Samerina (Akkadian: 𒊓𒈨𒊑𒈾 Samerina) was the province of the Neo-Assyrian Empire established following the c. 722 BCE Assyrian conquest of Samaria by Shalmaneser V, which resulted in the dissolution of the Kingdom of Israel and annexation of Samaria into the empire as a full imperial province administered by a governor.
The rule of the expansive Neo-Assyrian Empire went largely unchallenged for the next century until the rise of the Neo-Babylonian Empire brought about the total collapse of Assyrian power by 609, resulting in Assyrian properties, including the province of Samerina, passing into Babylonian control.
Among other effects, Assyrian rule resulted in significant population transfers into and out of Samerina as part of the standing policy of resettlement within the Assyrian empire, and close to 30,000 inhabitants of Samerina were deported to other parts of the empire, with other peoples resettled in Samerina.
History

The Neo-Assyrian province of Samerina was established in the 720s by Shalmaneser V following his conquest of Samaria, also known as the Kingdom of Israel or northern kingdom, which culminated in the capture of its capital city, which was also known as Samaria.
The siege of the city of Samaria has been tentatively dated to 725 or 724 BC, and its resolution in 722 BC, near the end of Shalmaneser's reign. The conquest of Samaria was the signature event of Shalmaneser V's reign, and is recorded in both the Babylonian Chronicles and in 2 Kings of the Hebrew Bible. The siege of Samaria was perceived by contemporaries as the most important event of Shalmaneser's time, as is the only event mentioned in the chronicles in association with his reign. It was possibly also highlighted in part due to its considerable remoteness from Assyria.
The first documented mention of the province of Samerina is from the reign of Shalmaneser V's successor Sargon II, who was credited with naming the province. This is also the first documented instance where a name derived from "Samaria", the capital city, was used for the entire region, although it is thought likely that this practice was already in place.
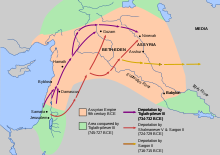
Following the Assyrian conquest, Sargon II claimed in Assyrian records to have deported 27,280 people to various places throughout the empire, mainly to Guzana in the Assyrian heartland, as well as to the cities of the Medes in the eastern part of the empire (modern-day Iran). The Medes were only conquered by Assyria in 716 BCE, six years after the fall of Samaria, suggesting that the relocation took years to plan before it was implemented.
The deportations were part of a standard resettlement policy of the Neo-Assyrian Empire to deal with defeated enemy peoples. The resettled people were generally treated well as valued members of the empire and transported together with their families and belongings. At the same time, people from other parts of the empire were resettled in the depopulated Samerina.
The resettlement is also called the Assyrian captivity in Jewish history and provides the basis for the narrative of the Ten Lost Tribes.
With the Medo-Babylonian conquest of the Assyrian Empire, the end of the Assyrian monarchy with the 609 Fall of Harran, and the rise of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, Samerina passed from Assyrian to Babylonian control.
Conflicting narratives
In several Babylonian inscriptions, Sargon II claims to have been the one who conquered Samaria, and various explanations have been proposed for this contradiction.
A prominent explanation is that Sargon's inscriptions relating to Samaria may be referencing another incident in which Sargon was forced to put down a large revolt in Syria that also involved the population of Samaria.
This revolt took place shortly after Sargon's failure to retake Babylonia from Marduk-apla-iddina in 720, and was led by Yahu-Bihdi, the Assyrian governor of Hamath who also rallied support from the cities of Arpad, Damascus, Sumur and Samaria. The claim of conquest therefore might be related to the city of Samaria being captured a second time during this revolt. In addition to these revolts, Sargon may have had to deal with unfinished conflicts from Shalmaneser's reign.
If the explanation of referral to two conquests is accepted however, then it becomes unclear which king was responsible for most of the resettlements, though it is clear from surviving inscriptions that Sargon took responsibility for it.
It has also been suggested that Sargon might have finished the initial siege of Samaria, which had been slow, inefficient and still ongoing at the time of Shalmaneser's death.
References
Citations
- ^ Yamada & Yamada 2017, pp. 408–409.
- Mills & Bullard 1990.
- Reid 1908.
- ^ Elayi 2017, p. 50.
- ^ Radner 2018, 0:51.
- ^ Mark 2014.
- Radner 2017, p. 210.
- Dalley 2017, p. 528.
- Frahm 2017, pp. 177–178.
- Gottheil et al. 1906.
- Yamada & Yamada 2017, pp. 406–408.
- Elayi 2017, p. 45.
- Frahm 2017, p. 181.
- Elayi 2017, p. 48.
Sources
- Dalley, Stephanie (2017). "Assyrian Warfare". In E. Frahm (ed.). A Companion to Assyria. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-444-33593-4.
- Elayi, Josette (2017). Sargon II, King of Assyria. Atlanta: SBL Press. ISBN 978-1628371772.
- Frahm, Eckart (2017). "The Neo-Assyrian Period (ca. 1000–609 BCE)". In E. Frahm (ed.). A Companion to Assyria. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-444-33593-4.
- Gottheil, Richard; Ryssel, Victor; Jastrow, Marcus; Levias, Caspar (1906). "Captivity, or Exile, Babylonian". Jewish Encyclopedia. Vol. 3. New York: Funk & Wagnalls Co.
- Mark, Joshua J. (2014). "Sargon II". World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved 9 February 2020.
- Mills, Watson E.; Bullard, Roger Aubrey, eds. (1990). Mercer Dictionary of the Bible. Mercer University Press. pp. 788–789. ISBN 978-0-86554-373-7. Retrieved 31 May 2018.
Sargon ... named the new province, which included what formerly was Israel,Samerina. Thus the territorial designation is credited to the Assyrians and dated to that time; however, "Samaria" probably long before alteratively designated Israel when Samaria became the capital.
- Radner, Karen (2017). "Economy, Society, and Daily Life in the Neo‐Assyrian Period". In E. Frahm (ed.). A Companion to Assyria. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-444-33593-4.
- Radner, Karen (2018). Focus on Population Management (video). Organising an Empire: The Assyrian Way. Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München. Archived from the original on 2018-05-09. Retrieved 2018-05-09 – via Coursera.
- Reid, George (1908). "Captivities of the Israelites". The Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- Yamada, Keiko; Yamada, Shiego (2017). "Shalmaneser V and His Era, Revisited". In Baruchi-Unna, Amitai; Forti, Tova; Aḥituv, Shmuel; Ephʿal, Israel; Tigay, Jeffrey H. (eds.). "Now It Happened in Those Days": Studies in Biblical, Assyrian, and Other Ancient Near Eastern Historiography Presented to Mordechai Cogan on His 75th Birthday. Vol. 2. Winona Lake, Indiana: Eisenbrauns. ISBN 978-1575067612.
Further reading
- Na'aman, N.; Zadok, R. (2000). "Assyrian deportations to the province of Samerina in the light of two cuneiform tablets from Tel Hadid". Tel Aviv. 27 (2): 159–188. doi:10.1179/tav.2000.2000.2.159. S2CID 162225582.
- Zertal, A. (2003). "The Province of Samaria (Assyrian Samerina) in the Late Iron Age (Iron Age III)". Judah and the Judeans in the neo-Babylonian Period. Eisenbrauns. pp. 377-412. ISBN 9781575060736.
| Neo-Assyrian Empire articles | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Politics | |||
| Economy |
| ||
| Culture | |||