| Rhinal sulcus | |
|---|---|
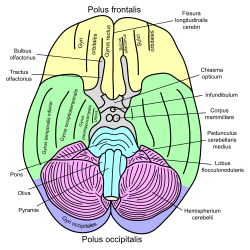 Basal view of diagram of human brain (rhinal sulcus not labeled, but is visible posterior to parahippocampal gyrus.) Basal view of diagram of human brain (rhinal sulcus not labeled, but is visible posterior to parahippocampal gyrus.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sulcus rhinalis; fissura rhinalis; sulcus rhinicus; fissura rhinica |
| NeuroNames | 41 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1368 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.240 |
| TA2 | 5443 |
| FMA | 83746 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy[edit on Wikidata] | |
In the human brain, the entorhinal cortex appears as a longitudinal elevation anterior to the parahippocampal gyrus, with a corresponding internal furrow, the external rhinal sulcus (or rhinal fissure). The rhinal sulcus separates the parahippocampal uncus from the rest of the temporal lobe in the neocortex. The rhinal sulcus and the hippocampal sulcus were both present in early mammals.
It is analogous to the collateral fissure found further caudally in the inferior part of the temporal lobe.
References
- ^ Ribas, Guilherme Carvalhal (February 2010). "The cerebral sulci and gyri". Neurosurgical Focus. 28 (2). doi:10.3171/2009.11.FOCUS09245.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 744 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 744 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
| Anatomy of the cerebral cortex of the human brain | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal lobe |
| ||||||||||||||
| Parietal lobe |
| ||||||||||||||
| Occipital lobe |
| ||||||||||||||
| Temporal lobe |
| ||||||||||||||
| Interlobar sulci/fissures |
| ||||||||||||||
| Limbic lobe |
| ||||||||||||||
| Insular cortex | |||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||
| Some categorizations are approximations, and some Brodmann areas span gyri. | |||||||||||||||
This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |