| Second Battle of Fort McAllister | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the American Civil War | |||||||
 A heavy gun in Fort McAllister | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| William B. Hazen | George Wayne Anderson | ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
| 2nd Division, XV Corps, Army of the Tennessee |
Fort McAllister Garrison Emmett Rifles Clinch's Light Battery 1st Regiment, Georgia Reserves | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 4,000 | 120 to 250 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 134 | 71 | ||||||
| Sherman's March to the Sea Savannah Campaign | |
|---|---|
The Second Battle of Fort McAllister took place December 13, 1864, during the final stages of Maj. Gen. William T. Sherman's March to the Sea during the American Civil War. Union forces overwhelmed a small Confederate force defending the strategically important Fort McAllister near Savannah, Georgia, a major Federal objective.
Battle

As Sherman's armies neared Savannah on December 10, following their lengthy march from Atlanta, his troops were in need of supplies. Just off the coast was Admiral John A. Dahlgren's fleet waiting with the needed supplies, as well as mail that had not been delivered to Sherman's men for six weeks during their march. However, Confederate fortifications around Savannah prevented Dahlgren from linking up with Sherman. As Sherman deployed his forces to invade Savannah, his cavalry reconnoitered Fort McAllister and other nearby fortifications, and determined that the lightly defended fort could be taken by a determined infantry attack. Sherman realized that if Fort McAllister was reduced, the Union Army would control the Ogeechee River, providing an avenue to the sea. Sherman ordered Maj. Gen. Oliver Otis Howard's Army of the Tennessee to reduce the fort. Howard chose the division commanded by Brig. Gen. William B. Hazen to lead the attack.
On December 13, 1864, Hazen's 4,000-man division was deployed to storm the fort. Sherman and Howard climbed to an observation platform erected on top of an abandoned rice mill to observe the progress. In the surrounding woods Hazen formed his three brigades commanded respectively by Colonels Theodore Jones, Wells Jones and John M. Oliver. As the Sun was setting, a Union Navy ship, USS Dandelion, steamed into view from Ossabaw Sound. Sherman signaled that the fort was still in enemy hands but would be theirs in a minute. Just then Hazen's men emerged from the woods and advanced towards the fort widely spaced apart to limit effectiveness of artillery. Confederate Major George Wayne Anderson commanded about 230 veteran troops in Fort McAllister. Hazen's troops charged through the abatis and buried torpedoes and soon reached the parapet and overwhelmed the defenders; the fort fell in 15 minutes.
Sherman was overjoyed with the victory and rowed down the Ogeechee to view the fort. That evening at Lebanon plantation, now serving as Gen. Hazen's Headquarters, Lt. Col Strong, General Sherman and Gen. Hazen had supper with Major George Wayne Anderson, Commander of the now defeated fortification who was confined there at Lebanon, in his childhood home. During this meeting, General Sherman expressed great frustration at Major Anderson having planting land mines along the land route into the fort, finding it a less-than gentlemanly tactic. General Sherman personally ordered Major Anderson to join the details of captured Confederates tasked with clearing these mines following the battle. Before being confined, Anderson observed a company of Union soldiers marching out of the fort, on a course that would lead them into some buried ordinance that would have detonated under their feet. Taking their hand, Anderson led them out of harms way. This story was fondly remembered years later in a letter from the once-young lieutenant George W. Sylvis of the 47th Ohio, when he wrote to his old adversary.
The day after the battle, Sherman rowed out to Dahlgren's flagship to greet the admiral. Sherman also had reason to be proud of the troops that had taken part in the victory at Fort McAllister; they were the same troops he had personally led as a division commander at Shiloh and a corps commander at Vicksburg.
With his supply line now open, Sherman was able to prepare for the siege and capture of Savannah, a goal he achieved by Christmas.
Gallery
-
 FortMcAllisterView
FortMcAllisterView
-
 SiegeGunatFortMcAllistair1864
SiegeGunatFortMcAllistair1864
-
 USS Montauk shells Fort McAllister
USS Montauk shells Fort McAllister
-
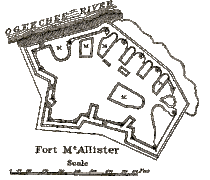 Fort McAllister Plan
Fort McAllister Plan
-
Fort McAllister 10
-
 GA Richmond Hill Fort McAllister Columbiad02
GA Richmond Hill Fort McAllister Columbiad02
-
 GA Richmond Hill Fort McAllister rifle mag01
GA Richmond Hill Fort McAllister rifle mag01
-
 William Babcock Hazen - Brady-Handy
William Babcock Hazen - Brady-Handy
-
 George W Anderson
George W Anderson
Opposing forces
Union
Military Division of the Mississippi - MG William T. Sherman
Army of the Tennessee - MG Oliver O. Howard
XV Corps - MG Peter J. Osterhaus
| Division | Brigade | Regiments and others |
|---|---|---|
|
2nd Division - BG William B. Hazen |
1st Brigade - Col Theodore Jones
|
|
| 2nd Brigade - Col Wells S. Jones
|
||
| 3rd Brigade - Col John M. Oliver
|
Confederate
Fort McAllister garrison - Maj George Wayne Anderson
See also
References
- National Park Service battle summary
- The Civil War - A Narrative (Vol. III), Shelby Foote,1974, ISBN 0-394-74622-8 (v. 3)(pbk)
- National Park Service battle description
- CWSAC Report Update
- Nevin, David, Sherman's March: Atlanta to the Sea, Time Life Books.
- Durham, Roger S, "Guardian of Savannah - Fort McAllister, Georgia, in the Civil War and Beyond", The University of South Carolina Press, 2008, ISBN 978-1-57003-742-9.
External links
31°53′20″N 81°11′39″W / 31.8888°N 81.1941°W / 31.8888; -81.1941
Categories: