ABCD are numerically equal to the sines of the angles
of any cyclic quadrilateral ABCD are numerically equal to the sines of the angles  and
and  which they subtend. Similarly the diagonals are equal to the sine of the sum of whichever pair of angles they subtend. We may then write Ptolemy's Theorem in the following trigonometric form:
which they subtend. Similarly the diagonals are equal to the sine of the sum of whichever pair of angles they subtend. We may then write Ptolemy's Theorem in the following trigonometric form:

 .
.
 and
and  . Then
. Then  (since opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary). Then:
(since opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary). Then:


 units where:
units where:





 . Then
. Then  . Hence,
. Hence,


 . Then
. Then  . Hence
. Hence




 inscribed in a circle of radius
inscribed in a circle of radius 


