 | |
 Subdivisions of Ukrainian Railways Subdivisions of Ukrainian Railways | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | Kyiv |
| Locale | Central Ukraine, North Ukraine |
| Dates of operation | 1870–present |
| Predecessor | Southwestern Railways (Soviet Union) |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 1,520 mm (4 ft 11+27⁄32 in) |
| Length | 4,668 km (2,900 mi) |
| Other | |
| Website | http://www.swrailway.gov.ua |

Southwestern Railways (PZZ), (Ukrainian: Південно-Західна залізниця) headquartered in Kyiv, the capital of Ukraine, is a component part of the Ukrzaliznytsia company, its regional branch.
It is named "Southwestern" because it is Southwest of Moscow, despite being in the Northern part of Ukraine.
Structure
As of 2008, SWR's rail system included 4,668 km (2,901 mi) of track, of which 93,3% were electrified.
The SWR consists of five sections (directions) named after the cities of their administration seat
The above mentioned directions administrative seats beside regular train stations have also locomotive and railcar depots. In addition such depots also are located in Shepetivka, Darnytsia (left-bank Kyiv), Bakhmach, Vorozhba, Hrechany (neighborhood of Khemlnytskyi), and Snovsk (formerly Shchors).
There are 315 railway stations in the SWR system.
Geography
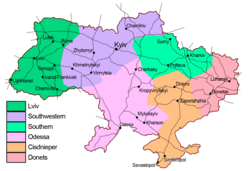
SWR's route map includes all the railroads in the Kyiv, Zhytomyr, Chernihiv, Vinnytsia, Khmelnytskyi and Sumy oblasts (provinces of Ukraine).
Its territory borders Belarusian Railway to the north in Belarus, Moscow Railway to the north and north-east in Russia, Calea Ferată din Moldova to the south-west in Moldova, and three Ukrainian territorial branches of Ukrainian Railways, Lviv Railways to the west, Southern Railways to the east, and Odesa Railways to the south.
The Chernihiv–Ovruch railway that passes Chernobyl Power Plant and has restricted use also passes across the territory of neighboring Belarus.
History
See also: Odesa RailwaysThe first railway to be built in the Ukrainian part of the Russian Empire was a track from Odesa to Balta. It was 213 km (132 mi) in length and was built in 1865. This railroad connected the agricultural regions of the northern part of today's Odesa Oblast with Odesa, a seaport on the Black Sea coast.
The direct predecessor of Southwestern Railways was Kyiv–Balta railways that, in 1870, linked Kyiv with Odesa Railways through [Balta. Just before that, in 1868 in Kyiv began construction of an important piece of infrastructure, the Struve Railroad Bridge, which, in 1870, connected both banks of the city over Dnieper. That year, Kyiv was also connected to the rest of the Russian Empire's railroad system by a track from Kyiv to Kursk with Kursk – Kyiv branch. The history of the SWR began on 7 June 1870, when the construction of these railroads was launched and making it the third oldest railway system in Ukraine after Lviv and Odesa. The Kyiv-Pasazhyrskyi railway station, the main railway station of the SWR and the Ukrzaliznytsia was also built in that year.
Between 1871 and 1876, lines from Zhmerynka to Volochysk and from Berdychiv to Shepetivka were added, and between 1890 and 1897, the lines from Zhmerynka to Mohyliv-Podilskyi, Koziatyn to Uman, Khrystynivka to Shpola and Berdychiv to Zhytomyr; 1897 was also the year when the Fastiv Railways were added to the SWR. Volyn Railways were brought into the SWR in 1902, the same year that the line from Kyiv to Korosten was built. By the beginning of World War I, the total length of the SWR system was 3,096 km (1,924 mi).
Directors
Among the most notable directors of Southwestern Railways was Sergei Witte, who later became the Prime Minister of Russia.
External links
| Ukrainian Railways | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regional branches | ||
| ||