| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Pistonless rotary engine" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
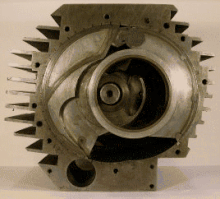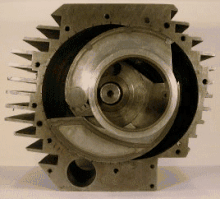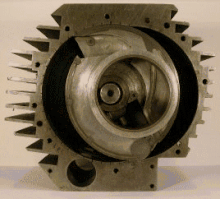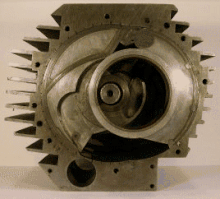
A pistonless rotary engine is an internal combustion engine that does not use pistons in the way a reciprocating engine does. Designs vary widely but typically involve one or more rotors, sometimes called rotary pistons. Although many different designs have been constructed, only the Wankel engine has achieved widespread adoption.
The term rotary combustion engine has been used as a name for these engines to distinguish them from early (generally up to the early 1920s) aircraft engines and motorcycle engines also known as rotary engines. However, both continue to be called rotary engines and only the context determines which type is meant, whereas the "pistonless" prefix is less ambiguous.
Pistonless rotary engines
A pistonless rotary engine replaces the linear reciprocating motion of a piston with more complex compression/expansion motions with the objective of improving some aspect of the engine's operation, such as: higher efficiency thermodynamic cycles, lower mechanical stress, lower vibration, higher compression, or less mechanical complexity. As of 2006 the Wankel engine is the only successful pistonless rotary engine, but many similar concepts have been proposed and are under various stages of development. Examples of rotary engines include:
- Production stage
- Wankel engine
- LiquidPiston engine
- Beauchamp Tower's nineteenth century spherical steam engine (in actual use as a steam engine, but theoretically adaptable to use internal combustion)
- Development stage
- Engineair engine
- Hamilton Walker engines
- Libralato rotary Atkinson cycle engine
- Nutating disc engine
- Quasiturbine
- RKM engine, German: RotationsKolbenMaschine
- Sarich orbital engine
- Swing-piston engine, Trochilic
- Wave disk engine
- Conceptual stage
- Gerotor engine
- Internally Radiating Impulse Structure: IRIS engine
See also
Further reading
- Jan P. Norbye: 'Rivals to the Wankel: A Roundup of Rotary Engines', Popular Science, Jan 1967, pp 80–85.
- Article referencing the October 1964 issue of Mechanix Illustrated and the AMC/Rambler rotary
| Heat engines | |
|---|---|
| Thermodynamic cycle |