| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Sawtooth wave" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Sawtooth wave | |
|---|---|
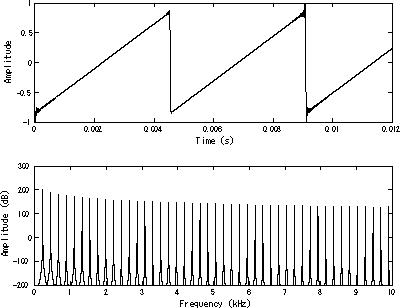 A bandlimited sawtooth wave pictured in the time domain (top) and frequency domain (bottom). The fundamental is at 220 Hz (A3). A bandlimited sawtooth wave pictured in the time domain (top) and frequency domain (bottom). The fundamental is at 220 Hz (A3). | |
| General information | |
| General definition | |
| Fields of application | Electronics, synthesizers |
| Domain, codomain and image | |
| Domain | |
| Codomain | |
| Basic features | |
| Parity | Odd |
| Period | 1 |
| Specific features | |
| Root | |
| Fourier series | |

Problems playing this file? See media help.
The sawtooth wave (or saw wave) is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is so named based on its resemblance to the teeth of a plain-toothed saw with a zero rake angle. A single sawtooth, or an intermittently triggered sawtooth, is called a ramp waveform.
The convention is that a sawtooth wave ramps upward and then sharply drops. In a reverse (or inverse) sawtooth wave, the wave ramps downward and then sharply rises. It can also be considered the extreme case of an asymmetric triangle wave.
The equivalent piecewise linear functions based on the floor function of time t is an example of a sawtooth wave with period 1.
A more general form, in the range −1 to 1, and with period p, is
This sawtooth function has the same phase as the sine function.
While a square wave is constructed from only odd harmonics, a sawtooth wave's sound is harsh and clear and its spectrum contains both even and odd harmonics of the fundamental frequency. Because it contains all the integer harmonics, it is one of the best waveforms to use for subtractive synthesis of musical sounds, particularly bowed string instruments like violins and cellos, since the slip-stick behavior of the bow drives the strings with a sawtooth-like motion.

Problems playing this file? See media help.
A sawtooth can be constructed using additive synthesis. For period p and amplitude a, the following infinite Fourier series converge to a sawtooth and a reverse (inverse) sawtooth wave:
In digital synthesis, these series are only summed over k such that the highest harmonic, Nmax, is less than the Nyquist frequency (half the sampling frequency). This summation can generally be more efficiently calculated with a fast Fourier transform. If the waveform is digitally created directly in the time domain using a non-bandlimited form, such as y = x − floor(x), infinite harmonics are sampled and the resulting tone contains aliasing distortion.

An audio demonstration of a sawtooth played at 440 Hz (A4) and 880 Hz (A5) and 1,760 Hz (A6) is available below. Both bandlimited (non-aliased) and aliased tones are presented.

Problems playing this file? See media help.
Applications
- Sawtooth waves are known for their use in electronic music. The sawtooth and square waves are among the most common waveforms used to create sounds with subtractive analog and virtual analog music synthesizers.
- Sawtooth waves are used in switched-mode power supplies. In the regulator chip the feedback signal from the output is continuously compared to a high-frequency sawtooth to generate a new duty cycle PWM signal on the output of the comparator.
- In the field of computer science, particularly in automation and robotics, allows to calculate sums and differences of angles while avoiding discontinuities at 360° and 0°.
- The sawtooth wave is the form of the vertical and horizontal deflection signals used to generate a raster on CRT-based television or monitor screens. Oscilloscopes also use a sawtooth wave for their horizontal deflection, though they typically use electrostatic deflection.
- On the wave's "ramp", the magnetic field produced by the deflection yoke drags the electron beam across the face of the CRT, creating a scan line.
- On the wave's "cliff", the magnetic field suddenly collapses, causing the electron beam to return to its resting position as quickly as possible.
- The current applied to the deflection yoke is adjusted by various means (transformers, capacitors, center-tapped windings) so that the half-way voltage on the sawtooth's cliff is at the zero mark, meaning that a negative current will cause deflection in one direction, and a positive current deflection in the other; thus, a center-mounted deflection yoke can use the whole screen area to depict a trace. The horizontal frequency is 15.734 kHz on NTSC, 15.625 kHz for PAL and SECAM.
- The vertical deflection system operates the same way as the horizontal, though at a much lower frequency (59.94 Hz on NTSC, 50 Hz for PAL and SECAM).
- The ramp portion of the wave must appear as a straight line. If otherwise, it indicates that the current isn't increasing linearly, and therefore that the magnetic field produced by the deflection yoke is not linear. As a result, the electron beam will accelerate during the non-linear portions. This would result in a television image "squished" in the direction of the non-linearity. Extreme cases will show marked brightness increases, since the electron beam spends more time on that side of the picture.
- The first television receivers had controls allowing users to adjust the picture's vertical or horizontal linearity. Such controls were not present on later sets as the stability of electronic components had improved.
See also

References
- Kraft, Sebastian; Zölzer, Udo (5 September 2017). "LP-BLIT: Bandlimited Impulse Train Synthesis of Lowpass-filtered Waveforms". Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Digital Audio Effects (DAFx-17). 20th International Conference on Digital Audio Effects (DAFx-17). Edinburgh. pp. 255–259.
- "Fourier Series-Triangle Wave - from Wolfram MathWorld". Mathworld.wolfram.com. 2012-07-02. Retrieved 2012-07-11.
- Dave Benson. "Music: A Mathematical Offering" (PDF). Homepages.abdn.ac.uk. p. 42. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
External links
- Hugh L. Montgomery; Robert C. Vaughan (2007). Multiplicative number theory I. Classical theory. Cambridge tracts in advanced mathematics. Vol. 97. pp. 536–537. ISBN 978-0-521-84903-6.
| Waveforms | |
|---|---|






 based on the
based on the 



 allows to calculate sums and differences of angles while avoiding discontinuities at 360° and 0°.
allows to calculate sums and differences of angles while avoiding discontinuities at 360° and 0°.