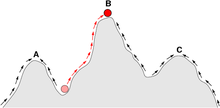
The shifting balance theory is a theory of evolution proposed in 1932 by Sewall Wright, suggesting that adaptive evolution may proceed most quickly when a population divides into subpopulations with restricted gene flow. The name of the theory is borrowed from Wright's metaphor of fitness landscapes (evolutionary landscapes), attempting to explain how a population may move across an adaptive valley to a higher adaptive peak. According to the theory, this movement occurs in three steps:
- Genetic drift allows a locally adapted subpopulation to move across an adaptive valley to the base of a higher adaptive peak.
- Natural selection will move the subpopulation up the higher peak.
- This new superiorly adapted subpopulation may then expand its range and outcompete or interbreed with other subpopulations, causing the spread of new adaptations and movement of the global population toward the new fitness peak.
Although shifting balance theory has been influential in evolutionary biology, inspiring the theories of quantum evolution and punctuated equilibrium, little empirical evidence exists to support the shifting balance process as an important factor in evolution.
References
- Coyne; Barton, Turelli (1997). "Perspective: a critique of Sewall Wright's shifting balance theory of evolution". Evolution. 3. 51 (3): 643–671. doi:10.2307/2411143. JSTOR 2411143. PMID 28568586.
- Coyne; Barton, Turelli (2000). "Is Wright's shifting balance process important in evolution?". Evolution. 1. 54 (1): 306–317. doi:10.1111/j.0014-3820.2000.tb00033.x. PMID 10937209. S2CID 22904457.
Further reading
| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (December 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
- Wade, M.J.; Goodnight, C.J. (1998). "Perspective: the theories of Fisher and Wright in the context of metapopulations: when nature does many small experiments". Evolution. 52 (6): 1537–1553. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.1998.tb02235.x. PMID 28565332. S2CID 20901475.
- Wright, S (1931). "Evolution in Mendelian populations". Genetics. 16 (2): 97–159. doi:10.1093/genetics/16.2.97. PMC 1201098. PMID 17246615.
- Wright, S. 1932. The roles of mutation, inbreeding, crossbreeding and selection in evolution. Proceedings of the 6th International Congress of Genetics: 356–366.
- Wright, S.W. (1948). "On the roles of directed and random changes in gene frequency in the genetics of populations". Evolution. 2 (4): 279–294. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.1948.tb02746.x. PMID 18104586. S2CID 30360594.
- Wright, S.W. (1982). "The shifting balance theory and macroevolution". Annual Review of Genetics. 16: 1–19. doi:10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.000245. PMID 6760797.
| Population genetics | |
|---|---|
| Key concepts |
|
| Selection | |
| Effects of selection on genomic variation | |
| Genetic drift | |
| Founders | |
| Related topics | |