| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (January 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Systolic geometry is a branch of differential geometry, a field within mathematics, studying problems such as the relationship between the area inside a closed curve C, and the length or perimeter of C. Since the area A may be small while the length l is large, when C looks elongated, the relationship can only take the form of an inequality. What is more, such an inequality would be an upper bound for A: there is no interesting lower bound just in terms of the length.
Mikhail Gromov once voiced the opinion that the isoperimetric inequality was known already to the Ancient Greeks. The mythological tale of Dido, Queen of Carthage shows that problems about making a maximum area for a given perimeter were posed in a natural way, in past eras.
The relation between length and area is closely related to the physical phenomenon known as surface tension, which gives a visible form to the comparable relation between surface area and volume. The familiar shapes of drops of water express minima of surface area.

The purpose of this article is to explain another such relation between length and area. A space is called simply connected if every loop in the space can be contracted to a point in a continuous fashion. For example, a room with a pillar in the middle, connecting floor to ceiling, is not simply connected. In geometry, a systole is a distance which is characteristic of a compact metric space which is not simply connected. It is the length of a shortest loop in the space that cannot be contracted to a point in the space. In the room example, absent other features, the systole would be the circumference of the pillar. Systolic geometry gives lower bounds for various attributes of the space in terms of its systole.
It is known that the Fubini–Study metric is the natural metric for the geometrisation of quantum mechanics. In an intriguing connection to global geometric phenomena, it turns out that the Fubini–Study metric can be characterized as the boundary case of equality in Gromov's inequality for complex projective space, involving an area quantity called the 2-systole, pointing to a possible connection to quantum mechanical phenomena.
In the following, these systolic inequalities will be compared to the classical isoperimetric inequalities, which can in turn be motivated by physical phenomena observed in the behavior of a water drop.
Surface tension and shape of a water drop

Perhaps the most familiar physical manifestation of the 3-dimensional isoperimetric inequality is the shape of a drop of water. Namely, a drop will typically assume a symmetric round shape. Since the amount of water in a drop is fixed, surface tension forces the drop into a shape which minimizes the surface area of the drop, namely a round sphere. Thus the round shape of the drop is a consequence of the phenomenon of surface tension. Mathematically, this phenomenon is expressed by the isoperimetric inequality.
Isoperimetric inequality in the plane
The solution to the isoperimetric problem in the plane is usually expressed in the form of an inequality that relates the length of a closed curve and the area of the planar region that it encloses. The isoperimetric inequality states that
and that the equality holds if and only if the curve is a round circle. The inequality is an upper bound for area in terms of length.
Central symmetry
Recall the notion of central symmetry: a Euclidean polyhedron is called centrally symmetric if it is invariant under the antipodal map
Thus, in the plane central symmetry is the rotation by 180 degrees. For example, an ellipse is centrally symmetric, as is any ellipsoid in 3-space.
Property of a centrally symmetric polyhedron in 3-space
There is a geometric inequality that is in a sense dual to the isoperimetric inequality in the following sense. Both involve a length and an area. The isoperimetric inequality is an upper bound for area in terms of length. There is a geometric inequality which provides an upper bound for a certain length in terms of area. More precisely it can be described as follows.
Any centrally symmetric convex body of surface area can be squeezed through a noose of length , with the tightest fit achieved by a sphere. This property is equivalent to a special case of Pu's inequality, one of the earliest systolic inequalities.
For example, an ellipsoid is an example of a convex centrally symmetric body in 3-space. It may be helpful to the reader to develop an intuition for the property mentioned above in the context of thinking about ellipsoidal examples.
An alternative formulation is as follows. Every convex centrally symmetric body in admits a pair of opposite (antipodal) points and a path of length joining them and lying on the boundary of , satisfying
Notion of systole

The systole of a compact metric space is a metric invariant of , defined to be the least length of a noncontractible loop in . We will denote it as follows:
Note that a loop minimizing length is necessarily a closed geodesic. When is a graph, the invariant is usually referred to as the girth, ever since the 1947 article by William Tutte. Possibly inspired by Tutte's article, Charles Loewner started thinking about systolic questions on surfaces in the late 1940s, resulting in a 1950 thesis by his student P. M. Pu. The actual term systole itself was not coined until a quarter century later, by Marcel Berger.
This line of research was, apparently, given further impetus by a remark of René Thom, in a conversation with Berger in the library of Strasbourg University during the 1961–62 academic year, shortly after the publication of the papers of R. Accola and C. Blatter. Referring to these systolic inequalities, Thom reportedly exclaimed: Mais c'est fondamental!
Subsequently, Berger popularized the subject in a series of articles and books, most recently in the March 2008 issue of the Notices of the American Mathematical Society. A bibliography at the Website for systolic geometry and topology currently contains over 170 articles. Systolic geometry is a rapidly developing field, featuring a number of recent publications in leading journals. Recently, an intriguing link has emerged with the Lusternik–Schnirelmann category. The existence of such a link can be thought of as a theorem in systolic topology.
The real projective plane
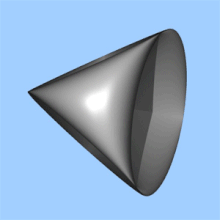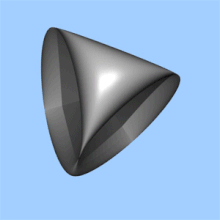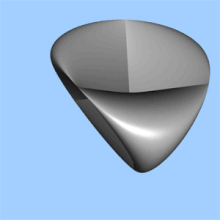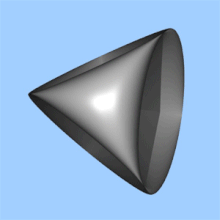
In projective geometry, the real projective plane is defined as the collection of lines through the origin in . The distance function on is most readily understood from this point of view. Namely, the distance between two lines through the origin is by definition the angle between them (measured in radians), or more precisely the lesser of the two angles. This distance function corresponds to the metric of constant Gaussian curvature +1.
Alternatively, can be defined as the surface obtained by identifying each pair of antipodal points on the 2-sphere.
Other metrics on can be obtained by quotienting metrics on imbedded in 3-space in a centrally symmetric way.
Topologically, can be obtained from the Möbius strip by attaching a disk along the boundary.
Among closed surfaces, the real projective plane is the simplest non-orientable such surface.
Pu's inequality
Pu's inequality for the real projective plane applies to general Riemannian metrics on .
A student of Charles Loewner's, Pao Ming Pu proved in a 1950 thesis (published in 1952) that every metric on the real projective plane satisfies the optimal inequality
where is the systole. The boundary case of equality is attained precisely when the metric is of constant Gaussian curvature. Alternatively, the inequality can be presented as follows:
There is a vast generalisation of Pu's inequality, due to Mikhail Gromov, called Gromov's systolic inequality for essential manifolds. To state his result, one requires a topological notion of an essential manifold.
Loewner's torus inequality

Similarly to Pu's inequality, Loewner's torus inequality relates the total area, to the systole, i.e. least length of a noncontractible loop on the torus :
The boundary case of equality is attained if and only if the metric is homothetic to the flat metric obtained as the quotient of by the lattice formed by the Eisenstein integers.
Bonnesen's inequality
The classical Bonnesen's inequality is the strengthened isoperimetric inequality
Here is the area of the region bounded by a closed Jordan curve of length (perimeter) in the plane, is the circumradius of the bounded region, and is its inradius. The error term on the right hand side is traditionally called the isoperimetric defect. There exists a similar strengthening of Loewner's inequality.
Loewner's inequality with a defect term
The explanation of the strengthened version of Loewner's inequality is somewhat more technical than the rest of this article. It seems worth including it here for the sake of completeness. The strengthened version is the inequality
where Var is the probabilistic variance while f is the conformal factor expressing the metric g in terms of the flat metric of unit area in the conformal class of g. The proof results from a combination of the computational formula for the variance and Fubini's theorem (see Horowitz et al, 2009).
See also
References
- Bangert, V.; Croke, C.; Ivanov, S.; Katz, M. (2005). "Filling area conjecture and ovalless real hyperelliptic surfaces". Geometric and Functional Analysis. 15 (3): 577–597. arXiv:math/0405583. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.240.2242. doi:10.1007/s00039-005-0517-8. S2CID 17100812.
- Berger, Marcel (1992–1993). "Systoles et applications selon Gromov" (PDF). Séminaire Bourbaki. 35: 279–310.
- Berger, M. (2003). A panoramic view of Riemannian geometry. Springer. ISBN 978-3-642-18245-7.
- Berger, M. (2008). "What is... a Systole?" (PDF). Notices of the AMS. 55 (3): 374–6.
- Buser, P.; Sarnak, P. (1994). "On the period matrix of a Riemann surface of large genus. With an appendix by J.H. Conway and N.J.A. Sloane". Invent. Math. 117 (1): 27–56. Bibcode:1994InMat.117...27B. doi:10.1007/BF01232233. S2CID 116904696.
- Gromov, M. (1983). "Filling Riemannian manifolds". J. Diff. Geom. 18: 1–147. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.400.9154. doi:10.4310/jdg/1214509283.
- Gromov, M. (1996). "Systoles and intersystolic inequalities". Actes de la Table Ronde de Géométrie Différentielle (Luminy, 1992). Sémin. Congr. Vol. 1. Soc. Math. France. pp. 291–362. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.539.1365.
- Horowitz, Charles; Katz, Karin Usadi; Katz, Mikhail G. (2009). "Loewner's torus inequality with isosystolic defect". Journal of Geometric Analysis. 19 (4): 796–808. arXiv:0803.0690. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.314.5106. doi:10.1007/s12220-009-9090-y. S2CID 18444111.
- Katz, M.; Semmes, S.; Gromov, M. (2007) . Metric Structures for Riemannian and Non-Riemannian Spaces. Progress in Mathematics. Vol. 152. Birkhäuser. ISBN 978-0-8176-4583-0.
- Katz, M. (1983). "The filling radius of two-point homogeneous spaces". Journal of Differential Geometry. 18 (3): 505–511. doi:10.4310/jdg/1214437785.
- Katz, M. (2007). Systolic geometry and topology. Mathematical Surveys and Monographs. Vol. 137. American Mathematical Society. ISBN 978-0-8218-4177-8.
- Katz, M.; Rudyak, Y. (2006). "Systolic category and Lusternik–Schnirelman category of low-dimensional manifolds". Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics. 59: 1433–56. arXiv:math/0410456. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.236.3757. doi:10.1002/cpa.20146. S2CID 15470409.
- Katz, M.; Sabourau, S. (2005). "Entropy of systolically extremal surfaces and asymptotic bounds". Ergo. Th. Dynam. Sys. 25 (4): 1209–20. arXiv:math/0410312. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.236.5949. doi:10.1017/S0143385704001014 (inactive 2024-11-21). S2CID 11631690.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - Katz, M.; Schaps, M.; Vishne, U. (2007). "Logarithmic growth of systole of arithmetic Riemann surfaces along congruence subgroups". J. Differential Geom. 76 (3): 399–422. arXiv:math.DG/0505007. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.240.5600. doi:10.4310/jdg/1180135693. S2CID 18152345.
- Pu, P.M. (1952). "Some inequalities in certain nonorientable Riemannian manifolds" (PDF). Pacific J. Math. 2: 55–71. doi:10.2140/pjm.1952.2.55.
External links
- Waner, Stefan (May 2014). "Introduction to Differential Geometry & General Relativity" (PDF). Lecture Notes. Departments of Mathematics and Physics, Hofstra University.
| Systolic geometry | |
|---|---|
| 1-systoles of surfaces | |
| 1-systoles of manifolds | |
| Higher systoles | |
| Introductory science articles | |
|---|---|
| Biology | |
| Physics | |
| Mathematics | |
 of a closed curve and the area
of a closed curve and the area  of the planar region that it encloses. The isoperimetric inequality states that
of the planar region that it encloses. The isoperimetric inequality states that


 , with the tightest fit achieved by a sphere. This property is equivalent to a special case of
, with the tightest fit achieved by a sphere. This property is equivalent to a special case of  in
in  admits a pair of opposite (antipodal) points and a path of length
admits a pair of opposite (antipodal) points and a path of length
 of
of 
 is a metric
invariant of
is a metric
invariant of 
 is defined as the collection of lines through the origin in
is defined as the collection of lines through the origin in  . The distance function on
. The distance function on  imbedded in 3-space in a centrally symmetric way.
imbedded in 3-space in a centrally symmetric way.
 on the real projective plane
on the real projective plane 
 is the systole. The boundary case of equality is attained precisely when the metric is of constant Gaussian curvature. Alternatively, the inequality can be presented as follows:
is the systole. The boundary case of equality is attained precisely when the metric is of constant Gaussian curvature. Alternatively, the inequality can be presented as follows:

 :
:

 by the lattice formed by the
by the lattice formed by the

 is the circumradius of the bounded region, and
is the circumradius of the bounded region, and  is its inradius. The error term
is its inradius. The error term  on the right hand side is traditionally called the isoperimetric defect. There exists a similar strengthening of Loewner's inequality.
on the right hand side is traditionally called the isoperimetric defect. There exists a similar strengthening of Loewner's inequality.
