This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
 | |
| Initial release | 2001, 22–23 years ago |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 62.2.0 |
| Written in | C++ |
| Operating system | Cross-platform (Qt) |
| Type | Text editor |
| License | GPL-3.0-or-later |
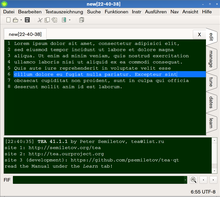
TEA is a graphical text editor for power users. It is designed for low resource consumption, a wide range of functions and adaptability, and is available for all desktop operating systems supported by Qt 6, 5 or 4.6+, thus also OS/2 and Haiku OS. Its user interface is localized in several languages.
UI concept
The functional scope of TEA exceeds that of a pure text editor since it is designed as a desktop environment for text editing. It has five tabs on the right border of the window:
- edit
- files
- options
- dates
- manual
edit represents the actual text editor. On the top of the text editor there is a tab bar for switching between multiple opened text files. The edit tab contains the text editing window. Below that window there is another window which displays the editing history and below the history there is the FIF, the "Famous Input Field" follows. The FIF is a special command line for entering TEA-specific commands. The editing history and the FIF are also visible in the four other tabs.
The tab files contains a file manager for navigating in the computers file system opening files.
options is a settings tab, for changing the behavior of TEA and modifying the content of the menu bar.
dates contains a calendar.
The tab manual contains a detailed user manual including instructions for the FIF.
Features
- Syntax highlighting: C, C++, Bash script, BASIC, C#, D, Fortran, Java, LilyPond, Lout, Lua, NASM, NSIS, Pascal, Perl, PHP, PO (gettext), Python, Seed7, TeX/LaTeX, Vala, Verilog, XML, HTML, XHTML, Dokuwiki, MediaWiki
- TEA includes a selection of color schemes and themes for changing the display colors
- In tune highlighting for the current line can be activated, a feature that is particularly useful for proofreading, where non-electronic texts and bitmaps containing text have to be compared to text on the screen. A typical use is editing of scanned text that were converted into text files with an OCR program, e.g. for creating corpora in linguistics.
- In File manager there is a bookmark menu in which folder paths for quick navigation can be stored.
- Spellchecker
- Freely definable text snippets
- Formatting for: HTML, XHTML, DocBook, LaTeX, Lout, DokuWiki and MediaWiki
- Text conversion functions (upper case, lower case, Morse, etc.)
- Text statistics functions: Text statistics; extract words; Words lengths; UNITAZ quantity sorting; UNITAZ sorting alphabet; Count the substring and count the substring (regexp)
- Math functions
FIF
The Famous Input Field is a TEA specific command line. In order to find and replace text, enter e.g. SOURCETEXT~TARGETTEXT and click on Replace, Replace All or Replace all in opened files in the Search menu. The string SOURCETEXT will be replaced by the string TARGETTEXT in the chosen way.
In addition, the FIF includes three separate search buttons, located on the right side.
History
Originally TEA was a program for Windows. In version 1.0.0.49, released on 30 December 2001, it is evident that the acronym TEA then still meant Text Editing and Authoring. Later on a version for Linux using GTK + was written, which made it possible to compile the program for both Windows and Linux. TEA is one of those programs that were later on rewritten using Qt (cf. e.g. the media player VLC).
The program and the website were initially available only in Russian, which has had a negative impact on the popularity and reach outside of Ukraine and Russia. Meanwhile, the website is bilingual (Russian and English) and the program itself has been localized in several languages.
| Release date | Win32 API | GTK+ | Qt | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| December 19, 2001 | 1.0.0.46 | — | — | Alpha |
| April 26, 2006 | 12.1 | 13.0 | — | First GTK+ version (still parallelly with Win32) |
| July 4, 2008 | — | — | 18.0.0 | First Qt version (Qt 3 & Qt 4) (rewrite from scratch) |
| August 6, 2008 | — | 17.6.6 | — | Last regular GTK+ 2 version (does not compile on modern systems) |
| December 24, 2010 | — | — | 28.1.4 | Last version supporting Windows 98 |
| April 27, 2013 | — | 17.6.7 | — | Adaptation of the old GTK+ 2 version for modern systems |
| July 3, 2013 | — | 18.0.0 | — | Port of the adapted GTK+ 2 version to GTK+ 3 |
| April 21, 2016 | — | — | 41.1.1 | newest version (Qt 4.6+ & Qt 5) |
Website history:
| From | To | Site |
|---|---|---|
| December 2001 | June 26, 2006 | http://www.roxton.kiev.ua/ |
| June 26, 2006 | March 24, 2013 | http://tea-editor.sourceforge.net/ |
| March 24, 2013 | now | semiletov.org/tea/ Archived 2017-10-06 at the Wayback Machine & tea.ourproject.org |
References
- "TEA".
- Archived 2017-08-03 at the Wayback Machine
- "www.roxton.kiev.ua". Archived from the original on January 9, 2002. Retrieved 2002-01-09.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
External links
- http://tea.ourproject.org/ tea.ourproject.org]
- historically: tea-editor.sourceforge.net / www.roxton.kiev.ua www.roxton.kiev.ua at the Wayback Machine (archived January 9, 2002)
- TEA: A Smooth Text Editor That Hits the Sweet Spot
- The Qt-based Tea Text Editor: Managing Image and Text Files in One Application