| Left coronary artery | |
|---|---|
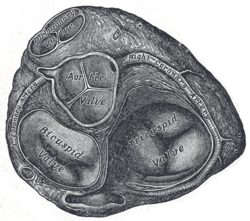 Heart viewed from above, atria removed, base of ventricles exposed. Left coronary artery visible at left. Heart viewed from above, atria removed, base of ventricles exposed. Left coronary artery visible at left. | |
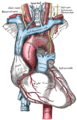
 Heart viewed from the front. Coronary arteries (labeled in red text) and other major landmarks (in blue text). Left coronary artery is at upper right in the image. Heart viewed from the front. Coronary arteries (labeled in red text) and other major landmarks (in blue text). Left coronary artery is at upper right in the image. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Ascending aorta |
| Branches |
|
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria coronaria sinistra |
| TA98 | A12.2.03.201 |
| TA2 | 4142 |
| FMA | 50040 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |

The left coronary artery (LCA, also known as the left main coronary artery, or left main stem coronary artery) is a coronary artery that arises from the aorta above the left cusp of the aortic valve, and supplies blood to the left side of the heart muscle. The left coronary artery typically runs for 10–25 mm, then bifurcates into the left anterior descending artery, and the left circumflex artery.
The part that is between the aorta and the bifurcation only is known as the left main artery (LM), while the term "LCA" might refer to just the left main, or to the left main and all its eventual branches.
Structure
Variation
Sometimes, an additional artery arises at the bifurcation of the left main artery, forming a trifurcation; this extra artery is called the ramus or intermediate artery.
A "first septal branch" is sometimes described.
Additional images
| This gallery of anatomic features needs cleanup to abide by the medical manual of style. Galleries containing indiscriminate images of the article subject are discouraged; please improve or remove the gallery accordingly. (May 2015) |
-
 Left coronary artery
Left coronary artery
-
 Cardiac vessels
Cardiac vessels
-
 The aortic arch and its branches
The aortic arch and its branches
-
 Diagram of the arch
Diagram of the arch
-
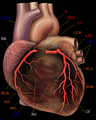 Human heart with coronary arteries
Human heart with coronary arteries
-
 Heart left lateral coronaries diagram
Heart left lateral coronaries diagram
-
 Diagram of a myocardial infarction
Diagram of a myocardial infarction
-
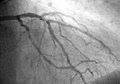 A coronary angiogram that shows the LMCA, LAD, and LCX
A coronary angiogram that shows the LMCA, LAD, and LCX
-
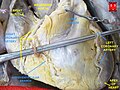
 Autopsy specimen showing the coronary ostia and proximal segments of the coronary arteries. Compare with Gray's Anatomy drawing above.
Autopsy specimen showing the coronary ostia and proximal segments of the coronary arteries. Compare with Gray's Anatomy drawing above.
-
Left coronary artery
-
Left coronary artery. Plastination technique
-
Left coronary artery. Plastination technique
See also
- Coronary circulation
- Pete Maravich – American basketball player whose congenital lack of a left coronary artery lead to his death at age 40
References
- Laird, Robert J.; Irwin, Scot (2004-01-01), Irwin, Scot; Tecklin, Jan Stephen (eds.), "Chapter 1 - Cardiovascular Structure and Function", Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy (Fourth Edition), Saint Louis: Mosby, pp. 3–38, doi:10.1016/b978-032301840-1.50005-0, ISBN 978-0-323-01840-1, retrieved 2020-11-20
- Fuster, V; Alexander RW; O'Rourke RA (2001). Hurst's The Heart (10th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 53. ISBN 0-07-135694-0.
- Verna E, Santarone M, Boscarini M, Ghezzi I, Repetto S (June 1988). "Unusual origin and course of the first septal branch of the left coronary artery: angiographic recognition". Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 11 (3): 146–9. doi:10.1007/BF02577106. PMID 3139296. S2CID 20395578.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 20:03-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center – "Anterior view of the heart."
- 00463 at CHORUS
| Arteries of the torso and chest | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lungs | |||||||||||||
| Heart | |||||||||||||
| Aorta |
| ||||||||||||