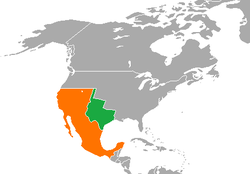
 | |
Texas |
Mexico |
|---|---|
Foreign relations between Mexico and the Republic of Texas were unofficially initiated in 1836 at the signing of the Treaties of Velasco, which de facto declared Texas independent from Mexico, though the Mexican Government never fully recognized Texas' Independence. The relations between the two countries, however hostile, continued until 1845 after the annexation of Texas by the United States, and the beginning of the Mexican–American War.
The transfer of power from the Republic to the new state of Texas formally took place on February 19, 1846.
Mexican Texas
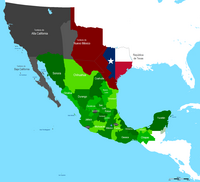
Before Texas was a Republic it was a Mexican Territory, with a population of just 4000 Tejanos. By 1824 The Mexican Government desperate to populate the region invited Americans to settle the region, under the requirement and assumption that the settlers would: a) learn the Spanish Language, b) convert to Roman Catholicism, and c) be loyal to the Mexican Government. In 1829, U.S. President Andrew Jackson made a failed attempt to buy Texas from Mexico (for $5 million). By 1832 the number of American settlers topped 30,000, very few of the settlers obeyed any of the three compromises, and most had also brought slavery into Texas, which was against Mexican Law. When the government began to enforce the ban on slavery, desire for secession reached its peak, eventually leading to the Texas Revolution, and de facto Texan Independence.
Continuation of conflict after Texan Independence


| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (July 2011) |
Just because General Santa Anna surrendered to the Texans did not end disputes, Texas claimed large portions of New Mexico they never occupied, and Mexico never gave up attempts to take back land from Texas.
Mexican Recognition of Texan Independence
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (July 2011) |
Mexico never recognized Texas' independence. Instead the Mexican Government considered Texas a rebellious territory still belonging to The Mexican Federation. By 1838, though Texas consolidated a firm hold over its eastern lands, a majority of territory claimed under the Treaty of Velasco remained under either Indian hegemony or Mexican control. Texas claimed the official southern and western border between the two countries to be the Rio Grande, Mexico considered it a ridiculous compromise to even allow the eastern part of Texas to remain independent while insisting any border that may exist was at the Nueces. Mexico's army made frequent attempts to reclaim its territory of Texas.
Bibliography
- Vigness, David M. (January 1954). Relations of the Republic of Texas and the Republic of the Rio Grande. Vol. 57. Texas State Historical Association. pp. 213–321.
See also
References
- Kelly F. Himmel (1999). The Conquest of the Karankawas and the Tonkawas: 1821–1859. Texas A&M University Press. p. 93. ISBN 978-0-89096-867-3.
- "TEXAS". Archived from the original on 2011-07-16. Retrieved 2011-07-16.
- "Texas Independence".
- Osborn, Carlyn (2015-12-18). "The Changing Mexico-U.S. Border | Worlds Revealed". The Library of Congress. Retrieved 2024-03-03.
- "Texas – My thoughts about things I come across…".
- "Answers - the Most Trusted Place for Answering Life's Questions". Answers.com.
- "Texas Revolution".
| Bilateral relations |  | |
|---|---|---|
| Diplomats of the Republic of Texas | ||
| Treaties of the Republic of Texas | ||
