| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Ralph Millard" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
David Ralph Millard, Jr. (June 4, 1919 – June 19, 2011) was a plastic surgeon who developed several techniques used in cleft lip and palate surgeries. He also popularized the double eyelid surgery or "Asian blepharoplasty" to “deorientalize” patients’ faces while stationed in South Korea during the Korean War. He was chief of the Division of Plastic Surgery at University of Miami's Miller School of Medicine for 28 years, and maintained a private practice in Miami.
Early life
Millard was born at Barnes Hospital, St. Louis, Missouri. He attended the Asheville School in Asheville, North Carolina. He played football at Yale, studied medicine at Harvard Medical School in 1944 and interned in pediatric surgery at Boston Children's Hospital. A U.S. Navy veteran, he served stateside in World War II but in Korea during the Korean War, where he became interested in local children with cleft lips.
The Millard repair procedure
The rotation-advancement procedure for cleft lip repair, also known as the Millard repair, is designed to create a softer, more natural-looking lip. Surgery performed prior to the Millard procedure involved pulling both sides of the cleft lip together resulting in a tightly closed upper lip. The Millard procedure rotates the tissue and creates a Z-shaped scar instead. The "Z" shape gives the tissue more elasticity, resulting in greater flexibility and restoration of the Cupid's bow.
-
 The blue lines indicate incisions.
The blue lines indicate incisions.
-
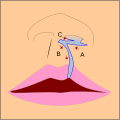 Movement of the flaps; flap A is moved between B and C. C is rotated slightly while B is pushed down. Note how the cupid's bow is created.
Movement of the flaps; flap A is moved between B and C. C is rotated slightly while B is pushed down. Note how the cupid's bow is created.
Recognition
In 2000, Millard was nominated as one of "10 Plastic Surgeons of the Millennium" by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons. In the April 2000 issue of Plastic Surgery News, Millard was described as "the most brilliant and creative plastic surgeon we have alive. His work and publications speak for themselves." He is considered to be one of the founders of modern reconstructive facial surgery.
Personal life
Millard had two sons,(Duke and Bond) a daughter (Meleney), and six grandchildren (Davey, Lindsey, Blake, Ryan, Jennifer, and Kelsey).
Bibliography
- Gillies HD, Millard DR. The Principles and Art of Plastic Surgery. Butterworth. 1958.
- Millard R, Pigott R, Zies P. Free skin grafting of full-thickness defects of abdominal wall. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1969
- Millard, DR, Total reconstructive rhinoplasty and a missing link. Plast. Reconstruct Surg 37:167-171, 1966.
See also
References
- Millard, D. R. Jr (November 1955). "Oriental Peregrinations". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 16 (5): 319–336. doi:10.1097/00006534-195511000-00001. ISSN 0032-1052. PMID 13273142. S2CID 36822324.
- "Notable Alumni - Asheville School".
- "Medicine: CLeft-Lip Craft". TIME. 1976-08-23. Archived from the original on February 20, 2011. Retrieved 2010-07-16.
- "April 2000-volume 105-issue 5: Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Journal. April 2000. Retrieved 2010-07-16.
- Jeffrey Weinzweig Plastic Surgery Secrets, Hanley & Belfus, ©1999 ISBN 1-56053-219-X / ISBN 978-1-56053-219-4
External links
This biographical article related to a physician in the United States is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |