| This article contains promotional content. Please help improve it by removing promotional language and inappropriate external links, and by adding encyclopedic text written from a neutral point of view. (May 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
RAPIEnet (Real-time Automation Protocols for Industrial Ethernet) was Korea's first Ethernet international standard for real-time data transmission. It is an Ethernet-based industrial networking protocol, developed in-house by LSIS offers real-time transmission and is registered as an international standard. (IEC 61158-3-21: 2010, IEC 61158-4-21: 2010, IEC 61158-5-21: 2010, IEC 61158-6-21: 2010, IEC 61784-2: 2010, IEC 62439-7)
Features
- An embedded Ethernet switch with two ports enables the network expansion in a daisy chain without the need for an additional external switch, easy installation and wiring reduction.
- 100 Mbit/s - 1 Gbit/s transmission speed, allowing electrical and optical media to be used together.
- Supports transmission modes such as Unicast, Multicast, and Broadcast.
- Supports "Store & Forward”and “Cut Through” switching.
RAPIEnet Technology
Protocol Stack Structure

Embedded dual port switch motion

- An embedded hardware-based switch is adopted for real-time data transmission.
- With the full-duplex communication support, each node has dual link routes in a ring topology.
Frame Format

- RAPIEnet Ether type: 0x88FE
Topology

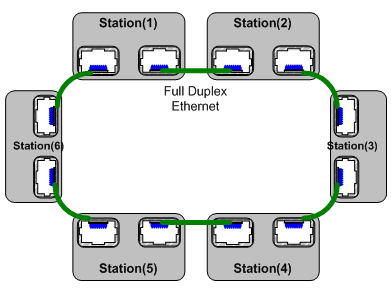
Recovery System
- With an embedded switch and full-duplex, it has dual link routes and communication fault tolerance, enabling fast recovery capabilities.
- - Recovery time < 10 ms

- Transmits signal from Device 1 to Device 3.
- A fault occurs between Device 2 and Device 3.
- Notify the fault from Device 2 to Device 1.
- Transmits signal back from Device 1 to Device 3.
Flexible Hybrid Structure

- Fiber Optics/Copper Media
- - Copper: Low installation costs with relatively big noise.
- - Optics: High installation costs with low noise and relatively long wiring.
- Simple and efficient wiring is available by combining the features of two wires that have advantages and disadvantages.
System Diagram Using RAPIEnet

Acquired Standards
International Standards
- IEC 61158-3-21: 2010, Industrial communication networks - Fieldbus specifications - Part 3-21: Data-link layer service definition - Type 21 elements.
- IEC 61158-4-21: 2010, Industrial communication networks - Fieldbus specifications - Part 4-21: Data-link layer protocol specification - Type 21 elements.
- IEC 61158-5-21: 2010, Industrial communication networks - Fieldbus specifications - Part 5-21: Application layer service definition - Type 21 elements.
- IEC 61158-6-21: 2010, Industrial communication networks - Fieldbus specifications - Part 6-21: Application layer protocol specification - Type 21 elements.
- IEC 61784-2: 2010, Industrial communication networks - Profiles - Part 2: Additional fieldbus profiles for real-time networks based on ISO/IEC 8802-3.
- IEC 62439-7, Industrial communication networks - High availability automation networks - Part 7: Ring-based Redundancy Protocol (RRP)
Others
Other international standards in process
- IEC 61784-5-17, Industrial communication networks - Profiles - Part 5-17: Installation of fieldbuses - Installation profiles for CPF 17 (to be registered as an IEC international standard in 2012)
References
- ^ IEC 61158-4-21: 2010
- RAPIEnet related articles
- ISO/IEC 8802-3: 2000
- IEEE - Ether type
- IEC 61158-3-21: 2010
- IEC 61158-5-21: 2010
- IEC 61158-6-21: 2010
- IEC 61784-2: 2010
- IEC 62439-7
- IEC 61784-5-17
