| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (November 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Part of a series on the |
| Norsemen |
|---|
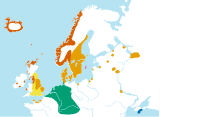 Extent of Norse language in CE 900: Western Norse in red and Eastern Norse in orange. Yellow and green denote related Germanic languages. Extent of Norse language in CE 900: Western Norse in red and Eastern Norse in orange. Yellow and green denote related Germanic languages. |
| History |
| Old Norse religion |
| Cosmology |
| Rituals and worship |
| Society |
| Events |
| Sources |
| WikiProject Norse history and culture |
There is some evidence that, in addition to being a writing system, runes historically served purposes of magic. This is the case from the earliest epigraphic evidence of the Roman to the Germanic Iron Age, with non-linguistic inscriptions and the alu word. An erilaz appears to have been a person versed in runes, including their magic applications.
In medieval sources, notably the Poetic Edda, the Sigrdrífumál mentions "victory runes" to be carved on a sword, "some on the grasp and some on the inlay, and name Tyr twice."
In the early modern period and modern history, related folklore and superstition is recorded in the form of the Icelandic magical staves. In the early 20th century, Germanic mysticism coined new forms of "runic magic", some of which were continued or developed further by contemporary adherents of Germanic Neopaganism. Modern systems of runic divination are based on Hermeticism, classical occultism, and the I Ching.
Historical evidence

Tacitus
Historically it is known that the Germanic peoples used various forms of divination and means of reading omens. Tacitus (Germania 10) gives a detailed account (98AD):
- They attach the highest importance to the taking of auspices and casting lots. Their usual procedure with the lot is simple. They cut off a branch from a nut-bearing tree and slice it into strips these they mark with different signs and throw them at random onto a white cloth. Then the state's priest, if it is an official consultation, or the father of the family, in a private one, offers prayer to the gods and looking up towards heaven picks up three strips, one at a time, and, according to which sign they have previously been marked with, makes his interpretation. If the lots forbid an undertaking, there is no deliberation that day about the matter in question. If they allow it, further confirmation is required by taking auspices.
It is often debated whether "signs" refers specifically to runes or to other marks; both interpretations are plausible and Tacitus does not give enough detail for a definite decision to be made.
Epigraphy
See also: Category:Historical runic magic
The Ansuz and Tiwaz runes in particular seem to have had magical significance in the early (Elder Futhark) period. The Sigrdrífumál instruction of "name Tyr twice" is reminiscent of the double or triple "stacked Tyr" bindrunes found e.g. on Seeland-II-C or the Lindholm amulet in the aaaaaaaazzznnn-b- muttt, sequence, which besides stacked Tyr involves multiple repetition of Ansuz, but also triple occurrence of Algiz and Naudiz.
Many inscriptions also have apparently meaningless utterances interpreted as magical chants, such as tuwatuwa (Vadstena bracteate), aaduaaaliia (DR BR42) or g͡æg͡og͡æ (Undley bracteate), g͡ag͡ag͡a (Kragehul I).
Alu is a charm word appearing on numerous artifacts found in Central and Northern Europe dating from the Germanic Iron Age. The word is the most common of the early runic charm words and can appear either alone or as part of an apparent formula. The origin and meaning of the word are matters of dispute, though a general agreement exists among scholars that the word either represents amulet magic or is a metaphor (or metonym) for it.
A few Viking Age rings with runic inscriptions of apparently magical nature were found, among them the Kingmoor Ring. The phrase "runes of power" is found on two runestones in Sweden, DR 357 from Stentoften and DR 360 from Björketorp. Runestones with curses include DR 81 in Skjern, DR 83 in Sønder Vinge, DR 209 in Glavendrup, DR 230 from Tryggevælde, DR 338 in Glemminge, and Vg 67 in Saleby.
Medieval sources
The most prolific source for runic magic in the Poetic Edda is the Sigrdrífumál, where the valkyrie Sigrdrífa (Brynhild) presents Sigurd with a memory-draught of ale that had been charmed with "gladness runes" (stanza 5),
|
|
She goes on to give advice on the magical runes in seven further stanzas. In all instances, the runes are used for actual magic (apotropaic or ability-enhancing spells) rather than for divination:
- "victory runes" to be carved on the sword hilt (stanza 6, presumably referring to the t rune named for Tyr),
- ølrunar "Ale-runes" (stanza 7, a protective spell against being bewitched by means of ale served by the host's wife; naudiz is to be marked on one's fingernails, and laukaz on the cup),
- biargrunar "birth-runes" (stanza 8, a spell to facilitate childbirth),
- brimrunar "wave-runes" (stanza 9, a spell for the protection of ships, with runes to be carved on the stem and on the rudder),
- limrunar "branch-runes" (stanza 10, a healing spell, the runes to be carved on trees "with boughs to the eastward bent"),
- malrunar "speech-runes" (stanza 11, the stanza is corrupt, but apparently referred to a spell to improve one's rhetorical ability at the thing),
- hugrunar "thought-runes" (stanza 12, the stanza is incomplete, but clearly discussed a spell to improve one's wit).
The Poetic Edda also seems to corroborate the magical significance of the runes the Hávamál where Odin mentions runes in contexts of divination, of healing and of necromancy (trans. Bellows):
- "Certain is that which is sought from runes / That the gods so great have made / And the Master-Poet painted" (79)
- "Of runes heard I words, nor were counsels wanting / At the hall of Hor" (111)
- "Grass cures the scab / and runes the sword-cut" (137)
- "Runes shalt thou find / and fateful signs" (143)
- " if high on a tree / I see a hanged man swing / So do I write and color the runes / That forth he fares / And to me talks." (158)
Other oft cited sources for the practice of runic divination are chapter 38 of Snorri Sturluson's Ynglinga Saga, where Granmar, the king of Södermanland, travels to the Temple at Uppsala for the seasonal blót. "There, the chips fell in a way that said that he would not live long" (Féll honum þá svo spánn sem hann mundi eigi lengi lifa).
Another source is in the Vita Ansgari, the biography of Ansgar the Archbishop of Hamburg-Bremen, which was written by a monk named Rimbert. Rimbert details the custom of casting lots by the pagan Norse (chapters 26–30). The chips and the lots, however, can be explained respectively as a blótspánn (sacrificial chip) and a hlauttein (lot-twig), which according to Foote and Wilson would be "marked, possibly with sacrificial blood, shaken and thrown down like dice, and their positive or negative significance then decided."
Egils Saga features several incidents of runic magic. The most celebrated is the scene where Egil discovers (and destroys) a poisoned drink prepared for him, by cutting his hand and cutting runes on the drinking horn, and painting the runes with blood. While the motif of blood painted runes also appears in other examples of early Norse literature it is uncertain whether the practice of painting runes with blood is merely a literary invention or whether it had precedence in magical practice.
Modern systems

In the 17th century, Hermeticist and Rosicrucian Johannes Bureus, having been inspired by visions, developed a Runic system based on the Kaballah and the Futhark which he called the Adulruna.
The Armanen runes "revealed" to Guido von List in 1902 were employed for magical purposes in Germanic mysticism by authors such as Friedrich Bernhard Marby and Siegfried Adolf Kummer, and after World War II in a reformed "pansophical" system by Karl Spiesberger. More recently, Stephen Flowers, Adolf Schleipfer, Larry E. Camp and others also build on List's system.
Several modern systems of runic magic and runic divination were published from the 1980s onward. The first book on runic divination, written by Ralph Blum in 1982, led to the development of sets of runes designed for use in several such systems of fortune telling, in which the runes are typically incised in clay, stone tiles, crystals, resin, glass, or polished stones, then either selected one-by-one from a closed bag or thrown down at random for reading.
Later authors such as Diana L. Paxson and Freya Aswynn follow Blum (1989) in drawing a direct correlation between runic divination and tarot divination. They may discuss runes in the context of "spreads" and advocate the usage of "rune cards".
Modern authors like Ralph Blum sometimes include a "blank rune" in their sets. Some were to replace a lost rune, but according to Ralph Blum this was the god Odin's rune, the rune of the beginning and the end, representing "the divine in all human transactions".
Ralph Blum
In 1982, a modern usage of the runes for answering life's questions was apparently originated by Ralph Blum in his divination book The Book of Runes: A Handbook for the Use of an Ancient Oracle, which was marketed with a small bag of round tiles with runes stamped on them. This book has remained in print since its first publication. The sources for Blum's divinatory interpretations, as he explained in The Book of Runes itself, drew heavily on then-current books describing the ancient I Ching divination system of China.
Each of Blum's seven books on runic divination deals with a specialized area of life or a varied technique for reading runes:
- The Book of Runes: A Handbook for the Use of an Ancient Oracle: The Viking Runes (1982); revised 10th Anniversary Edition (1992); revised 25th Anniversary Edition (2007).
- The Rune Cards: Sacred Play for Self Discovery (1989); reissued as The Rune Cards: Ancient Wisdom For the New Millennium (1997). Rather than rune stones, this book uses images of the runes printed on card stock, much like a set of trading cards or tarot cards.
- The Healing Runes with co-author Susan Loughan (1995) teaches methods for using runic divination in the context of health and personal integration.
- Rune Play: A Method of Self Counseling and a Year-Round Rune Casting Record Book (1996)
- The Serenity Runes: Five Keys to the Serenity Prayer with co-author Susan Loughan (1998); reissued as The Serenity Runes: Five Keys to Spiritual Recovery (2005) utilizes runic divination as a method for assisting self-help and recovery from addictions; the title is a reference to the well-known Serenity prayer widely used in the 12-step program of Alcoholics Anonymous.
- Ralph H. Blum's Little Book of Runic Wisdom (2002).
- The Relationship Runes: A Compass for the Heart with co-author Bronwyn Jones (2003) shows how to use runic divination in matters of love and friendship.
Blum has also written books on the Tao Te Ching, Zen Buddhism, and UFOs.
Stephen Flowers
In the wake of a 1984 dissertation on "Runes and Magic", Stephen Flowers published a series of books under the pen-name "Edred Thorsson" which detailed his own original method of runic divination and magic, "odianism", which he said was loosely based on historical sources and modern European hermeticism. These books were:
- Futhark: A Handbook of Rune Magic (1984)
- Runelore: A Handbook of Esoteric Runology (1987)
- At The Well of Wyrd (1988) which was later reprinted under the title Runecaster’s Handbook: The Well of Wyrd.
- Northern Magic: Rune Mysteries and Shamanism (2002).
Runic divination is a component of Flowers' "esoteric runology" course offered to members of his Rune-Gild, as detailed in The Nine Doors of Midgard: A Curriculum of Rune-Work. Besides runic divination, Flowers also advocated the "runic gymnastics" (Runengymnastik) developed in the 1920s by Friedrich Marby, under the name of "Rune-Yoga" (also "Runic Yoga", "Stadhagaldr").
Stephan Grundy
In 1990, Stephan Grundy, a.k.a. Kveldulf Gundarsson, described runic magic as the active principle as opposed to passive interpretations based on runic divination. He held that runic magic is more active than the allegedly shamanic practice of seid practiced by the Seiðkona. Runic magic, he states, uses the runes to affect the world outside based on the archetypes they represent.
Most of Gundarsson's runic magic entails being in possession of a physical entity that is engraved with any or all of the individual runes or "staves", so as to practically work with their energies. The individual runes are reddened with either blood, dyes, or paints. The act of possessing the stave in its final form serves the purpose of affecting the world of form with "the rune might" of that particular stave. After use, the staves are discarded or destroyed.
Gundarsson holds that each rune has a certain sound to it, to be chanted or sung; the sound has in common the phonetic value by which it is represented. This act of singing or chanting is supposed to have more or less the same effect of using the staves in their physical form.
Other
- Nigel Pennick proposes "Germanic Runic Astrology" in publications such as Runic Astrology: Starcraft and Timekeeping in the Northern Tradition (1995), ISBN 1-898307-45-8.
- Freya Aswynn has published interpretations of the runes based on her own meditations in Leaves of Yggdrasil: Runes, Gods, Magic, Feminine Mysteries, and Folklore Llewellyn Worldwide (1990), ISBN 0-87542-024-9 and Northern Mysteries and Magick: Runes, Gods & Feminine Powers (1998), Llewellyn Worldwide ISBN 1-56718-047-7.
- Adam Byrn Tritt, in Runic Divination in the Welsh Tradition (2011) presents a system based on a 10-stone set, including nine symbols which are unrelated to the historical runes, plus a blank stone, which represents the querent (inquirer).
- Diana L. Paxson deals with the subject of runic divination and the use of the runes in magical spell-casting in her book Taking Up The Runes: A Complete Guide To Using Runes In Spells, Rituals, Divination, And Magic (2005).
- Wendy Christine Duke in Spiral of Life (2008) presents a divination system based on organizing a set of 41 "revealed images" based on the runic letters.
- A. D. Mercer, Runen - The Wisdom of the Runes (2016) reintroduces the Armanen Runes.
- Saemarr þorsgoði (Peter Seymour), Produced during the 1980s, a tape recording "Runes" giving advice on the use and divination practice of runes, including theoretical Galdrar (chanting) of the rune names of the Elder Futhark for ritual use.
See also
- Galdr
- Germanic neopaganism
- Icelandic magical staves
- List of runestones
- Runic Gymnastics
- Uthark theory
References
- Birley (1999:42).
- J. B. Rives, Germania By Cornelius Tacitus, Oxford University Press p. 166
- Spurkland, Terje (2005). Norwegian Runes and Runic Inscriptions. Boydell Press. p. 16. ISBN 1-84383-186-4.
- Macleod and Mees (2006), 91-101.
- Nielsen, M. L. (1998). "Glavendrup". In Hoops, Johannes; Beck, Heinrich (eds.). Reallexikon der Germanischen Altertumskunde. Vol. 12. Walter de Gruyter. p. 198. ISBN 3-11-016227-X.
- translation and numbering of stanzas after the edition by Henry Adams Bellows (1936).
- Enoksen, Lars Magnar. Runor: Historia, tydning, tolkning (1998) ISBN 91-88930-32-7
- "Such runes were believed to transfer sickness from the invalid to the tree. Some editors, however, have changed limrunar ("branch runes") to lifrunar ("life-runes")" Bellows (1936), p. 392.
- "Here the list of runes breaks off, though the manuscript indicates no gap, and three short passages of a different type, though all dealing with runes, follow." Bellows (1936) p. 393.
- Archived 2007-07-29 at the Wayback Machine
- "Internet History Sourcebooks".
- Foote and Wilson (1970), 401.
- MacLeod and Mees (2006), 235.
- Susanna, Åkerman (1998), Rose Cross over the Baltic: the Spread of Rosicrucianism in Northern Europe, Brill, pp. 34-35, 61-62 ISBN 90-04-11030-5
- Blum, Ralph (2000). The Book of Runes: 20th Anniversary Edition. Eddison Sadd. pp. 133–134. ISBN 1-85906-042-0.
- Thorsson, Edred (1987), Runelore; A Handbook of Esoteric Runology.
Unfortunately, Thorsson's work is highly speculative and he has noted ties to the AFA (Asatru Folk Assembly) which impact his credibility. - Thorsson, Edred (1984), Futhark: A Handbook of Rune Magic. Weiser Books. ISBN 0-87728-548-9
-
Edred Thorsson, Futhark: A Handbook of Rune Magic, Weiser Books, 1984, p. 15.
Edred Thorsson, Rune Might: Secret Practices of the German Rune Magicians, Llewellyn's Teutonic Magick series, 1989.
Edred Thorsson, The Truth About Teutonic Magick, Llewellyn's vanguard series, 1994.
Later also: L. E. Camp, A Handbook of Armanen Runic-Wisdom: History, World-View, Rune-Yoga, Divination, the Sidereal Pendulum and the Runic-Zodiac, 2005.
Criticized by Sweyn Plowright, The Rune Primer, 2006 (esp. pp. 137-139). - Gundarsson (1990), 27; 211; 211-212.
- Gundarsson (1990), 33; 34; 27.
- Gundarsson (1990), 37-156.
- Gundarsson (1990), 31-32.
- ISBN 978-0-9793935-1-8.
- Paxson, Diana L. (20 April 2005). Taking up the Runes: A Complete Guide to Using Runes in Spells, Rituals, Divination, and Magic. Weiser Books. ISBN 978-1-57863-325-8.
- Spiral of Life - A Guidebook For Your Journey (2008) Cloud Haven Studio Incorporated, ISBN 978-0-9818693-0-8.
Sources
- Birley, A. R. (Trans.) (1999). Agricola and Germany. Oxford World's Classics. ISBN 978-0-19-283300-6
- Blum, Ralph (1993). The Book of Runes : A Handbook for the Use of an Ancient Oracle: The Viking Runes with Stones, St. Martin's Press; 10th anniversary ed. ISBN 0-312-09758-1.
- Flowers, Stephen (1986), Runes and magic: magical formulaic elements in the older runic tradition, vol. 53 of American university studies: Germanic languages and literatures, P. Lang, ISBN 978-0-8204-0333-5.
- —, as Thorsson, Edred (1983). A Handbook of Rune Magic, Weiser Books. ISBN 0-87728-548-9
- —, as Thorsson, Edred (1987). A Handbook of Esoteric Runology. Weiser Books, ISBN 0-87728-667-1
- Fries, Jan, Helrunar: A Manual of Rune Magick, Second Edition, Mandrake of Oxford (2002), ISBN 978-1-869928-38-4
- Foote, Peter G., and Wilson, D. M. (1970). The Viking Achievement, Sidgwick & Jackson: London, UK. ISBN 0-283-97926-7
- Gundarsson, Kveldulf (1990). Teutonic Magic. St. Paul, MN: Llewellyn Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-87542-291-8.
- MacLeod, Mindy; Mees, Bernard (2006). Runic Amulets and Magic Objects. Boydell Press. ISBN 1-84383-205-4.
- Meadows, Kenneth (1996). Rune Power: The Secret Knowledge of the Wise Ones. Milton, Brisbane: Element Books Limited. ISBN 1-85230-706-4
- Plowright, Sweyn (2006). The Rune Primer. Lulu Press. ISBN 1-84728-246-6
- Tritt, Adam Byrn (2011), Tellstones: Runic Divination in the Welsh Tradition. Smithcraft Press. ISBN 978-0-9793935-1-8
External links
- Mystic Uses of the Runes bibliography
- Magic Runes
- On line readings
- Runic Magic
| Runes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germanic Elder Futhark 24-type Fuþark (ca. AD to 9th c.) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anglo-Frisian Futhorc 28-type Fuþorc (ca. 5th c. to 9th c.) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Later Anglo-Saxon Futhorc 33-type Fuþorc (ca. 8th c. to 12th c.) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Norse Younger Futhark 16-type Fuþark (ca. 8th c. to 11th c.) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Later Younger Futhark Stung Fuþark (ca. 11th c. to 13th c.) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Medieval runes Medieval Fuþark (ca. 13th c. to 18th c.) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dalecarlian runes Dalecarlian alphabet (ca. 16th c. to 19th c.) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Methods of divination | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||